What is 4D Printing?
4D printing is an advanced additive manufacturing technology that combines 3D printing and stimulus-responsive materials to generate dynamic, intelligent structures. The generated structures’ shape and size change under the influence of environmental stimuli, such as heat, light, humidity, water, chemicals, magnetic fields, and others. With this additional dimension, 3D-printed structures can alter their shape over time without any electromechanical or moving parts.

Figure 1: Key players of 4D printing technology and materials
Who developed 3D Printing and 4D Printing?
The first primitive 3D printer was developed by Dr. Hideo Kodama in 1981. Kodama invented the first rapid-prototyping machine that created objects layer by layer with the use of resins. But in 1986, Chuck Hull, considered the inventor of 3D printing, filed its first patent for SLA and STL file format – the most common file type used for 3D printing.
In 2013, Skylar Tibbits, an associate professor from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), introduced the concept of “4D printing.” Tibbits and his co-workers invented an entirely new 3D printing technology, including smart materials with inherent properties that can alter their shape under the influence of external stimuli. The external stimuli could be heat, moisture, light, electro-waves, or magnetic waves.
Workflow in 4D Printing
It is unique from other printers because of its ability to use smart materials to create dynamic structures that respond to external stimuli. The workflow in 4D printing is depicted below.
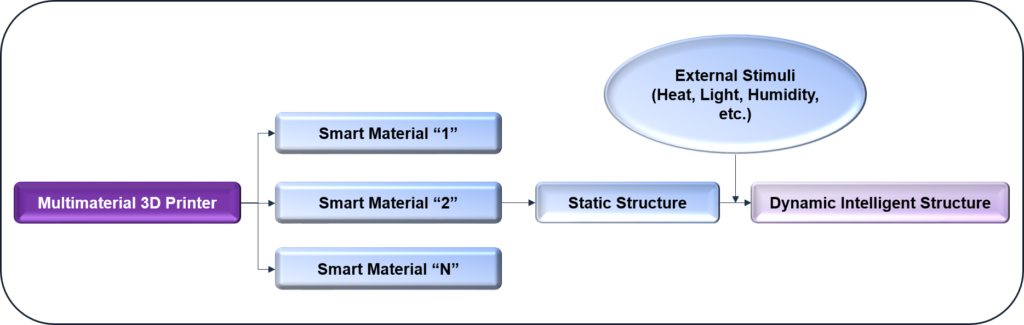
Figure 2: Workflow in 4D Printing
What is 4D Printing Used for?
This technology will have numerous applications in various industries in the near future. Since it is a novel technology, most of the applications are still in the research & development phase. Significant end uses of 4D printing technology are anticipated in aerospace, automotive, healthcare, and consumer industries. It is anticipated that the potential of 4D printing technology will also have an impact on other industries such as electronics, construction, industrial, etc. Some of the end uses products of 4D printing are discussed below:
- 4D Printed Metal Fabric: Raul Polit-Casillas, a system engineer at NASA’s jet propulsion laboratory, has developed a new metal fabric through 4D printing technology. This fabric is square, reflecting light on one side and absorbing it on the other, which makes it ideal for passive heat control. The durable and flexible metal fabric will be used to insulate spacecraft, space suits, and antennas.
- Smart Valves for Water Handling: The ARC Centre of Excellence team for Electromaterials Science has developed a “smart valve” through 4D printing of hydrogels. These hydrogels are mechanically robust and thermally actuating. The valve comprises four components, each printed with a different material ink.
- Programmable Carbon Fiber: Airbus Ltd. and MIT have developed programmable carbon fiber to cool airplane engines by maintaining airflow automatically. This bidirectional material replaces the need for a robotic mechanism or an opening that causes drag at the top of a jet engine.
- 4D Bioprinting: Poietis, a French Bioprinting firm, was the first to develop and commercialize bioprinted synthetic skin. It still has a long way to go from providing skin tissue for reconstructive surgery and cosmetic testing. The 4D bioprinting platform includes bioextrusion, micro-valve printing, and laser-assisted bioprinting. It also promises to deliver customized and personalized medical products, drugs, and equipment for the benefit of healthcare providers and patients.
