Exploring the Benefits and Future of Cultured Meat Products
Cultured meat is meat produced by in-vitro cell cultures of an animal cell. It is a form of cellular agriculture and is a cheap, humane, and sustainable alternative to slaughtered meat. However, there is a requirement for consumer acceptance of cultured meat as its effects on health are still under consideration. But, the rising know-how of cultured meat is inculcating consumer acceptance. This lab-grown and clean meat is not only nutritious but also a sustainable choice. Therefore, to meet contemporary demands, there is a need to dive deep and explore this potent, promising technology for cultured meat.
Cultured Meat Technology
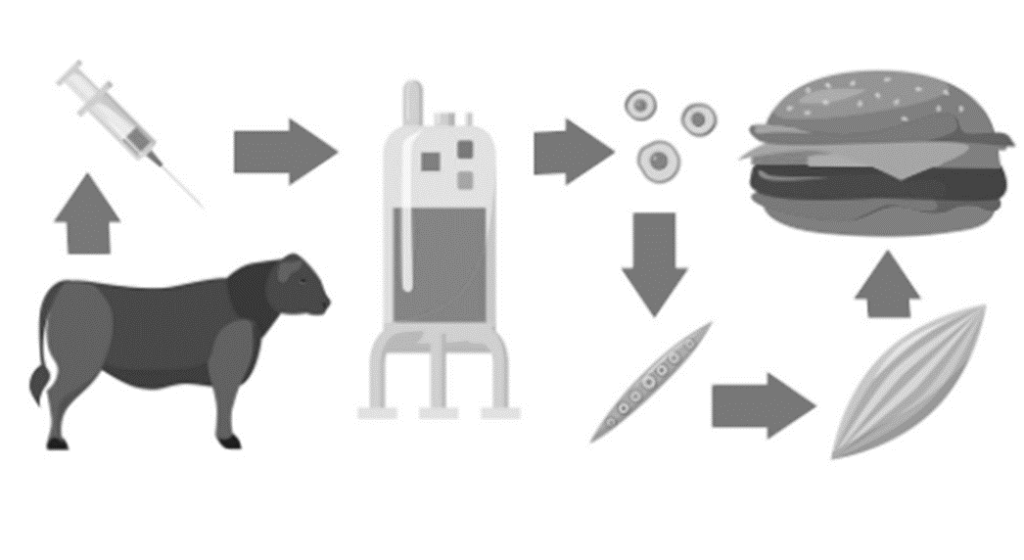
The process starts with a few ‘satellite’ cells, which can be obtained from a small sample of muscle taken from a live animal. These stem cells can turn into the cells found in the muscle. Just one cell could, in theory, be used to grow an infinite amount of meat. When fed a nutrient-rich serum, the cells turn into muscle cells and proliferate, doubling in number roughly every few days.
After the cells have multiplied, they are encouraged to form strips, like muscle cells forming fibers in living tissue. These fibers are attached to a sponge-like scaffold that floods the fibers with nutrients and mechanically stretches them, ‘exercising’ the muscle cells to increase their size and protein content. The resulting tissue can then be harvested, seasoned, cooked, and consumed as boneless processed meat.
Cultured Meat Market
The rising demand for alternative protein sources, adoption of technological advancement in cellular agriculture, increasing focus on animal welfare, and the rising demand for environmental sustainability are projected to drive its market growth during the forecast period. The cultured meat market in the US is projected to reach $593 million by 2032, recording a CAGR of 15.7% from 2025 to 2032 in the normal scenario. However, speculation is rife that the market may reach 25 billion by 2030 alone. One thing is certain: the market has enough potential for first movers.
The market for cultured meat is experiencing significant advancements, marked by notable regulatory approvals. In mid-2023, the FDA approved two U.S. companies to market cultured chicken, signaling a pivotal moment in the industry’s evolution. Concurrently, Israel has emerged as a trailblazer by granting regulatory clearance for the sale of lab-grown beef in January 2024, charting a unique course in the development of cultured meat products. With regulatory barriers now surmounted, the focus shifts towards scaling up production to meet consumer demand and fostering acceptance of cultured meat among consumers.
Earlier, the cost of cultured meat was high because of the high-density culture comprising 55-95% of its cost due to TGF-β. This TGF- β accounts for the majority of that cost. Organizations like Good Food Institute are working on finding alternatives to this costly culture medium. According to the Good Food Institute, the lowest possible cost of cultured meat could be as low as $0.10 per gram. Additionally, another analysis says that the cost of meat can be reduced to as low as $5.66/kg or $2.57 per pound by 2030. These cost reductions are possible by maximizing cell density during the proliferation stages of a cell. Increasing investment by various key players is projected to drive the growth of cultured meat.
