A floor finish is a liquid that dries to a durable, long-lasting, and smooth covering when applied to resilient tiles, wooden, or other floors. This waxed paper-thick covering is expected to protect the flooring from damage and create a lovely look and a slip-resistant surface while increasing lifespan. Natural substances like carnauba wax, beeswax, shellac, and paraffin were used in the early days of floor care. Several floor products are still generically referred to as “wax” because of this early use of natural waxes. Wax-based floor finish products strongly connect with the flooring materials, so making them removable is challenging. It is also tough to get rid of that floor finish. Thus, Zinc-free floor finishes are the need of the hour.
In the 1940s, artificial floor coatings made of polystyrene were created. Early floor finishes were glossy and durable, but they also had problems with detergent resistance and reparability, a tendency to become powdered, and a tendency to turn yellow with time. In the 1960s, metal was used as a cross-linker in floor coatings. Different polymer chains can be joined together with metals like zinc through cross-linking. This enables floor products to be more resilient to soil and detergents, last longer, and offer a mechanism for quick product removal when needed. Despite solving various issues related to earlier floor finishes, zinc-based floor finishers have some demerits concerning environmental and regulatory concerns. This article summarizes the problems associated with zinc-based floor finishes, their possible alternatives, the working mechanism of those alternatives, and market analysis.
Problems Associated with Zinc
Cross-linking with zinc solved different drawbacks of previous floor finishes, like reducing yellowing issues, enhanced coating stiffness, scratch resistance, and chipping resistance. It is found as zinc ammonium carbonate complex rather than as elemental zinc. However, polymer and zinc ammonium carbonate molecules interact to form bonds and release little ammonia as water evaporates from the freshly applied floor finish. This is the source of the characteristic ammonia smell of floor coatings. Regulation of zinc discharges has been implemented in several places due to environmental concerns over zinc production and potential build-up in water and soil. Due to its difficulty in removal during wastewater treatment, zinc has been restricted in wastewater discharge limitations. Products without metal cross-linking agents started to be developed and offered as the need for less zinc usage grew.
Various Zinc Replacers in Floor Finishes
Various zinc-replacing materials are being explored for effective and ecological floor finishing. Hence, zinc replacers for crosslinking the polymer floor finish became time-intensive.
Synthetic floor finishes based on styrene-acrylic polymers serve as better zinc-free floor-finishing binders. Most of the environmentally- friendly ingredients provide a better floor finish.
Polymer Replacement: The specific monomers used for industrial coatings crosslink internally during polymerization. The formulations form additional latent crosslinking, increasing the polymer’s cross-linking density.
Divalent Metal Replacement: Polymer synthesized from ethylenically unsaturated monomer is used as a vehicle, and copper ion is used as a cross-linking agent for floor finishing, providing durability and gloss.
Pre-polymer: Generally, pre-polymers consist of the aliphatic NCO- group and silane-terminated chains. These compounds are very effective for industrial or domestic floor coatings. Adducts or pre-polymers of isocyanate are used as crosslinkers in the 1K (one pack) or 2K (two pack) system. These cross-linkers provide better adhesion to the floor. Bayhydur® water-dispersible aliphatic hydrophilically modified polyisocyanate crosslinkers by Covestro provide better chemical and impact resistance, high gloss, and less haze.
Working Mechanism
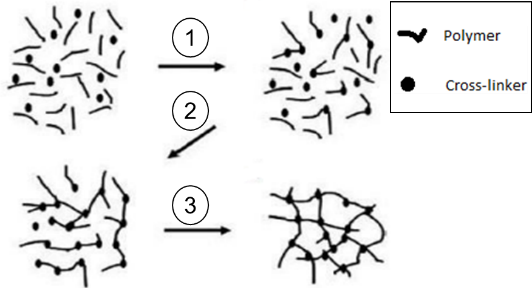
Cross-linkers are added to connect with different polymer chains in the floor finish film. As the film is applied to the floor, the polymer forms an intertwined network by cross-linking, as shown in Figure 1. The short sequence of bonds links one polymer chain to the other. Thus, crosslinking increases the durability of the polymer network and provides stiffness and abrasion resistance.
Zinc Free Floor Finishes: Current Products and Technologies
ENCOR® 7340: This product is manufactured by Arkema and is metal-free. It helps in protecting the floor from moisture and enhances its durability.
GTC® Zinc-Free Floor Finish: This is a zinc-free and green seal-approved product with a durable floor finish. It consists of water-borne acrylic emulsion and is suitable for all tile floors.
Scotchgard™ Resilient Floor Protector: Using a proprietary (and patented) ingredient, ScotchgardTM Resilient Floor Protector uses alternative cross-linking technologies to produce a resilient, repairable, and removable solution. Because of this, customers can utilize products that are zinc-free while still enjoying their exceptional toughness and repairability. As compared to the top rival standard acrylic floor coatings, it increases initial hardness 40% faster and has improved gloss retention, filth resistance, and hand sanitizer resistance.
Elements Zinc Free Floor Finish: It effectively protects synthetic floors. It contains no zinc or other heavy metals, which threatens the environment.
Zinc Free Floor Finishes: Market Analysis
A good number of companies for coating are working on developing zinc-free floor finishes, which can provide prominent floor coatings without de-escalating the benefits of zinc-based floor finishes. Some of the well-known companies are provided below.
OMNOVA Solutions: This company works to replace zinc in the floor-finishing industry. They came up with a twin-linked crosslinking mechanism. The product consists of an epoxy-modified acrylic copolymer with a short curing time. The coating provides performance equal to conventional zinc-free floor finishes in terms of durability, maintenance, and easy removal. The data obtained led to the conclusion of a potential replacement for zinc-based technology.

US Specialty Coating: Headquartered in the Southern US, US specialty coating is a paint manufacturing industry. It has launched a white tiger floor finishing product, which is zinc-free, eco-friendly, and high-performance floor polish. It provides vinyl composite tiles with an intense, challenging, durable, protective finish.
Diversey: Diversey also works on the manufacturing of floor-finishing polymers. EP84 UHS Floor Finish, a zinc-free product from Diversey, uses environmentally preferable polymer technology and provides a high gloss finish. The coat is recommended for optimal performance for vinyl composition, vinyl concrete, quarry, and Mexican tile, with various operating domains, such as floor cleaners, disinfectants, etc.
3M: It used alternative cross-linking technologies and a proprietary (and patented) additive to build a resilient, repairable, and detachable product. This allows customers to use a zinc-free product while maintaining exceptional durability and reparability.
Odoban: The company focuses on zinc-free floor finishes, which are environmentally friendly. Earth Choice® Zinc-Free Floor Finish is a blend of acrylic polymer and oxidized wax that gives superior gloss and shine to all resilient flooring and long-lasting protection.
Acquisitions
Pidilite established a joint venture with CIPY Polyurethanes Private Ltd. (‘CIPY). They manufacture and sell floor coatings based on polyurethanes, epoxies, polyurea, and polyaspartic polymers.
Conclusions
Zinc eluded from floor finishes kills essential bacteria, which are necessary for biodegradation, in waste treatment plants. Thus, zinc replacers in floor finishes can serve as a better alternative. Novel self-crosslinking polymer technology, which does not use metallic cross-linkers, provides a durable finish to the coating. Polymers, waxes, and surface active agents form a tough film after drying without the need for zinc. Many companies have also patented their formulations to have exclusive rights over their usage. Moreover, Allnex Netherlands BV has patented castor oil-based polyol emulsion, which uses methylene diphenyl diisocyanate as a cross-linker. This formulation provides better durability to the coating and can serve as a potent example of bio-based coatings.