4D printing also promises to change the face of the fashion industry. Clothes that adapt to weather conditions are being researched. Shoes that can be shaped based on the activity being undertaken can promise custom levels of comfort & ergonomics. Some of the researchers have also created a series of self-assembled plastic objects. These objects can fold themselves into predetermined shapes when heated. Researchers believe this process could be the first step towards producing products, such as flat-pack furniture, which could assume its final shape with the help of a heat gun.
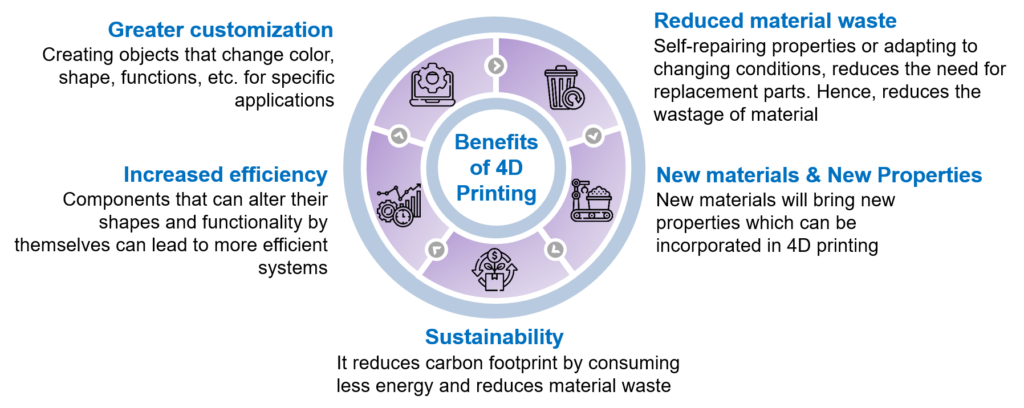
Figure 3: 4-dimensional printing benefits
Challenges Associated with 4D Printing
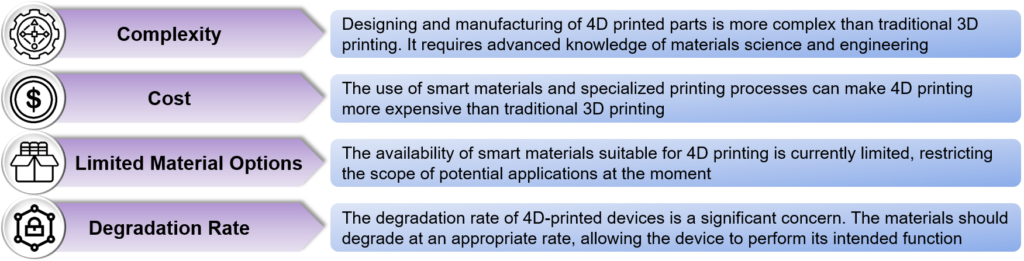
Figure 4: Challenges in 4-dimensional Printing
Collaboration
Recently, 4D printing companies, universities, and space agencies collaborated to develop some interesting 4D printed products with the use of advanced materials. Some of them are listed below:
- Self-Assembly Lab, Stratasys, and Autodesk: Researchers from MIT at Self-Assembly Lab have collaborated with Stratasys and Autodesk to create materials that are not only capable of folding themselves but also stretching and bending in response to external stimuli.
- Zortrax and European Space Agency (ESA): The Zortrax R&D team collaborated with the European Space Agency (ESA) to develop electrically conductive materials made of shape memory polymers. They used an M300 Dual FDM printer and a modified version of Z-SUITE, Zortrax’s printing software.
- BMW and Self-Assembly Lab: BMW’s design Department, in collaboration with MIT’s (Massachusetts Institute of Technology) Self-Assembly Laboratory, has successfully developed printed inflatable material technologies that self-transform, adapt, and morph from one state to another.
Conclusion
4D printing is a booming technology that is gaining traction in various applications. Many companies and universities continuously research and develop it further to reap its benefits. From shape-changing furniture to implants that fit any body type, self-healing pipes, self-adapting clothing, and bridges that build themselves, it promises real-life magic with discernable cost, material, and time efficiency advantages.
Contact us to learn more about the 4D printing technology and its implementation aspects!
- How does the programming of shape memory material affect its performance?
- What are the newly researched 4D printable materials, and what are their benefits?
- What are the key mechanical and medical applications explored with 4D printing?
- Which entities are researching in collaboration, and for what purpose?
- What is the future of magnetically controlled 4D printing technology?