Vision For Cybersecurity In The Medical Technology
In today’s dynamic healthcare landscape, fortifying the healthcare system against cyber threats like malware and ransomware attacks is pivotal. Ensuring cybersecurity is paramount across the medical industry, including biotechnology firms, insurers, healthcare providers, pharmaceutical companies, and medical device manufacturers. Also, it encompasses a range of measures to protect organizations from internal and external cyber-attacks, maintain uninterrupted medical services, preserve data confidentiality, ensure the optimal functioning of medical systems, safeguard patient information integrity, and comply with industry regulations. In this blog, we will delve into the crucial importance of healthcare cybersecurity and medical device cybersecurity (MedTech). Moreover, we’ll explore the multifaceted aspects of the proactive steps undertaken and the vision to safeguard the integrity of our healthcare infrastructure along with cybersecurity in the medical technology
Understanding The Importance Of Cybersecurity In Medical Technology
In recent years, the healthcare industry has become increasingly reliant on medical devices and systems, making cybersecurity an essential component of healthcare. Moreover, cyber-attacks on Protected Health Information (PHI), Personal Identification Information (PII), and other programs pose a risk to patient safety and privacy. Additionally, healthcare organizations possess a lot of information of high monetary and intelligence value to cyber thieves, making them particularly vulnerable and targeted by cyberattacks. Cybersecurity in healthcare ensures the privacy and safety of patients’ information to medical providers.
Global Cybersecurity Market In The Healthcare Sector 2023-2027
As of 2023, the global healthcare cybersecurity market has been valued at 20.1 billion U.S. dollars. This market is projected to experience substantial growth and is estimated to surpass 58 billion U.S. dollars worldwide by the year 2027.
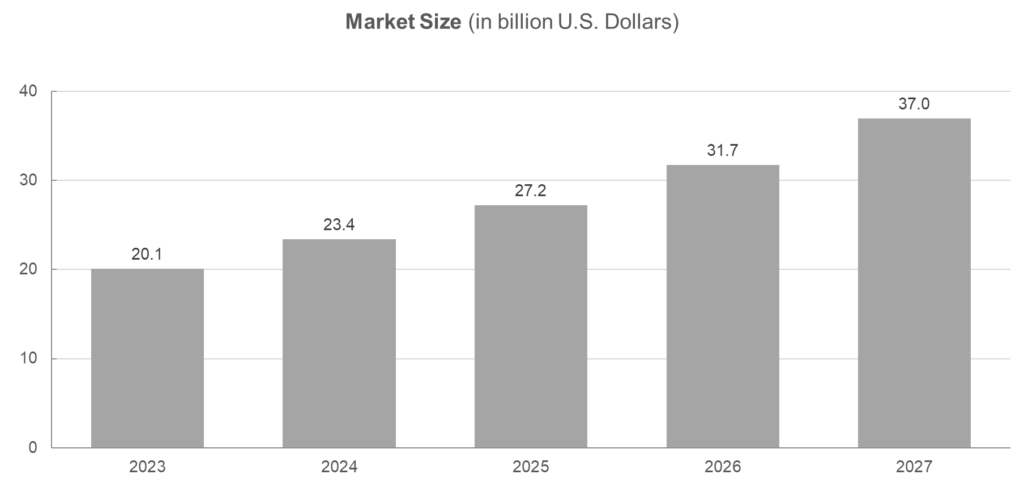
Figure 1: Global Cybersecurity Market in the Healthcare Sector 2023-2027
Key Market Players In The Cybersecurity Healthcare Market
Censinet, Cynerio, Virta Laboratories, Palo Alto Networks, Cisco, IBM, Claroty, Juniper, CrowdStrike, Check Point, Forescout, MedCrypt, Protenus, Zeguro, JFrog, Sophos, Kudelski Security, Trend Micro, Fortinet, Imprivata, Armis, Saviynt, Sophos, Forcepoint, Verimatrix, CloudWave, Sternum, Dell EMC and others.
