IFRA Ingredients Restrictions & Sustainability Aspects
Fragrance is a blend of natural extracts or synthetic aroma compounds designed to impart a pleasant scent. It is used in fine perfumes as well as consumer products such as cosmetics, personal care items, cleaning agents, and air fresheners to provide distinctive, long-lasting aromas that enhance product appeal and user experience.
Approximately 20% of the general population is sensitized to at least one allergen, with fragrance ingredients among the most common triggers. Fragrance allergy specifically affects an estimated 2–11% of people worldwide, representing tens of millions of individuals globally.
The companies that manufacture perfume or cologne do not always provide information about the additives and fragrance compounds present in the product. The fragrance composition is not listed on the label and is kept as a trade secret and described only as “fragrance”. Also, for the consumer products, the fragrances used are in a combination of ingredients and are only indicated as the ‘fragrance’ or ‘parfum’.
The law does not provide for the disclosure or public safety of fragrance compounds. Due to trade secrets, certain fragrance compounds are excluded from being mentioned on the label. The International Fragrance Association (IFRA) and the Research Institute for Fragrance Materials (RIFM) develop and set voluntary standards for chemicals in the “fragrance” component of products. Compliance with IFRA Standards provides an additional self-regulation framework, which is widely adopted by fragrance companies and national authorities to ensure consumer safety and environmental protection. The regulation brings restrictions on the use of irritating, harmful, and toxic compounds, while the sustainability aspects address the environmental problems and bring opportunities for eco-friendly innovations.
IFRA Regulatory & Safety Framework
The International Fragrance Association (IFRA) has developed IFRA Standards, which serve as a globally recognized risk-management system to ensure the safe use of fragrance ingredients. These standards establish limits, restrictions, or prohibitions on specific fragrance compounds when safety concerns are identified.

The IFRA Standards Library is a searchable, regularly updated database containing all current standards. The IFRA Transparency List is a comprehensive register of fragrance ingredients and functional components used in fragrance mixtures supplied to consumer goods companies for personal care products, home care products, and fine fragrances worldwide.
Ingredients on the Transparency List are governed by the IFRA Code of Practice and comply with IFRA Standards, as well as national and local regulations and good manufacturing practices. Manufacturers are accountable for ensuring the safe use of these ingredients. All listed materials undergo evaluation within the RIFM Safety Assessment Program, where each assessment is reviewed and approved by the independent Expert Panel for Fragrance Safety. After approval, RIFM submits the findings for peer-reviewed publication and makes the final assessments freely available through the open-access Fragrance Material Safety Resource Center, ensuring scientific rigor, transparency, and public accessibility.
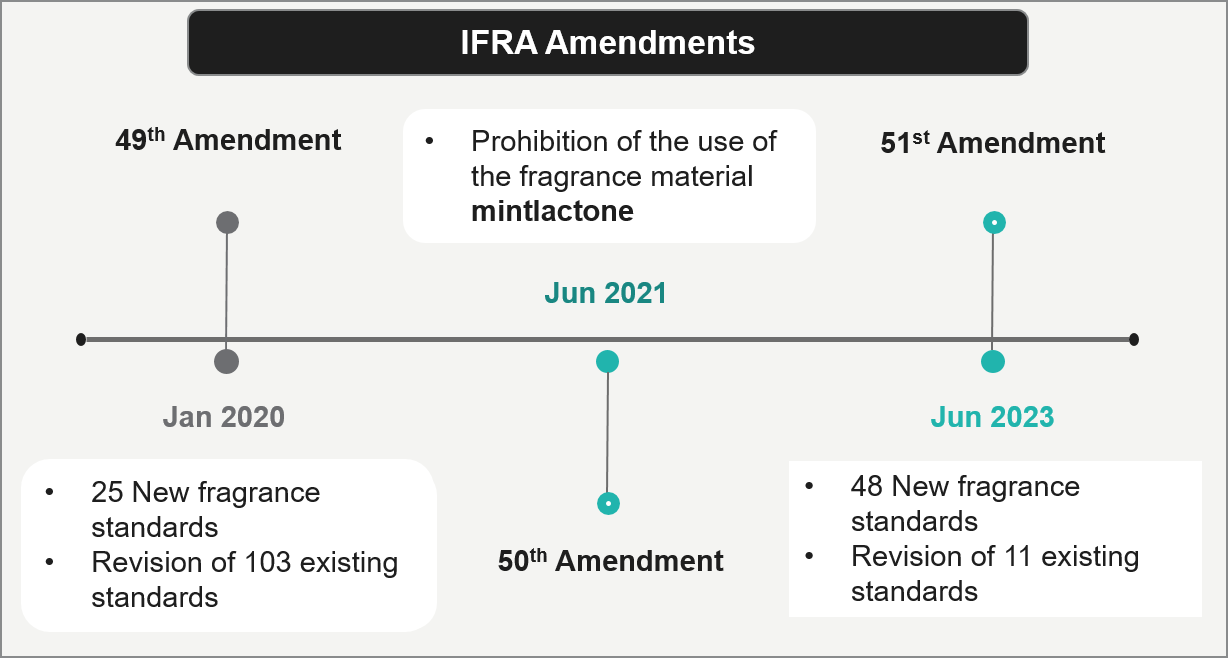
IFRA Amendment
