Endosomal Escape: Unlocking Critical Hurdles of Intracellular Delivery
How Endosomal Escape Determines Success in Modern Medicine
The “Endosomal trap” is responsible for eliminating 90–99% of the administered vaccine dose, resulting in low therapeutic potency, dose inefficiency, and limited clinical translation.
When nanoparticles, viral vectors, and lipid carriers are taken into membrane-bound endosomes, these are sent to lysosomal degradation if the therapeutic cargo does not escape during early maturation. This, in turn, has a direct impact on:
- Efficacy – Because of the loss of payload, higher doses are needed; thus, the toxicity and manufacturing cost are increased.
- Translation to Clinic – A majority of RNA and gene-editing therapies that are intracellularly delivered to the cytosol fail due to low delivery.
- Design Strategy – Delivery systems have now become the integration of escape mechanisms as a main feature, rather than a secondary feature.
Hence, as precision medicine has progressed, the endosomal escape has become a fundamental design principle for the next generation of intracellular delivery platforms.
That is why endosomal escape is so important: if the payload cannot escape the endosome, it cannot do its job inside the cell, and the consequences are degraded molecules and a weak therapeutic response.
Uncovering the Mechanisms of Endosomal Escape
Endosomal escape is the process by which a therapeutic agent escapes from the endosomal vesicle before it is delivered to a lysosome. The reality is that – if the endosome becomes more acidic and accumulates enzymes, the time for the release becomes very short.
The key highlights for the endosomal entrapment and lysosomal degradation risks involve –
- Nanoparticles and biologics are, for the most part, trapped in a vesicle barrier that has been created by endocytosis.
- Endosomes become acidified as they mature, thus increasing the likelihood of payload degradation.
- If escape does not happen at an early stage, the therapeutic agent will be rendered inactive in lysosomes.
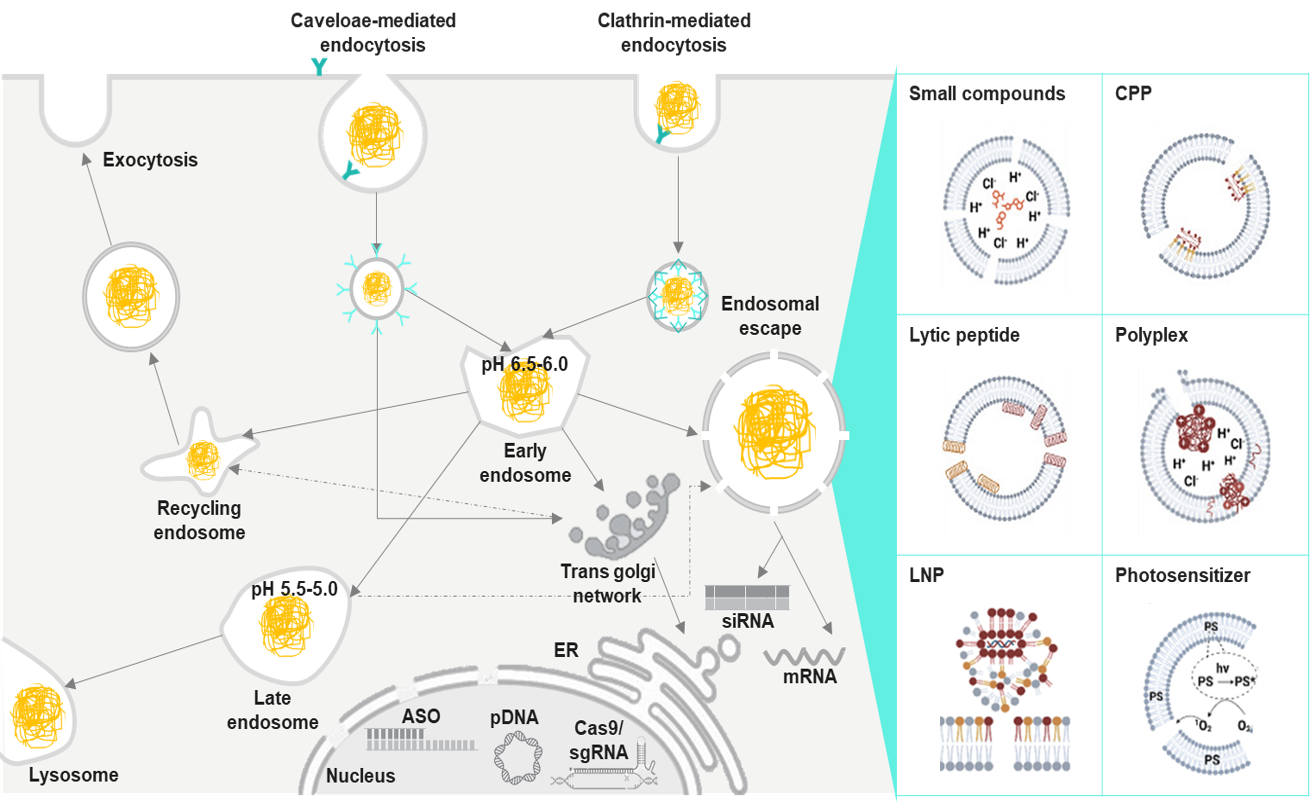
The Essential Pathways Powering Endosomal Escape
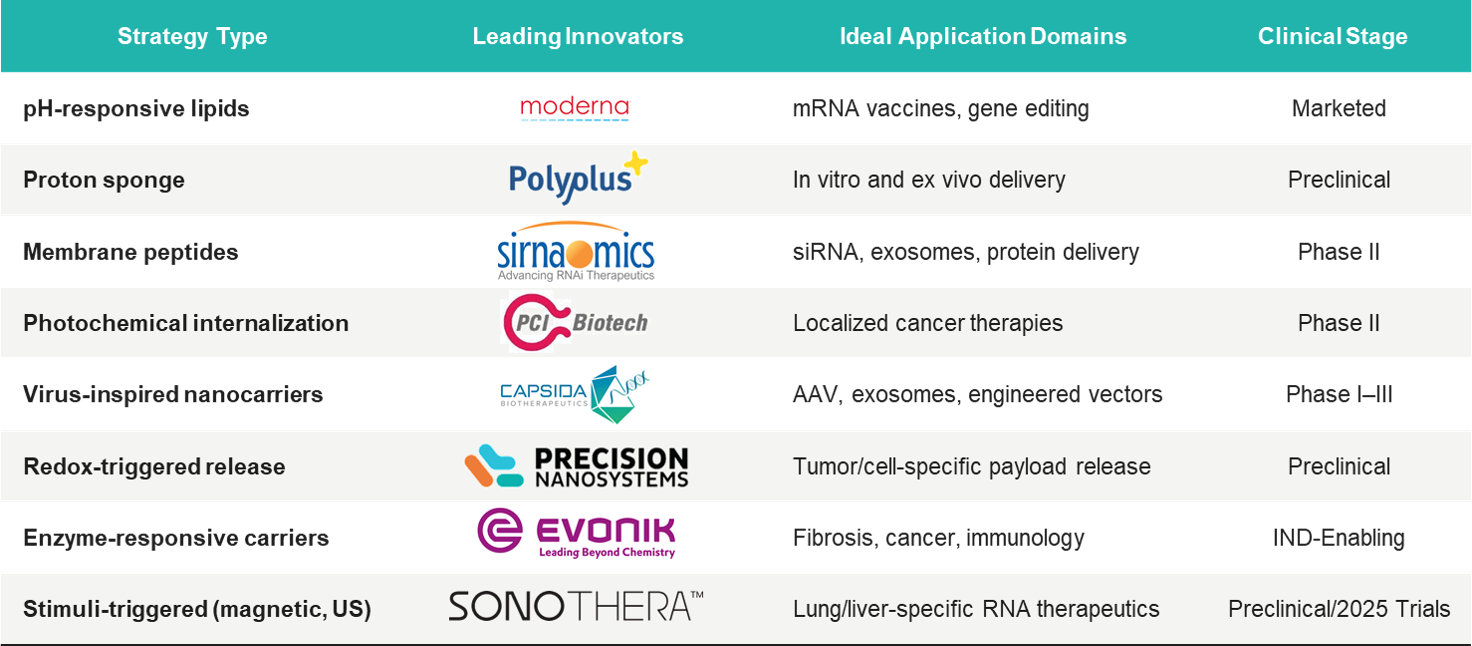
Many molecular engineering approaches have been developed to enable therapeutic molecules to escape from endosomes and access the cytosol. Each of these approaches utilizes different biological or chemical triggers and includes –
- pH-responsive Materials: Materials that are activated in acidic endosomes to disrupt or soften the membrane.
- Proton Sponge Effect: The osmotic swelling that eventually bursts the endosomes is caused by cationic polymers, which attract protons.
