Adoption of 3D Printing in Various Industries
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, was first developed in 1980. It was only an idea in 1980; it has come long since then. Earlier, it was mainly used for prototyping. Since then, this technology has significantly expanded across various industries. Almost anything can be 3D printed — parts of a house, liver tissues, a part of a human ear, designer clothing, manufacturing components, and so on. Some recent advancements in the adoption of 3D printing include Food and cloud-based 3D printing services.
The benefits of adopting 3D printing have been numerous, including rapid prototyping, print-on-demand, strong and lightweight parts, minimizing waste, cost-effectiveness, and environmental friendliness.
As the range of potential uses for 3D printing expands, industries are starting to discover methods to create new business models and opportunities with the technology.
3D Printing and Adoption Stages in Various Industries
The level of adoption and research intensity of 3D printing varies greatly across different industries, as shown below:
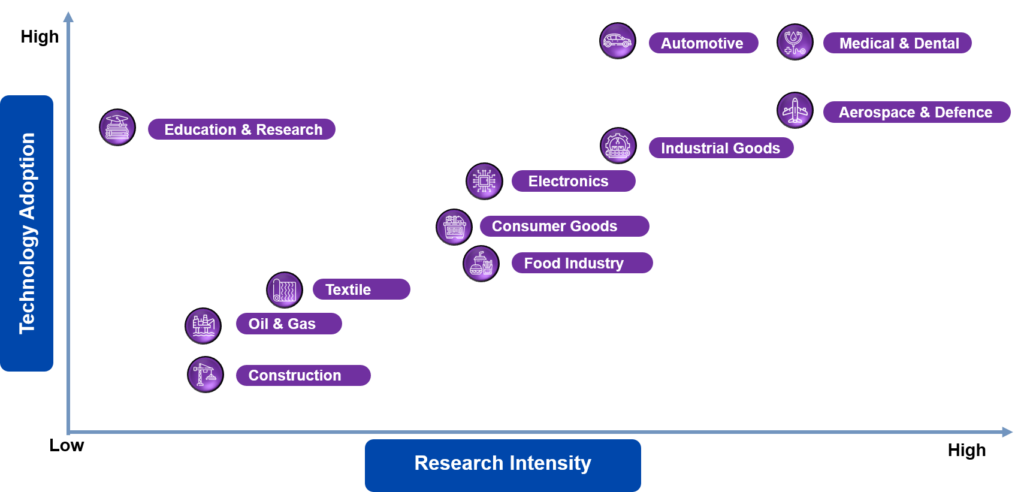
Figure 1: 3D Printing Adoption stages and Research intensity in Various Industries
- Aerospace & Defense: One of the first industries to adopt 3D printing was the aerospace & defense industry, which started using the technology in 1989. The advancement of 3D printing within this sector on a large scale is driven by some key players such as GE, Airbus, Boeing, Safran, and GKN. 3D printing in this sector is used to develop combustion chambers, rocket engine parts, wall panels, surveillance drones, submarine hulls, air ducts, and their structural metal components. Complex parts or complex geometries can be created with this technology in less time without investing in expensive tool equipment.
- Automotive Industry: The automotive industry is a growing user of 3D printing. According to Stellarix research, global automotive additive manufacturing revenues reached $1.36 billion in 2019 alone and are expected to reach $5.7 billion by 2025. Some key players, such as Porsche, Ford, and BMW, have started using this technology to develop “3D-printed body foam full-bucket seats,” powertrain components, tooling equipment such as injection molds, jigs & fixtures, and spare and replacement parts.
- Medical and Dental: The medical and dental industry is one of the fastest-growing adopters of 3D printing or additive manufacturing. 3D printing can develop everything from medical devices to therapeutic liver tissue. This sector also uses 3D printing for clear aligners and sterile surgical instruments (forceps, hemostats, scalpel handles, and clamps). 97% of medical additive manufacturing professionals are confident that 3D printing technology will continue to rise in this sector.
- Consumer Goods: The applications of 3D printing in this sector are mostly focused on prototypes used in product design. The technology’s true potential may lie in the direct manufacturing of consumer products. As of 2019, footwear, eyewear, jewelry, and bike manufacturing are the biggest segments leveraging 3D printing in production.
- 3D Food Printing: The possibility of printing food is one of the most fascinating recent advancements in 3D printing. This technology is relatively new and has already started to gain popularity in the world of gastronomy. Some of the popular materials for 3D food printing are cheese, chocolate, and dough. However, this technology is not limited to only these ingredients. There is a growing trend to create more complex dishes such as sushi and pizza. This technology helps fight food wastage by printing food directly at the location and supplying fresh food only when demanded.
