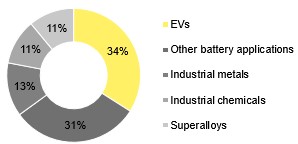
Cobalt is a key component of lithium-ion batteries in many consumer electronics and electric vehicles. The demand for these batteries is increasing as the world moves towards sustainable energy sources. However, the extraction and processing of cobalt are fraught with ethical and environmental risks. Hence, the need for cobalt-free batteries is desperate.
Fortunately, researchers are developing cobalt-free batteries that could potentially replace traditional lithium-ion batteries. These batteries have the potential to be more efficient, have a longer lifespan, environmentally friendly, and are less expensive to produce.
Since battery requirements differ depending on the application, various Co-free/Co-poor cathodes will be required to meet multiple commercial requirements. The article examines the need for and feasibility of creating and commercializing cobalt-free cathode materials for LIBs. Cobalt-free compositions that show promise and important research topics are emphasized.
Background and Need for Cobalt-free Lithium Batteries
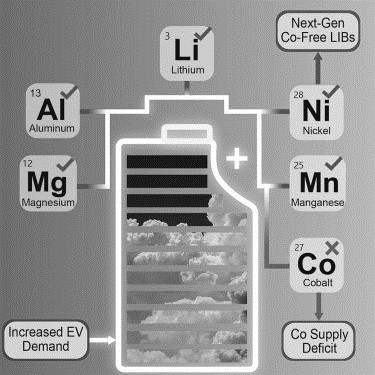
Cobalt is a key component in lithium-ion batteries used in many common electronic devices. It contributes to batteries’ high energy density and long life. However, cobalt is a rare and expensive element that must be mined and processed, with most of these activities occurring in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC).
More than 70% of the global cobalt production occurs in the DRC, of which 15–30% comes from so-called artisanal and small-scale mines where independent miners use their resources to extract the mineral. This has led to concerns about the environmental and social impacts of cobalt mining and its economic cost. In addition, cobalt mining can lead to deforestation, the destruction of wildlife habitats, and other forms of environmental degradation.
The Helmholtz Institute Ulm (HIU) in Germany predicted that the metal supply will hit critically low levels by 2050, leading to an increased need to replace its use with new technology.
Benefits of Cobalt-free Batteries
Cobalt-free batteries could offer several benefits over their cobalt-based counterparts.
- First, they would be much cheaper and more readily available, as they would not rely on the expensive and scarce element of cobalt. This could lead to lower prices for consumers and more reliable and stable battery supplies.
- Second, cobalt-free batteries would be much safer and more environmentally friendly than cobalt-based ones. They would not rely on hazardous chemicals, such as mercury, and would not require the large-scale mining activities associated with cobalt production.
- It can help reduce the environmental and social impacts of cobalt mining and make batteries safer for people and the environment.
- Finally, cobalt-free batteries could be more efficient and powerful than cobalt-based ones. This is because they would not rely on the heavy and bulky cobalt element and would instead use lighter and more robust materials. This can lead to longer-lasting, more powerful batteries, and smaller, lightweight devices.
Feasibility & Current Research Hurdles
The future of cobalt-free lithium batteries holds potential for the scope of improvement in the following aspects:
- Doping with other transitional metals: Al and Mg-doped LNO has the best thermal decomposition stability. Al-doped LNO also demonstrates that the second phase is delayed due to a stronger Al3+-oxygen connection. This could prevent cation migration during phase transitions as the temperature rises.
- Monocrystalline structure: One strategy to overcome this hurdle is synthesizing lithium nickel manganese oxides at the micron scale of single crystal particles. Single crystal size morphology has the fewest grain boundaries, thereby reducing particle cracking and side effects with electrolytes.
- Solid electrolyte interphase: A multiscale exploration of high-voltage degradation cascades associated with oxygen stacking chemistry in cobalt-free LiNiO2 was proposed having a graphene-based hermetic surface coating preventing oxygen loss in lithium nickel oxide at high states of charge.
- Project COBRA: COBRA (Cobalt-free Batteries for Future Automotive Applications) is a collaborative research and innovation project on next-generation batteries, co-funded by the European Commission’s Horizon 2020 program. COBRA uses an LNMO cathode in combination with a composite anode based on nanometre silicon and graphite as active particles.
Technologies & Innovations for Cobalt-free Batteries
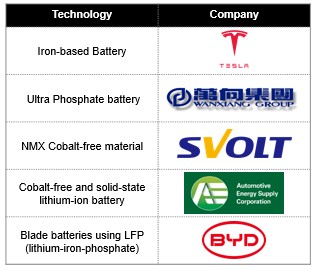
Companies and institutions are researching and developing various cobalt-free battery technologies. One promising solution uses solid-state electrolytes, which are non-flammable and more efficient than liquid electrolytes. Other technologies, such as graphene-based anodes, non-flammable solvents, and aluminum-based cathodes, are also being researched.
Other innovations include utilizing silicon-based anodes, aluminum-graphite anodes, and other materials. Further, there is research into new electrolyte materials, such as ionic liquids, that can improve the performance of cobalt-free batteries.
Active Startups in Cobalt-free Batteries
The development of cobalt-free batteries has also attracted the attention of startups and entrepreneurs. Many companies and startups are working on alternative battery technologies that do not rely on cobalt. For example,
- A California-based startup, QuantumScape, is developing solid-state batteries that use a silicon-based anode and lithium metal as the cathode.
- The startup Sila Nanotechnologies is developing a silicon-based anode that promises to improve battery energy density and safety.
- Envia Systems is developing a high-energy-density battery that uses manganese instead of cobalt. This could reduce the cost of producing batteries by as much as 50%.
- Another company, Sakti3 (a wholly owned subsidiary of Dyson Ltd.) is working on a solid-state battery technology that replaces cobalt with a silicon-based anode. This could significantly increase the energy density of batteries while reducing the production cost.
- Startups are also taking advantage of advances in nanotechnology to develop cobalt-free batteries. Nano One Materials is working on a technology that uses nanostructured materials to create a more efficient battery that reduces the amount of cobalt needed.
Conclusion
The growing demand for batteries, including sodium-ion batteries, is driving the urgency for cobalt-free alternatives. Various companies and startups are actively working on developing battery technologies that eliminate the need for cobalt. These alternatives are not only more cost-effective and abundant but also more sustainable. They can be applied across various sectors, including electric vehicles and renewable energy storage, potentially reducing emissions and addressing climate change.
In summary, the importance of cobalt-free batteries is increasing due to the environmental, economic, and social concerns associated with cobalt mining and usage. By eliminating cobalt, these batteries provide more reliable supplies and enhanced safety. The development of such materials is an ongoing process characterized by numerous innovations, emerging startups, diverse use cases, and the latest advancements in the field.