Common Cybersecurity Threats Faced By Healthcare Providers
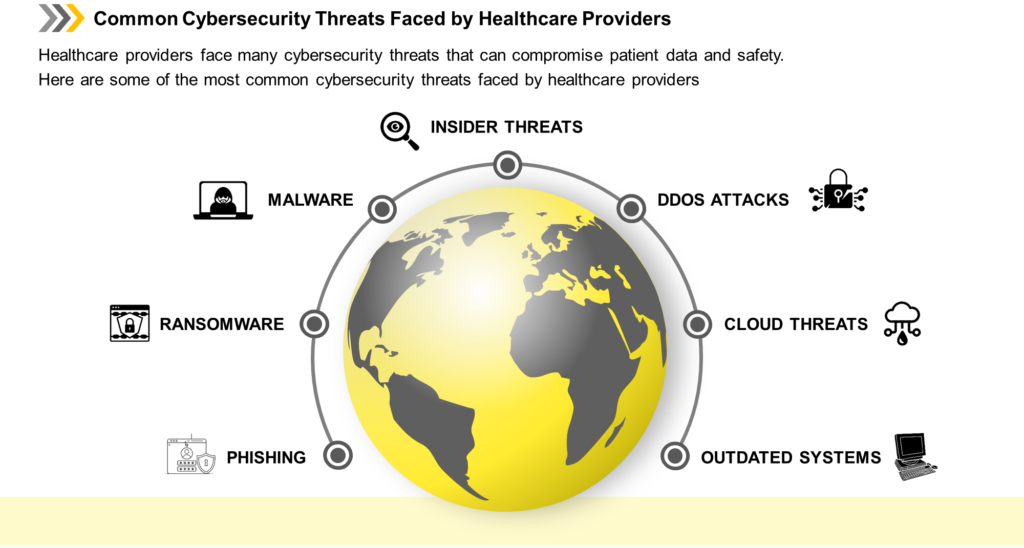

Figure 2: Cybersecurity Threats Face In Healthcare
- Phishing: It is the most common cybersecurity threat in healthcare. It involves infecting a seemingly innocuous email with malicious links, compromising the integrity of systems and patients’ privacy.
- Ransomware: Ransomware is another common and expensive threat to healthcare organizations. It encrypts data and demands payment to restore access to it.
- Malware is software designed to harm or exploit any computer system. It can compromise system integrity and patient privacy.
- Insider threats: Insider threats are cybersecurity threats involving contractors or employees who have access to sensitive information and use it for malicious purposes.
- DDoS Attacks: Distributed Denial of Service attacks are cybersecurity threats that involve overwhelming a system with traffic, making it unavailable to users.
- Cloud Threats: Cloud threats are a type of cybersecurity threat that involves exploiting vulnerabilities in cloud-based systems.
- Outdated Systems: Outdated systems are a type of cybersecurity threat that involves using outdated software or hardware no longer supported by the vendor, making it vulnerable to cyber-attacks.
Enhancing Security Measures In Medical Technology
Enhancing security measures in medical technology is crucial to protect patient data and ensure patient safety. Here are some ways healthcare providers can improve the security of medical devices, such as automated diagnosis using AI, blockchain, IoT, and other smart devices :
- Ensure All Medical Devices have a Secure Password: Secure passwords should have at least eight characters and contain numeric, alphabetic, and special characters.
- IoT and Smart Devices: They are revolutionizing patient care, empowering patients to monitor their health with connected devices, while smart beds and medication dispensers enhance at-home care. Clinicians benefit from improved patient behavior monitoring. Healthcare transformed through IoT.
- Blockchain: It has revolutionized healthcare with improved data security, interoperability, and privacy. Also, streamlined electronic records, eliminated intermediaries, and enhanced identity management to drive innovation.
- Artificial Intelligence: Automated AI in healthcare improves outcomes with evaluated medical knowledge. It aids rapid diagnosis, offers affordable care, and prevents cybersecurity attacks.
- Follow FDA Guidelines: The FDA provides guidelines for medical device safety that can be a starting point for securing medical devices.
- Find Medical Device Cybersecurity Companies: They may include McAfee, Imprivata, Protenus, Check Point Software, Philips, GE Healthcare, Trellix, CrowdStrike, etc. They may help provide some solutions.
