In an era where sustainability is inevitable, the transportation industry is not exempt from the call for change. Electric vehicles (EVs) will be pivotal in decarbonizing road transport, which accounts for more than 25% of global emissions. The adoption of electric vehicles is rapidly accelerating. It reduces fossil fuel consumption significantly and, in turn, reduces CO2 emissions. With the more widespread use of electric vehicles in the form of electric bicycles, electric cars, and electric buses, the charging requirement of these EVs from the grid would overload the network and place a significant burden on the energy sector. EVs do not emit exhaust gases, but this isn’t the only consideration for a truly sustainable mobility system if charged by electricity produced from conventional fossil fuel sources. To ensure that electric vehicles are sustainable, we need to ensure that sustainable electricity is used to charge them.
EV charging infrastructure plays a key role in facilitating sustainable transportation and reducing emissions and overall costs. This drives demand for a grid-independent and renewable energy-based, stand-alone electrical vehicle charging station.
Importance of Sustainable Charging
Sustainable energy comes from resources that can endure continuous operations without impacting future generations’ energy requirements or climate. The most popular renewable energy sources include wind, solar, hydropower, etc., which have immense potential to produce electricity. Energy production using these sources will be a major step towards a clean environment by reducing carbon footprint, decreasing energy costs, and successively promoting the use of electric vehicles.
Advantages of Sustainable Sources of Energy for Vehicle Charging
- Cleaner and more environment-friendly source
- Low cost
- Helps in achieving long-term economic growth
- Not subjected to price fluctuations due to geopolitical events & market changes
- Offsets the need for fossil fuels
The above benefits are, in general, for all renewable energy sources. However, it does not imply that they will offer the same benefits. The table below benchmarks non-conventional energy sources and ranks them based on various parameters.
Comparison of Renewable Sources of Energy
The comparative assessment of some of the sustainable energy sources are:
The top 3 energy sources, evident from comparison and most promising, are wind, solar, and biomass energy. The main limitation of tidal energy is its location since it is only available in selected regions. Further, it has a negative impact on marine life, high upfront cost, and low power generation due to the variable intensity of sea waves.
There are a lot of innovations in the above-stated NCES to improve power generation and increase efficiency, as shown below.
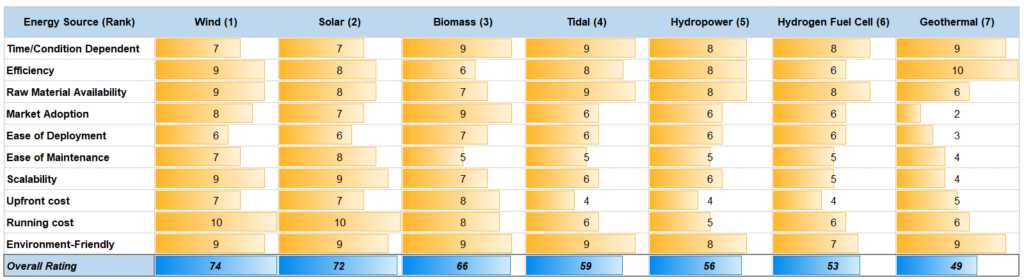
Figure: Comparison of sustainable energy sources
Innovative Technologies of Sustainable Charging
Some of the recent innovative technologies involved in sustainable EV charging are:
Concentrated Photovoltaic–Thermal(CPV/T):
It is a promising solution combining both CPV and thermal collectors. Here, the undesirable thermal energy is harvested in a useful manner. It produces electricity and thermal energy, concurrently reducing the electricity production cost and increasing the overall utilization of solar energy. Solar cells have evolved from photovoltaic cells (PV) cells to concentrated photovoltaic cells (CPV) and concentrated photovoltaic and thermal cells (CPV/T). The stored thermal energy is used for heating, cooling, or energy generation.
EV charging stations can purchase power from these CPVTs installed at a low price to charge a fixed battery. This stored power can, in turn, be used to charge electric vehicles.
Novel Catalyst for Hydrogen Fuel Cell
Researchers have developed a novel way to structure the catalyst to provide high activity. They have used a more significant catalyst support, a 130-nanometre carbon particle, rather than a 30-nanometre one used for the past 30 years. They also changed the surface chemistry of the catalyst support. Just like we place plants apart so that they do not compete with each other, they are planted closer so that maximum ground is utilized. The catalysts are spread similarly so that they do not compete for food and oxygen but not too far to leave unutilized surfaces. This new catalyst provides higher performance and consumes less catalyst, thus reducing the cost.
