Prebiotic Soda: Consumer & Market Trend to Everything in Between
Human gut health, plant fibers, and nature (soil) have something in common- the microbiome. Recently, carbonation and prebiotics together have formed an interesting consumer thread in the FMCG/CPG space. The consumers’ quest for enhanced health and newer taste has kept the food and beverage ‘market liquid’ from club soda to probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotic drinks.
The key synbiotic strands in the prebiotic soda market space include burgeoning gut health issues among millennials and Generation Z and subsequent demand for functional drinks. With supermarket aisles full of alluring prebiotic soda drinks, consumers must distinguish between fuzzy prebiotic soda drinks and real fiber-containing prebiotic drinks with healthier and right salts. This blog will cover how prebiotic soda affects health, the top brands, key market statistics, and other interplaying factors in the prebiotic drinks spectrum.
Interconnection B/W Fibre, Prebiotics & GI Health
The human gastrointestinal (GI) or the second brain (Enteric Nervous System) health is a by-product of regularly what we eat and drink. Going by Hippocrates’ saying, “all diseases begin in the gut,” wouldn’t be an overstatement. In Ayurveda, food (ahara) is called Mahabhaisajya, meaning that it has great healing efficacy and ability.
Prebiotics in the form of plant-based roughage are necessary for producing healthy gut bacteria, referred to as probiotics that ferment undigested fibrous foods in the large intestines/colon. The presence of prebiotics makes it possible for the body to produce Short-Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs), primarily acetate, propionate, and butyrate, necessary for various body functions. The synergy between prebiotics and probiotics creates nerved myenteric reflexes (peristalsis), and submucosal reflexes, and produces a number of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), amino acids, vitamins, lipids, bile acids, and SCFAs.
This symbiotic relationship between fiber, resistant starch, and polyphenols substrates strengthens probiotic gut strains namely bifidobacterium, lactobacillus, enterococcus, saccharomyces, Escherichia, and yeast strains, etc. The synbiotic relationship of prebiotics and probiotics promotes good colon bacteria/microbiota, increased mineral homeostasis, a strong intestinal barrier, and human gut eubiosis.
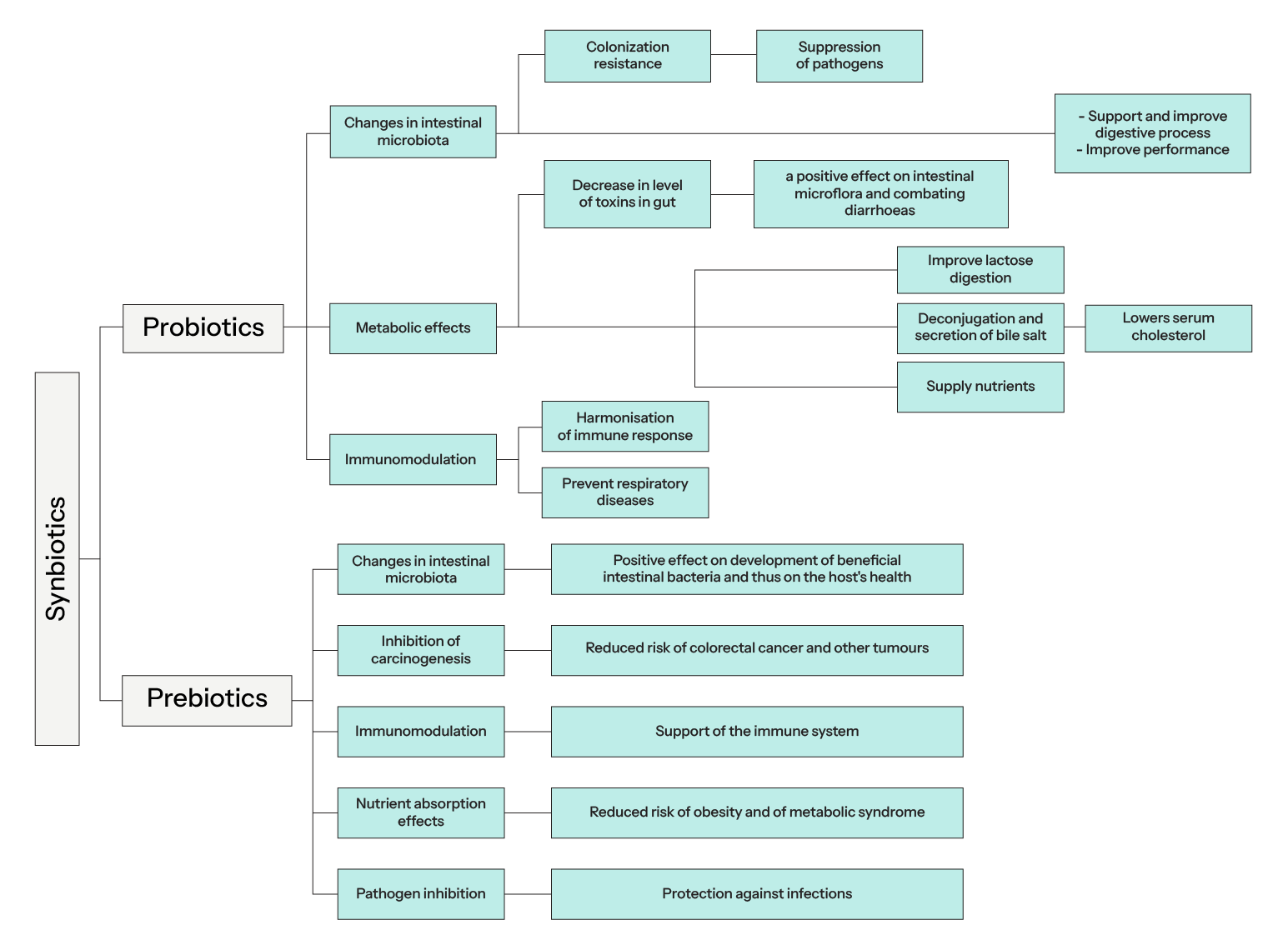
Figure1: Synbiotic Action of Prebiotics and Probiotics on Gut Health
The GI protects one from tens of painful and life-threatening diseases like high blood pressure, cancers, obesity, liver diseases, Parkinson’s disease, heart diseases, etc. As early as 3000 years ago or in the early 18 century, the center of the digestive system was considered the sens vital interieur (internal vital sense) that produced vital fluids/ojas in the human organism/being.
| Disorder | ENS Involvement | Clinical Feature (s) | Therapautic Targets |
| Gut Inflammation | Proinflammatory cytokine-mediated alteration of afferent nerves and enteric galia | Specific to inflammatory disorders (Crohn’s, ulcerative colitis, or infectious diarrhea) | IL – 1β, TNF-α, mast cell products, 5-HT3 agonist, substance P, and CGRP |