IFRA periodically introduces amendments to regulate new ingredients and update restrictions on existing ones. These amendments require manufacturers of commercial fragrances to reformulate products when ingredients are prohibited or newly restricted. As a result, manufacturers must identify and use suitable alternative materials to replicate the original scent profile while maintaining safety and regulatory compliance.
Case Study
Givaudan proactively addressed regulatory restrictions on Lyral by developing its in-house replacement Mahonial™. This three-year initiative allowed perfumers to continue creating floral fragrances seamlessly while ensuring compliance and opening opportunities for innovative, safer fragrance molecules.
Restricted & Banned Ingredients
Several fragrance ingredients are restricted or prohibited by regulatory authorities due to their toxicity, skin or respiratory irritation, and adverse environmental impact.
Examples:
- Nitro Musks (Musk ketone, Musk xylene)
- Essential oil compounds
- Safrole – classified as carcinogenic.
- Eugenol (from clove oil) – restricted due to skin sensitization.
- Coumarin (naturally in tonka beans) – limited because of allergy concerns.
- Chloroatranol and Atranol (from Oakmoss and Treemoss)
- Highly allergenic, capable of causing severe dermatitis in sensitive individuals.
- Lilial (Butylphenyl Methylpropional)
- Classified as a reproductive toxin and banned in EU cosmetics since 2022.
Sustainability Aspects
Fragrance sustainability focuses on reducing the environmental and social impact of aroma creation while ensuring product safety and performance. Together, these efforts help brands meet regulatory requirements and growing consumer demand for eco-friendly and traceable fragrances.
Renewable Sourcing
Bio-based ingredients are derived from renewable sources, including plant feedstocks, agricultural or food industry byproducts, and other sustainable raw materials.
Biodegradability
Fragrance compounds with high biodegradability, as defined by OECD guidelines, address issues such as aquatic toxicity and bioaccumulation. It leaves minimal environmental impact and reduces waste.
Carbon Footprint Reduction
Optimizing energy use and reducing greenhouse gas emissions in fragrance manufacturing through processes such as extraction, synthesis, and formulation helps minimize environmental impact and supports sustainable production practices.
Green Manufacturing
Adoption of solvent-free or low-solvent extraction methods (e.g., supercritical CO₂, enzymatic) and closed-loop systems for water and solvent recovery.
Safe Fragrance Solutions
Minimizing or eliminating sensitizing allergens and developing non-sensitizing aroma molecules with controlled-release systems to maintain scent quality while reducing exposure.
Eco-friendly Innovations
Use of pro-fragrances for controlled release, biodegradable encapsulation systems, biotech-derived fragrance ingredients, and green solvents to enhance performance while reducing environmental impact.
Solutions for Environmental and Regulatory Challenges
- Gucci’s “Where My Heart Beats” fragrance uses alcohol made entirely from recycled carbon emissions (carbon capture), turning waste into a luxurious raw material. This innovative method reduces water usage and cuts down the need for agricultural land compared to traditional alcohol production. It delivers premium-quality alcohol while making the production process environmentally friendly.