Some other sectors have also adopted 3D printing and are in the early stages, including construction, oil & gas, and textile industries.
3D Printing in the Automobile Industry
Over the past decade, one of the most significant advancements in the automobile industry is the adoption of 3D printing technology. The advantage of utilizing 3D printing technology in this industry is its ability to revolutionize the prototyping and design validation process. It enables automakers to unlock new potential in vehicle design, production, and sustainability. The following list includes a few automobile components that are being produced by 3D printing:
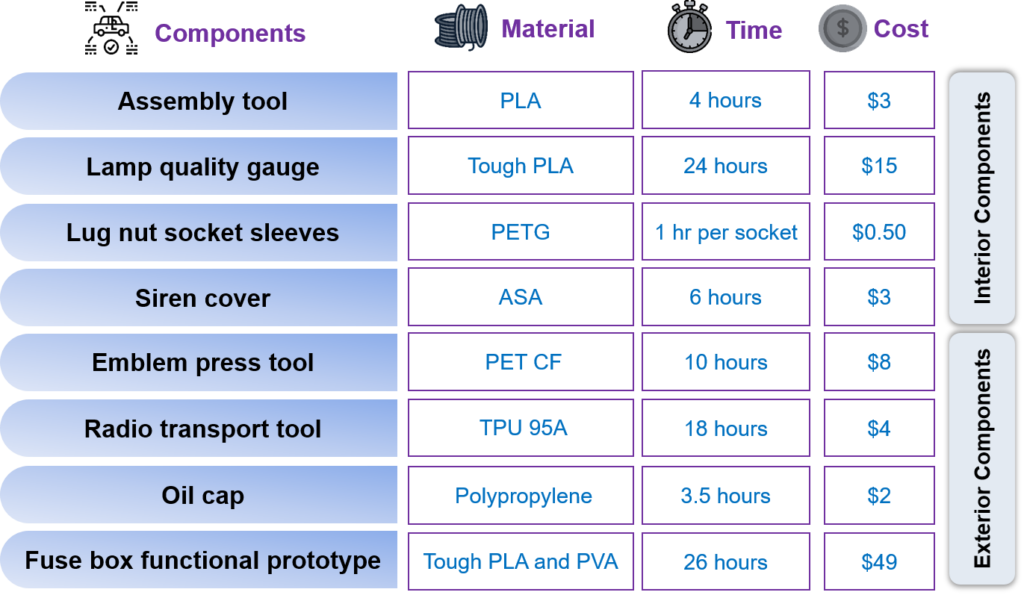
Figure 2: Adoption of 3D printing in various Automobile Components
The adoption of 3D printing in automobiles has significantly reduced the manufacturing time of lamp quality gauges from 4 weeks to 24 hours. Similarly, it reduces the time and cost of other automobile components.
Recently, The Technology Innovation Institute (TII) announced the first metal additive manufacturing alloy, AMALLOY-HT, used for 3D printing pistons in racing cars. The material demonstrates excellent thermal stability for harsh operating conditions.
Know About 4D Printing
In recent years, 3D printing technology has revolutionized industries by enabling the employment of various materials, including plastic, metal, resins, sandstone, wax, and ceramics. These refinements are offering significant business benefits, including streamlined supply chains, enhanced prototyping, and manufacturing new designs that were not possible in the past.
But what if we could take this technology one step further and create objects that can change shape and functionality independently? This is the idea behind 4D printing, an emerging technology that adds a fourth dimension to the printing process.
4D printing is an advanced form of additive manufacturing that involves creating objects with smart materials that can transform their shape and properties over time. The “fourth dimension” in 4D printing refers to the ability of the printed object to change its shape or functionality in response to external stimuli, such as temperature, light, or moisture.
Conclusion
The adoption of 3D printing across industries represents a watershed moment in the evolution of manufacturing and design. From automotive and healthcare to aerospace, consumer goods, and construction, additive manufacturing has transcended boundaries, reshaping industries and driving innovation.
As the technology continues to mature and adoption rates soar, the full potential of 3D printing will be realized, ushering in a new era of manufacturing excellence, customization, and sustainability. In the journey towards a more efficient, resilient, and interconnected future, 3D printing stands as a beacon of innovation, inspiring creativity and driving progress across diverse sectors around the globe.
Let's Take the Conversation Forward
Reach out to Stellarix experts for tailored solutions to streamline your operations and achieve
measurable business excellence.