Other Security Measures
- Maintain Device Health: Keeping up with software updates, health, and maintenance of medical devices is another way to secure clinical devices.
- Segment the Network: Segmentation of the network can help to isolate medical devices from other network traffic, reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
- Detect Network Attacks with AI: Artificial intelligence (AI) can be used to detect network attacks and other security threats to medical devices.
- Monitor System Alerts: Monitoring system alerts can help identify and respond to security threats promptly.
- Use Basic and Advanced Security Controls: Essential security controls like anti-virus, backup, data recovery, data loss prevention, email gateway, encryption, firewall, intrusion detection, mobile device management, and patch management bolster healthcare cybersecurity. Advanced measures such as anti-theft devices, business continuity, disaster recovery, digital forensics, multi-factor authentication, network fragmentation, login testing, information sharing, and risk scans further enhance cybersecurity for healthcare organizations.
A Vision For Robust Medical Technology Cybersecurity
- Cybersecurity Investment: An integrated and robust cybersecurity framework in the medical technology sector is crucial for ensuring the safety and security of medical devices and protecting patients’ confidential data.
- Building Digital Resilience: Healthcare’s digital transformation requires a resilient ecosystem, focusing on securing medical devices and digitalization across institutions and healthcare delivery to counter cyber threats.
- Adopting Cybersecurity Frameworks: Healthcare organizations benefit from established frameworks like NIST CSF, helping bolster cybersecurity, complemented by other compliance efforts like HIPAA Security Rule.
- Securing Supply Chain: Ensuring medical device integrity throughout its lifecycle demands stringent supply chain security to mitigate vulnerabilities comprehensively.
- Continuous Assessment and Improvement: Regularly evaluating and improving security programs, roles, and responsibilities while prioritizing measures are vital to stay ahead of evolving cyber threats in healthcare organizations.
Real-time Monitoring For Swift Cybersecurity Threat Detection And Response
To implement real-time monitoring solutions for detecting and responding to cybersecurity threats promptly in the medical technology sector, the following steps can be taken:
- Embrace Cybersecurity Monitoring Tools: Employ real-time cybersecurity monitoring tools for network traffic, system logs, and user activities. Proactively detect unusual or malicious behavior.
- Automate Security Monitoring: Deploy automated systems for continuous network and endpoint security monitoring. Also, it swiftly detects and alerts cybersecurity teams about potential threats for rapid response and mitigation.
- Implement Real-time Data Monitoring: Establish capabilities for real-time data monitoring to track and manage organizational data access. In addition, it analyzes system event logs, user activities, and system access instantly to identify security threats as they occur.
- Deploy Threat Detection and Response Software: Utilize threat detection and response software with real-time monitoring. Additionally, it detects advanced attacks and receives customizable alerts for immediate response and incident management.
- Establish Continuous Monitoring and Analysis: Implement continuous monitoring and analysis to monitor the network and systems continuously. Moreover, regularly review security logs, analyze events, and conduct vulnerability assessments for proactive threat identification.
- Integrate with Incident Response Plan: Integrate real-time monitoring solutions with an incident response plan. In addition, ensure a predefined process for prompt and effective response to cybersecurity threats, including containment, eradication, and recovery procedures.