| Hirschsprung’s Disease | Aganglionosis of myenteric and submucosal plexuses due to defective migration of neural crest cells, disruption of ICC network | Chronic constipation, obstruction, failure to thrive, toxic megacolon | Neural stem cell therapy; exploitation of proliferative ICC signaling pathways |
| Infectious Secretory Diarrhea | Prostanoid- and 5HT-mediated stimulation of secretomotor neurons triggered by inflammatory mediators released by mast cells and neutrophils | Loose and watery stools, +/- blood, abdominal pain, dehydration, nutrient loss, sepsis | Neural blockade, Loperamide |
| Diabetic Diarrhea | Diabetic autonomic neuropathy resulting in vagal and sympathetic nerve damage | Nocturnal watery and painless stools, +/- incontinence | Unclear, codeine phosphate Eluxadoline |
| Short Bowel Syndrome | Intestinotrophic effects mediated by the presence of GLP-2 receptor on submucosal neurons and endocrine cells | Intestinal failure resulting in malabsorption and malnutrition | GLP-2 analogs such as Teduglutide |
| Chronic Intestinal Pseudoobstruction (CIPO) | Hyperactive but disorganized excitatory motor neurons due to dysfunctional or damaged inhibitory motor neurons and loss of ICC | Nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, distention, constipation, diarrhea, malnutrition | Metroclopramide, erythromycin, octreotide, and neostigmine: proliferative ICC pathways |
| Postoperative ileus | Increased sympathetic activity resulting from inhibitory neural reflexes from the spinal cord: release of inhibitory neurotransmitters and ICC loss (NO, VIP, substance P) | Nausea, vomiting, abdominal distention, obstipation | Octreotide and CGRP as potential therapies: proliferative ICC pathways |
| Parkinson’s Disease (PD) and Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease | Deposits of alpha-synuclein and misfolded proteins found in enteric neurons/glia | GI dysfunction, constipation, reservoir of prions | Explore ENS’s role as a biomarker in these diseases |
Figure 2: Diseases Caused Due to Unhealthy Gut Microbiome
Prebiotic Soda Market Size
The prebiotic soda market is expected to experience a robust growth trajectory, with an average Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 8.43% from 2023 to 2030. In 2023, the market size was approximately USD 442.18 million, and by 2030, it is projected to reach around USD 913.41 million, demonstrating significant growth potential. This upward trend reflects the increasing consumer demand and the expanding presence of prebiotic soda in the global beverage industry.
Top Brands in the Prebiotic Drink Market
The prebiotics soda market is marking the presence of several companies that are catering to the demand of consumers. Here are a few startups that are focusing on the domain:
Olipop: The low-sugar prebiotic soda is offering a healthier alternative to conventional soft drinks. The brand has infused it with prebiotic fibers to support gut health, botanicals, and real fruit juice while ditching additives and artificial flavors.
