Smart Packaging: Technology Transforming Packaging Industry
The smart packaging industry is currently experiencing a dynamic transformation driven by the growing demand for advanced solutions catering to the specific needs of various sectors. Whether in healthcare or the food and beverage industry, smart packaging revolutionizes how products are stored, transported, and distributed to a global consumer base. A detailed exploration of the smart packaging sector covers its market size, growth trends, opportunities, analysis, driving forces, and challenges. It provides a comprehensive overview that benefits investors, business leaders, and research and development professionals.
A Glimpse Into The Future Of Product Quality And Safety
Smart packaging pertains to packaging systems incorporating sensor technology, which is utilized in various products such as food, pharmaceuticals, and other commodities. Its primary function is to prolong the shelf life of products, monitor their freshness, display quality information, and enhance product and customer safety. Furthermore, smart packaging presents novel business opportunities founded on digitization, aligning with the broader scope of Industry 4.0. Smart packaging is specifically engineered to mitigate food spoilage, elevate the taste profile of food, and provide additional functionalities. According to projections, the market worth of intelligent food and beverage packaging within the United States is anticipated to reach approximately 2.3 billion U.S. dollars by 2024.
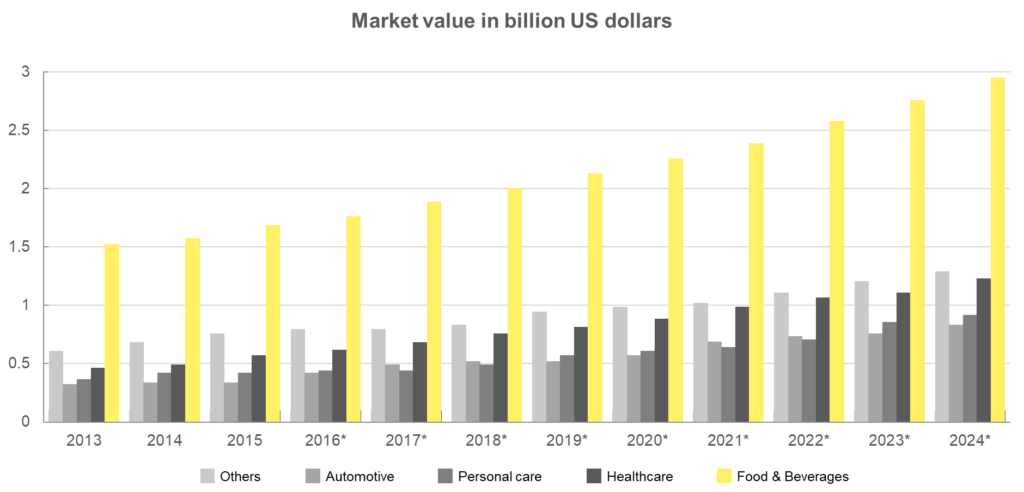
Figure: Intelligent Food and Beverage Packaging Market Worth in The US
(*Forecast)
Smart packaging employs unique digital identities such as QR codes, barcodes, and other identifiers to engage with consumers, authenticate products, and trace the journey of a product. It incorporates sensors and indicators that monitor the product’s condition to provide information about its status. Smart packaging can be categorized into two subtypes: intelligent packaging and active packaging. Intelligent packaging employs information and communication technologies to monitor the condition of a product. In contrast, active packaging involves adding or removing components in the packaged food or immediate surroundings to enhance the product’s shelf life or quality. The global smart packaging industry is expanding as more brands adopt this innovative technology.
Types of Smart Packaging
Smart packaging is an umbrella term that describes different types of packaging with enhanced functionality to create an improved packaging experience.
1. Intelligent Packaging:
Intelligent packaging involves sensors and indicators that monitor the product’s condition to provide information about its status, such as freshness, quality, safety, and security. Examples of intelligent packaging include:
- Time-temperature indicators
- Intelligent skin packaging
- Packaging that uses diagnostic and indicator technologies to communicate with the outside world
2. Active Packaging:
Active packaging refers to packaging that interacts with what’s inside, and the goal is often to increase the product’s shelf life. Examples of active packaging include:
- Temperature-controlled packaging
- Oxygen absorbers
- Food packaging is made of materials that reduce the amount of moisture that reaches the food
3. Passive Packaging:
Passive packaging is packaging that does not interact with the product inside. Examples of passive packaging include:
- Biodegradable and carbon-neutral packaging
- Traditional packaging, such as cardboard boxes and plastic bags
4. Near-Field Communication (NFC) Packaging
NFC packaging uses near-field communication technology to allow consumers to interact with the packaging using their smartphones. Examples of NFC packaging include:
- Packaging that allows customers to access product information, promotions, and other digital content by tapping their smartphones on the package
5. QR Code Packaging
QR code packaging uses QR codes to give customers access to product information, promotions, and other digital content. Examples of QR code packaging include:
- Packaging that allows customers to scan a QR code to access product information, recipes, and other digital content
6. Connected Packaging
Connected packaging uses technology to connect the physical package with the digital platform. Examples of connected packaging include:
- Packaging that allows customers to reorder products by scanning the package with their smartphones and tapping a “buy” button.