Rising urbanization, growth in environmental awareness, and technological advancements also support market growth in this region. Consumers in this region are increasingly realizing the importance of healthy eating, which has increased the need for cultured meat production to provide nutritional requirements and offer enhanced food security.
By the end of 2019, 55 companies worldwide were working on it. Some are Balletic Foods, Biftek, BioBQ, BlueNalu, etc.
A few companies, such as Good Meat Inc. and Supermeat, The Essence Of Meat Ltd., are filing patents for this technology. This indicates that this sector will grow rapidly.
Companies Known for Lab-Grown Meat:
- Eat Just: The maker of GOOD Meat lab-grown chicken, already being sold in Singapore. This California-based company also produces plant-based foods like Just Egg.
- UPSIDE Foods: Formerly known as Memphis Meats, this company has produced cultured beef, chicken, and duck meat. Its investors include food giants Tyson Foods and Cargill.
- Shiok Meats: This Singapore-based company produces cell-based seafood, including shrimp, crab, and lobster. To reach consumer markets in 2022, Shiok Meats recently purchased another lab-grown meat company, Gaia Foods.
- BlueNalu: In early 2021, Start-up BlueNalu raised $60 million. The company is using the money to build its factory and develop lab-grown versions of Mahi and Bluefin tuna. Tuna is on the brink of extinction due to overfishing, and the introduction of cultivated tuna could have a huge impact on the health of our oceans.
- Finless Foods: This Silicon Valley start-up also produces lab-grown seafood, focusing on tuna. The company already makes plant-based tuna.
- Mosa Meat: Based in the Netherlands, Mosa Meat is currently scaling up the production of its lab-grown beef and what it calls “the world’s kindest burger.”
- Bond Pet Food: Thanks to Bond Pet Food, even our beloved companion animals can try lab-grown meat. This company is starting with cultured chicken to reduce the number of chickens suffering in factory farms for pet food products.
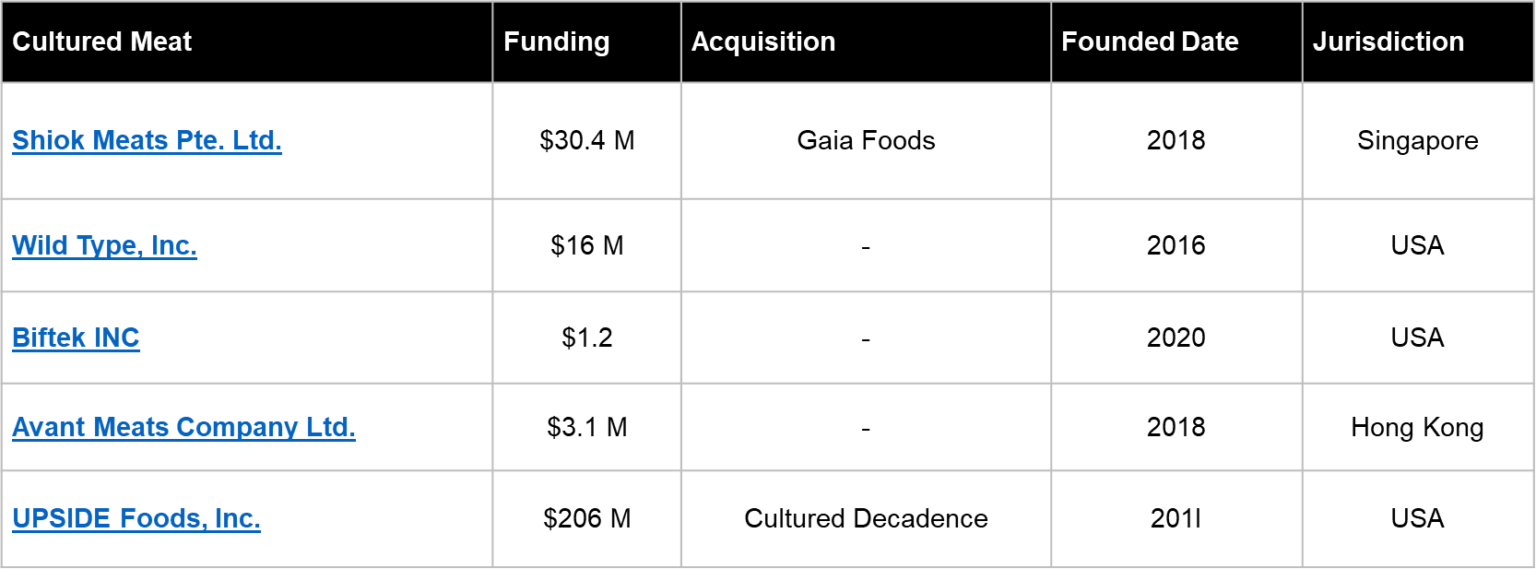
Table: Investments in Cultured Meat Companies
Cultured Meat Products
Naturally, meat cuts have a definite shape. However, cultured meat’s structure is more like that of minced meat. Therefore, its usage is currently restricted to a specific type of meat product. These products are as follows –
- SuperMeat Burger: Researchers from Impossible SuperMeat in Israel have prepared a cultured meat burger that is 100% chicken and perfectly edible. The burger looks like a regular chicken burger and is sustainable and animal-friendly. According to SuperMeat, the process is scalable and accepted by consumers.