Cybersecurity In The Medical Technology: Collaboration In Healthcare
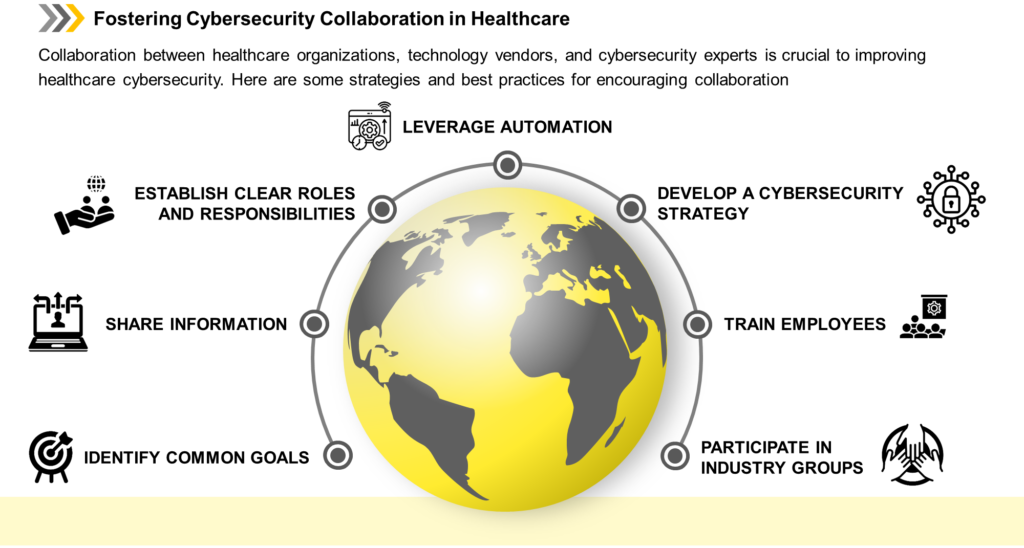

Figure 3: Cybersecurity Collaboration
- Identify Common Goals: Healthcare organizations, technology vendors, and cybersecurity experts should identify common goals and work together to achieve them.
- Share Information: Sharing information about cybersecurity threats and best practices can help improve medical technology’s overall security.
- Establish Clear Roles and Responsibilities: Establishing clear roles and responsibilities can help to ensure that everyone is working towards the same goal.
- Leverage Automation: Implementing security automation can significantly enhance the effectiveness and expediency of identifying and swiftly responding to potential threats.
- Develop a Cybersecurity Strategy: A comprehensive cybersecurity strategy can ensure all stakeholders are aligned and working towards the same goal.
- Train Employees: Training employees on cybersecurity best practices can help reduce the perils of human mistakes and improve overall security.
- Participate in Industry Groups: Industry groups can facilitate collaboration and information sharing between healthcare organizations, technology vendors, and cybersecurity experts.
Ethical Considerations In Data Privacy And Patient Consent
Ensuring data privacy and patient consent are critical ethical aspects of cybersecurity in medical technology. Here are the key findings:
Growing for-profit companies acquiring extensive healthcare system databases raise fresh hurdles in protecting patients’ privacy despite existing privacy laws in the United States.
- Sharing patient data with entities that could exploit it for commercial gain or target vulnerable populations raises significant ethical concerns
- Breaches in the confidentiality of extensive databases put millions of patients at risk of exploitation, necessitating new regulations to govern the sharing of patient data
- Addressing ethical considerations surrounding patient data contribution to research is crucial, especially when the potential for commercial exploitation exists by sharing patient data with third-party companies
- Privacy and confidentiality of personal information, including electronic medical records and genomic data, raise important ethical and regulatory considerations
- Obtaining informed consent becomes essential when using individuals’ health information for research, regardless of its direct relevance to clinical or insurance purposes
- Applying the respect principle for persons in health information research requires safeguarding patient privacy, dignity, and confidentiality while minimizing potential harm
- Regulations should prioritize patient agency, consent, and advanced data anonymization methods to address privacy concerns related to artificial intelligence
Conclusion
The healthcare industry faces heightened vulnerability to cyberattacks due to the abundance of valuable information, making it an attractive target for cybercriminals and nation-state actors seeking monetary gain or intelligence. While the primary objective of the healthcare and pharmaceutical sectors is to preserve lives and promote well-being, the digital age has brought about the computerization of personal and sensitive data. This digitization has facilitated easier access to information and drawn the attention of malicious individuals seeking to exploit vulnerabilities. Notably, biomedical devices are vulnerable to cyberattacks.
Establishing best practices for securing medical devices is crucial to ensure comprehensive cybersecurity measures. One key step is to utilize inventory data to identify all devices within the healthcare system. Moreover, given the significant attention and investments in healthcare cybersecurity, it is essential to address the potential risk posed by disgruntled individuals who intentionally disclose patient information out of personal resentment or for illicit gains in the black market where protected health information is in demand. Looking ahead, technology will continue to wield a significant influence in shaping the future of healthcare.
Let's Take the Conversation Forward
Reach out to Stellarix experts for tailored solutions to streamline your operations and achieve
measurable business excellence.



