Collaborative robots, also known as cobots, are industrial robots designed to work safely alongside humans in a shared workspace. Unlike traditional industrial robots, cobots can perform a variety of tasks and are not confined to safety cages. The use of cobots is becoming increasingly popular in various industries, including automotive, manufacturing, and healthcare.
Challenges and Solutions in Collaborative Robots for Industrial Automation
1) Challenge: Zero Incidents Workplace Safety
Solution: Collaborative robots need to operate safely to prevent accidents in the workplace. Cobots may have special safety mechanisms such as collision detection and light curtains. SICK AG Provides safety sensors and systems in a manner to prevent accidents in the workplace.
2) Challenge: Programming Complexity
Solution: A hybrid interaction mode, where automation tasks are programmed using a natural language chat and finalized through a block-based interface, can help. Universal Robots’ software called Polyscope offers built-in programming flexibility through the URScript API.
3) Challenge: Limited Payload Capacity
Solution: Developing more powerful and versatile robots that can handle larger payloads with increased reach and increased footprint can help. Kassow Robots’ KR1018 7-axis cobot arm provides a payload capacity of 18kg and a reach of 1000mm.
Key Enabling Technologies:
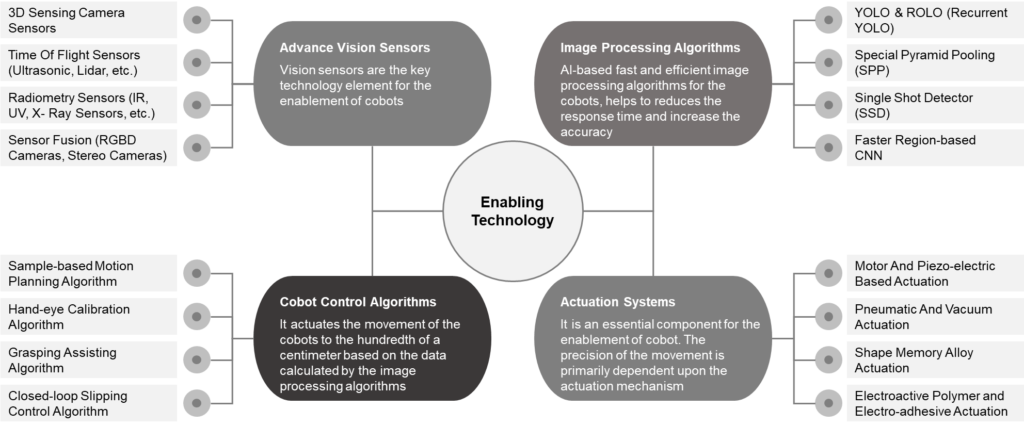
Future Technology Trends:
Integration with Artificial Intelligence (AI): Cobots can be integrated with artificial intelligence (AI) to perform more complex tasks. For example, a cobot can be programmed to recognize and sort different types of objects, which makes it easier to automate tasks such as packaging and quality control.
Increased Safety Features: Although there is always a risk of accidents, creators design cobots to work safely alongside human workers. To reduce the risk of accidents, cobots are being equipped with more advanced safety features. For example, some cobots are equipped with sensors that detect when a human worker is nearby, and they automatically stop working to prevent accidents.
Expansion into New Industries: Various industries, including automotive, manufacturing, and healthcare, are using cobots. In the future, we can expect to see cobots being used in new industries, such as agriculture and construction. For instance, a cobot can be used to plant and harvest crops, which reduces the need for human workers to perform repetitive tasks.
Increased Customization: Cobots are becoming more customizable, which makes them more adaptable to different production needs. For example, a cobot can be programmed to perform a variety of tasks, such as welding, painting, and assembly. Equipping cobots with different end-effectors, such as grippers and suction cups, makes them more versatile.
Key Market Activities:
The following business partnerships and acquisitions of key players in the market are expected to help grow and boost the market further.
- Universal Robots announced a partnership with global technology integrator Denali, the partnership is focused on bringing the best automation designs with the integration of emerging technologies such as Automation-As-A-Service (AaaS), data-driven decision-making, and others.
- OMRON announced an agreement to invest in Techman Robot, a Taiwan-based developer of collaborative robotic arms. OMRON held a stake of ~10% in Techman Robot.
- Novanta acquired ATI Industrial Automation for $172 million in cash. ATI Industrial Automation is a world-leading engineering-based developer of robotic accessories and robot arm tooling.
Collaborative robots are changing the way industries operate. They offer a cost-effective, safe, and flexible solution to automate repetitive and dangerous tasks, freeing up human workers to focus on more complex tasks. With the integration of artificial intelligence and advanced safety features, cobots are becoming more adaptable and customizable to different production needs. However, to ensure the safe and efficient operation of cobots, we need to address challenges such as programming complexity and cybersecurity.