- Iberchem’s upcycled fragrances transform traditional waste materials into high-quality scent ingredients, contributing to a circular economy. By repurposing byproducts that would otherwise be discarded, this innovative approach reduces environmental impact and minimizes waste. The use of upcycled materials not only conserves natural resources but also supports sustainable sourcing practices, as Iberchem ensures that 99% of its total waste is recycled and recovered.
- Debut Biotechnology has introduced a groundbreaking innovation in the fragrance industry by launching a plant cell biotechnology platform that produces fragrance ingredients without traditional cultivation. This technology enables the creation of complex fragrance molecules through fermentation, bypassing the need for growing and harvesting plants. The first product, Rare Orris, is derived from the root of the iris flower, a prized ingredient in perfumery that can cost up to $100,000 per kilogram.
- Bordas developed Mugal, a fresh, floral-aquatic ingredient designed to replicate Lilial’s olfactory profile. Unlike Lilial, Mugal is non-toxic, fully compliant with current safety regulations, and stable across various applications. By providing this alternative, Bordas enables the industry to maintain desired fragrance qualities while adhering to modern safety standards.
- Symrise has developed Lilybelle®, a readily biodegradable fragrance ingredient with a refreshing lily-of-the-valley note, made from renewable sources. Produced using byproducts of the orange juice industry, 83% of its composition comes from renewable raw materials, offering a sustainable alternative for modern perfumery.
Fragrance Market & Sustainable Partnerships
The global fragrance and perfume market is valued at USD 68142.5 million in 2024 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 8% from 2024 to 2031. According to 2024 global fragrance and perfume market data, North America and Europe accounted for a market share of approximately 40% and 30% respectively. Perfume is the leading market category, characterized by its high fragrance oil concentration and long-lasting aroma, making it especially appealing to the luxury consumer segment.
Sustainable Partnerships
- L’Oréal and Cosmo International Fragrances have developed a pioneering green science-based extraction process that utilizes only air to capture fragrance molecules from flowers, fruits, and other natural sources. This waterless, low-energy method preserves the authentic olfactory profile of ingredients without the need for heating, cooling, or chemical solvents. The process is designed to be scalable and aligns with L’Oréal’s sustainability goals.
- Unilever develops sustainable fragrances by giving new life to waste flowers. In collaboration with the University of Nottingham, the initiative reduces emissions and cuts reliance on petrochemical-based ingredients, promoting greener production practices. By using an enhanced Soxhlet extraction method along with ultrasonication, essential oils are efficiently obtained from surplus blooms such as petunias, roses, and marigolds. This technique not only accelerates extraction by 40%, achieving the desired compounds in just 20 minutes, but also minimizes waste and conserves natural resources, contributing to a sustainable production system.
- BGene and TechnicoFlor have established a strategic partnership to develop sustainable fragrance ingredients through synthetic biology. Leveraging BGene’s expertise in bioinformatics, metabolic engineering, and fermentation, alongside TechnicoFlor’s experience in fragrance development and market insights, the collaboration seeks to produce novel molecules via renewable and environmentally responsible processes.
- The collaboration between Givaudan and LanzaTech leverages LanzaTech’s biocatalyst technology to convert waste carbon emissions, such as industrial CO₂, into ethanol, which serves as a renewable feedstock for producing fragrance ingredients. Givaudan then uses this ethanol to synthesize key fragrance molecules, employing synthetic biology to create novel scent profiles while reducing reliance on fossil-based materials and minimizing environmental impact.
Conclusion
In the fragrance industry, it is essential that solutions are sustainably sourced, safe for use, and free from adverse effects on human health and the environment. Restrictions on fragrance ingredients protect consumers and the environment by limiting the use of allergenic, toxic, and non-biodegradable substances. IFRA regulations drive the fragrance industry to innovate biodegradable, renewable, and safer fragrance solutions, enhancing both brand reputation and regulatory compliance.
Let's Take the Conversation Forward
Reach out to Stellarix experts for tailored solutions to streamline your operations and achieve
measurable business excellence.