- Guilt-free Sausage: Ivy Farm Technologies has introduced guilt-free sausage. According to their prediction, the guilt-free sausage will be available on market shelves by 2023. It also ensures the effective use of land so that the land earlier used for animal feed could be used for another purpose. In addition, this guilt-free sausage is comparable to conventional sausage.
- JUST Meat’s Cultured Meat: JUST Meat analysis said that “at current rates, production of meat and seafood worldwide will be double to 1.2 trillion pounds by 2050. Not all consumers want to adopt a fully plant-based lifestyle; JUST Meat has introduced this sustainable meat alternative.
- Cultured seafood: Cultured meat production is not limited to beef or chicken rather. It can be used for seafood as well. Companies have emerged with cultured seafood products such as Atlantic salmon fillets or ahi tuna steaks. There is a future scope for culturing technology that can also be used for other seafood such as crabs, oysters, etc.
Cultured Meat Benefits
- Cultured meat eliminates the need to raise animals for food.
- The production of cultured meat does not require the slaughter of animals, offering a more humane approach to meat production. It eliminates the need for harmful procedures used in traditional farming
- Cultivated meat is made of the same cell types arranged in the same or similar structure as animal tissues. Hence, it replicates the sensory and nutritional profiles of conventional meat.
- Prospective life cycle assessments indicate that cultivated meat will use significantly less land and water, emit fewer greenhouse gases, and reduce agriculture-related pollution.
- Cultured meat is not limited to beef or chicken but also includes seafood such as fish, crab, mussels, oysters, etc.
- The controlled lab environment in which cultured meat is produced significantly reduces the chances of contamination by pathogens like E. coli, making it a safer option with a lower risk of foodborne illnesses.
- This also reduces expensive labor and the risk of zoonotic diseases.
- The production of cultured meat enables meticulous regulation of the nutritional composition, which has the potential to result in healthier meat products with controlled levels of fat and cholesterol.
- Research carried out at the University of Oxford suggests that producing Cultured 6. Beef could use as much as 99% less space than needed for current livestock farming methods.
- In situations like stations in Polar Regions, troop encampments in isolated theatres of war and bunkers, etc., designed for long-term survival, it is difficult to procure meat as animal rearing is difficult. Hence, cultured meat can be a game-changer.
Safety Assessment of Cultured Meat
The production of cultured meat involves animal cell culture technology. It’s relatively new to food production and significantly different from the production of conventional meat products. Therefore, it is important to inculcate trust among consumers. It can happen by regulating the process to address consumers’ potential food safety risks.
Safety Assessments of cultured meat have the potential to influence consumer decisions by increasing the reliability of its production.
Currently, countries such as Mainland China, the European Union, Australia, New Zealand, Canada, and Singapore have considered different aspects of their control of cultured meat and established assessment criteria for evaluating the food safety of cultured meat products before marketing.
Nutritional Aspect
Cultured meat consumption can mitigate disorders arising from protein deficiency. Another added advantage is that cultured meat’s fat and cholesterol levels can be customized, which is impossible with conventional meat.
Conclusion
One-third of global greenhouse gas emissions caused by humans are linked to food. Food management is an important aspect of meeting the global sustainable development goals set up in 2015 by the United Nations General Assembly and is intended to be achieved by 2030. However, there are a few challenges, such as selecting cell sources, the right volume of cell culture media, scaling, etc. However, despite these challenges, current trends show consumers’ inclination towards cruelty-free products. Thus, it again ensures the demand and acceptability of cultured meat products in the coming time.