7. Tracking and Tracing Packaging:
Tracking and tracing packaging uses RFID tags or other tracking devices to track the movement of a product through the supply chain. Examples of tracking and tracing packaging include:
- Packaging that allows companies to monitor the location of their assets in real-time and prevent theft
Different Types Of Sensors Utilized In Smart Packaging?
Smart packaging employs a variety of sensors to identify and monitor various aspects of the product. The following are some of the sensor types utilized in smart packaging:
- Colorimetric Indicators: These sensors can detect changes in the product’s color and provide information on any alterations to a food product or other products.
- RFID Sensors: These sensors are more appropriate for smart packaging in terms of sensing ability and data transmission. They are simpler, low-cost, more robust, and less power-consuming.
- Biosensors: These sensors are utilized to detect and quantify biological or biochemical reactions. They can detect pathogens, chemical contaminants, and food spoilage and alter its properties.
- Gas Sensors: These sensors detect the presence of gases such as oxygen, carbon dioxide, and nitrogen. They are commonly used in food packaging to monitor the freshness of the product.
- Chemical Sensors: These sensors are utilized to detect the presence of specific chemicals in the product. They can detect changes in the product’s pH, moisture, and other chemical properties.
Advantages Of Utilizing Smart Packaging
Smart packaging provides numerous advantages to both consumers and businesses. The following are some of the key benefits of utilizing smart packaging:
1. Enhanced Customer Experience:
Smart packaging offers consumers greater access to product and company information, resulting in a more satisfactory shopping experience. Consumers are promptly redirected to a designated encounter using the provided code, such as a webpage. At this location, they can peruse a recipe, video, or promotion, enroll in a loyalty program, subscribe to a newsletter, engage in a game, or even acquire a coupon through downloading.
2. Enhanced Supply Chain Transparency:
Smart packaging enables businesses to track product locations in real time, which can improve traceability and logistics.
3. Maintained Quality Control And Product Integrity:
Smart packaging can assist companies in maintaining quality control and product integrity, which can significantly impact a company’s reputation. Certain types of packaging have the capability to extend the duration of shelf life by eliminating undesirable particles from the substance, whereas others aid in the identification of fraudulent offerings. Consequently, this leads to enhanced accessibility to authentic products of superior quality directly from the producer. Additionally, intelligent packaging contributes to the provision of more durable solutions.
4. Brand Transparency:
Smart packaging allows businesses to communicate authenticity and detailed information on boxes, which can help to create brand transparency. Moreover, smart packaging has the potential to assist consumers (and businesses) in monitoring the origins of product materials, the manufacturing process, the responsible parties involved, and any other pertinent information that may be crucial for consumers to decide whether or not they can ethically and socially support a brand through their purchase.
5. Theft And Counterfeit Prevention:
Smart packaging can help prevent theft, unauthorized access, and tampering. Furthermore, in instances where the quality of products does not meet the high standards set by your business, it can harm your brand image and public perception. By employing intelligent packaging solutions, businesses can effectively monitor their products and convey authenticity to consumers.
6. Increased Customer Engagement:
Smart packaging can direct customers to web-linked informational videos, tutorials, and more, which can help increase customer engagement.
7. Enhancing Probability Of Positive Experience:
Certain products may present greater complexity for consumers to comprehend, particularly if they are novel or incorporate unfamiliar ingredients or materials. Facilitating captivating opportunities for consumers to interact with and acquire knowledge about the products they purchase constitutes a crucial measure in ensuring their comprehensive understanding of the unparalleled capabilities that render your product superior in the market. Intelligent packaging can serve as a means to guide customers toward web-based informative videos, tutorials, and other resources. Furthermore, it enables expedited access to a customer support helpline, where they can promptly seek clarification, voice concerns, and avail themselves of other assistance, all within a time-efficient framework.
8. Predictive Planning:
One of the significant and challenging issues that every company faces is the effective management of customer orders when they deplete their product supply or require a replacement. Incorporating intelligent packaging systems allows manufacturers to gain a more comprehensive insight into the depletion status of their products, enabling them to communicate with customers through messages or emails, inquiring if they desire a replacement. Moreover, smart packaging can automate this entire process. Additionally, integrating QR codes or other cloud-based solutions presents alternative strategies to facilitate customer repurchases by directing them to the company’s website.
Conclusion
The rise of smart packaging represents a transformative leap forward in the packaging industry. As technology continues to evolve, it empowers businesses to offer consumers an elevated experience and unlocks unprecedented transparency and efficiency across the supply chain. The diverse categories of smart packaging, from intelligent to active, cater to various needs and preferences, making it a versatile solution for a wide range of products.
The utilization of sensors in smart packaging has revolutionized how we monitor and interact with products, fostering consumer confidence, brand transparency, and quality control. The advantages are abundant, from enhanced customer experiences to theft prevention and predictive planning, reflecting the broader trend of Industry 4.0.
As we look ahead, the future of smart packaging holds the promise of even more innovation, further blurring the lines between the physical and digital worlds. With ongoing research and development, the potential for smart packaging to reshape our interaction with products and information is virtually limitless.