Some additional technological innovations that can be used as supporting sources of energy in combination with other sources of power generation are:
- Innovation in biomass gasification involving a CaO-based catalyst for tar removal will make it a cleaner option.
- Passive morphing blades for tidal energy are used to reduce unsteady thrust without reducing the mean torque and, hence, the harvested power
- A cogeneration system includes a proton membrane electrolyzer, the Rankine cycle, and a water absorption chiller. It generates power, cooling, and hydrogen-based on geothermal energy. The system helps improve overall efficiency and increases power generation.
- A hybrid combination of subsystems, such as CPV/T, wind turbine, and biomass combustion-based steam Rankine cycle plant, can be used to integrate hydrogen and ammonia-based fuel cells into the design to ensure uninterrupted charging during nighttime and unfavorable weather conditions.
Initiatives to Promote Sustainable Charging
To support the growth of sustainable EV charging infrastructure, governments and private organizations are collaborating to invest in research and development and provide incentives for the deployment of clean sources of energy in EV charging infrastructure.
The USA Company Electrify America announced a 75 MW solar PV project named Solar Glow™1, with the aim to provide even more renewable energy to EVs through its network of 800 DC fast charging stations nationwide.
The UAE, through the Dubai Electricity and Water Authority PJSC (DEWA), is directly contributing to sustainable development goals by exploring the potential of green mobility to revolutionize transportation. It also contributes by being involved in innovation and conducting cutting-edge research and development for solutions adapted to Dubai’s climate.
The Indian Ministry of New and Renewable Energy has drafted guidelines to encourage the establishment of decentralized solar power plants, which promoted many EV charging stations to adopt solar panels to generate their own power.
Innovations in Sustainable Vehicle Charging Technology
Many impressive companies are already in the market with innovative and sustainable charging products for clean mobility. To get a better idea of the landscape, mentioned are some of the players in this domain:
Beam Global is a dominant company working on contemporary sustainable products and technologies for EV charging, energy storage, energy security, and outdoor media. Its EV ARC™ system generates and stores its own electricity and tracks the sun to generate up to 25% more energy. Battery storage allows charging during the night, inclement weather, and power outages.
GPS Renewables, in association with BIRAC and AeroCare Clean Energy, has developed and installed a biogas-powered EV fast charging station. Spreading awareness about the benefits of this concept will help in its mass adoption.
Harting Technology is working as a pioneer and technology partner in providing e-mobility solutions using power from wind turbines to the EV charging station.
Future of Sustainable Charging
Instead of fossil fuels, the energy sector will largely depend on renewable energy. Two-thirds of the total energy supply in 2050 will be from wind, solar, bioenergy, geothermal, and hydro energy. Solar has become the largest source, accounting for one-fifth of energy supplies.
Sustainable charging has extraordinary potential for a cleaner and greener world. With technological advancement, we can expect new innovations in the domain. With more adoption of EVs, sustainable EV charging infrastructure will become more extensive and appropriate, making the transition to truly clean, zero-carbon, and sustainable transportation.
Conclusion
The charging requirement of millions of EVs from the grid can overload the network and significantly burden the energy sector. Thus, power generation companies need to consider this properly. The responsibility to drive net-zero targets is collective, and players’ agility across the spectrum is crucial in achieving it. The path to net-zero emissions is very clear. Staying on it demands quick and large-scale deployment of all possible clean and efficient energy technologies. Emphasis is needed on power generation at the EV charging station level so that challenges arising due to grid overload can be avoided. Wind and solar sources of energy are regarded as good alternatives for EV charging infrastructure. Research literature on the control and optimization of wind turbines also indicates that wind energy is a suitable alternative for EV charging infrastructure.
Regarding optimal planning, it was indicated that the active research concerns the charging scheduling issue. Some literature also considers integrating renewable sources with V2G during the initial planning phase. Sustainable EV charging station infrastructure planning is challenging because of the availability of renewable sources, uncertainties in traffic demands, the complex nature of location design, and other factors affecting hourly power management. It includes renewable sources, grid peak hours, and V2G. However, combining energy sources such as solar, wind, geothermal, and hydrogen-based can help mitigate these challenges. It can provide continuous green energy for EV charging.