XOXO Beverages: The startup offers a range of low-calorie prebiotic sodas with low sugar, focusing on gut health and taste. They provide multiple flavors, including ginger, lemon, watermelon, and tropical fruits.
Jones Soda: The brand launched its all-natural prebiotic soda line with the name Pop Jones. It offers five different flavours to compete with existing companies in the segment.
Humm Kombucha: The startup has expanded in the prebiotic segment after its stint in the probiotic sector. The company aims to draw the attention of consumers interested in beverages providing gut health benefits.
Poppi: It is a well-established brand in the prebiotic soda segment offering a wide range of flavors, including watermelon lime, and cherry cola, infused with apple cider vinegar. The company aims at health-conscious consumers.
Rise Better Soda: The brand has made its presence in the prebiotic section with flavors like lemon-lime and cola. The company emphasizes primarily all-natural ingredients to maintain a healthy beverage profile while offering familiar soda flavors.
Almost all the above brands use very slow sugars, no chemicals or citric acids, and are GMO-free. Moreover, the covered prebiotic soda brands have their products designed in poppy packaging and marketing replete with pro-gut health and one that is based on digestive knowledge.
Various Health Benefits of Prebiotic Soda Drinks
A healthy self is the progenitor of all joys and life’s riches. Prebiotic drinks surely bring real functional health ingredients closer to a health-conscious and alert audience. Here are listed benefits of prebiotic-based competitive drinks:
- Bring better choices to consumers compared to unhealthy sodas
- Helps consumers make better beverage choices and thus feel better
- Improves market offering and research aimed toward health
- True-value for money products availability in the market
Prebiotic Research Statistics and Regulations
Prebiotic research is focused on how to primarily derive Short-Chain Fatty Acids (SCFA) from plant-based products in the quest to improve the commensal intestinal bacteria. So far, the research has been focussed on Fructo-oligosaccharides (FOS), which are carbohydrate sugars (plant-based) that don’t get digested in the stomach/small intestines. The others are Galacto-oligosaccharides (GOS), polydextrose (PDX), Isomaltooligosaccharide (IMO), and Resistant Dextrin. As we can see, inulin (oligo- and polysaccharides), research is already strong, and more research is needed in the area of oligosaccharides, polyphenols, and polypeptide carbohydrates.
| Prebiotic | Component | Source | Function |
| Polyphenol | Blueberry polyphenol extract | Blueberry | Reduce weight and normalize lipid metabolism |
| Wine grape seed flour | Grape seed | Intestinal permeability is enhanced, and adipocyte gene expression is to inhibit high-fat-induced obesity and inflammation. | |
| Orange albedo | Orange | Stimulates the growth, reproduction, and metabolism of Lactobacillus acidophilus and Lactobacillus animalis | |
| Catechin and punicalagin | Fermented pomegranate juice | Increases antioxidant capacity and improves survival of lactic acid bacteria | |
| Polypeptide Polymers | Poly-gamma-glutamate (PGA) | Bacillus fermentation | Increases the abundance of Lactobacillus and reduces the abundance of Clostridium, helping to regulate the intestinal microbiota. |
| Polysaccharides | Algae polysaccharides | Algae | Improves the activity of some beneficial flora and stimulates the production of functional metabolites in the intestinal microbiota. |
| Lotus seed-resistant starch (LRS3-20%) | Lotus seed | Shows high probiotic activity against Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus acidophilus. | |
| Longan pulp polysaccharides | Logan | Promotes the growth of Lactobacillus plantarum, Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Lactobacillus fermentum |
Figure 3: Different Kinds of Emerging Prebiotics
The U.S. regulations mainly consider prebiotic soda drinks as functional drinks, and the FDA doesn’t take onus/proof of the ingredients. They come under the National Center for Complementary and Alternative Medicine (NCCAM), Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA), or PHS Act. It can be seen that most prebiotic drinks are not marketed as dietary supplements like probiotics. Likewise, prebiotic drinks are regulated by other organizations like Functional Food Science in Europe (FUFOSE), Food Standards Australia and New Zealand (FSANZ), WHO, and other quality control divisions and health/welfare ministries.
Conclusion
Spiritedly, the prebiotic soda drinks are being enjoyed in good taste and good health by all and sundry. Prebiotic drink buyers must use their good discretion and read the ingredient list to ensure the intended function of these beverages. As consumption often is a nebulous space, moderation/right intake of these functional drinks is recommended.
Prebiotics have found other uses in animal feeds, packaged baby milk, and prebiotic Powders/supplements apart from prebiotic soda drinks. We are yet to see how the prebiotic space will wholly develop in the future.
Let's Take the Conversation Forward
Reach out to Stellarix experts for tailored solutions to streamline your operations and achieve
measurable business excellence.