- Membrane-disruptive Peptides: Peptides generated from the viral peptides that fuse with membranes during acidification are thus able to disrupt membranes.
- Photochemical Internalization: When light-activated molecules absorb a certain wavelength of light, they generate ROS that break vesicles.
- Virus-mimicking Carriers: Nanoparticles showcasing similar behavior to viral fusion systems allow the viruses to use them to enter the cell.
- Redox-responsive Systems: The disulfide or redox-sensitive linkers that release the cargo in the reductive cytosol are examples of such systems.
- Gas-generating Particles: Endosomes can be ruptured by the generation of CO₂/N₂ bubbles inside them.
- Enzyme- or Mechano-responsive Carriers: Release the drug when their shape is changed or when the enzyme cleaves the carrier.
- Co-delivery of Endosomolytic Agents: Small molecules that are temporarily able to weaken the endosomal membranes can be delivered together with the drug.
Despite their differences, all these strategies serve a single purpose: enabling the payload to escape the endosome and reach the cytosol quickly before degradation, so the drug can work effectively.
Breaking Barriers: The Challenges of Endosomal Escape
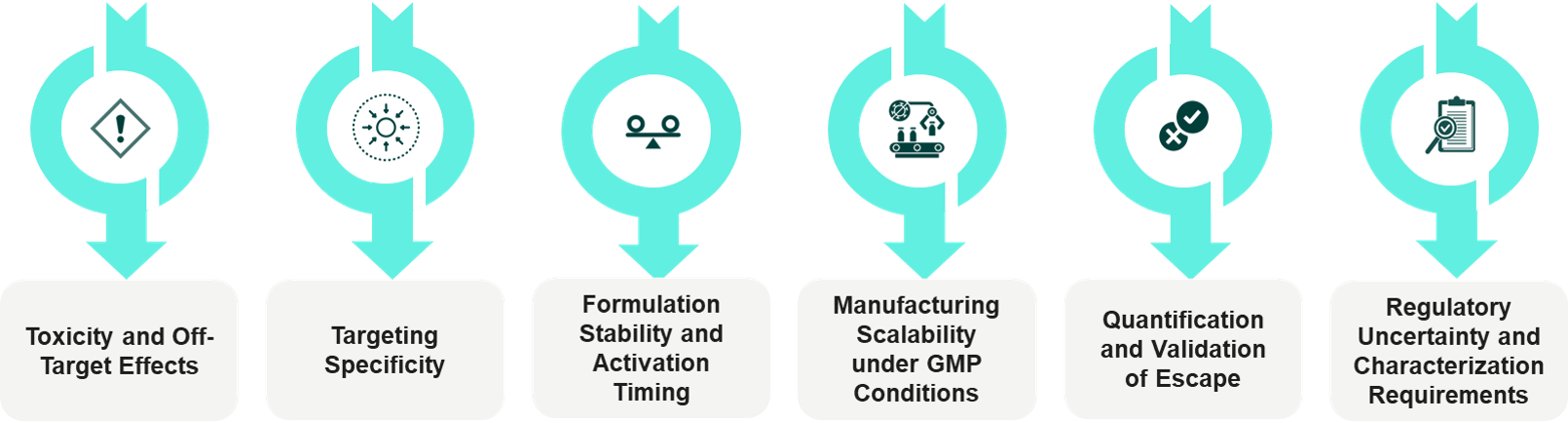
Significant progress has been made in this field; however, several practical challenges still hinder the large-scale implementation of escape technology.
The major challenges are:
- Risk of Toxicity: The use of strong membrane-disruptive methods can be detrimental to the compartments of healthy cells.
- Drop-in-targeting Precision: The upshot of the improvement of tissue specificity during systemic delivery is that the loss of targeting precision can occur.
- Pre-mature Activation: The carriers should be stable in the blood and only activate when they are in the endosomes.
- Production Restrictions: The production of peptides, polymers, and stimuli-responsive materials that are GMP-compliant is quite challenging.
- Unavailability of Standard Assays: Detecting escape remains a challenge, which is why regulators are still not very receptive to this idea.
What’s next for Endosomal Escape
Technologies for endosomal escape will be crucial for advancing RNA therapeutics, gene editing tools, and intracellular biologics. Smarter delivery systems are now employing AI to guide polymer, lipid, and multi-trigger platforms that respond to pH, enzymes, and redox signals, offering greater precision and fewer off-target effects. Improved quantification methods and evolving regulations will also accelerate development and enhance therapeutic effectiveness and translation. Many companies worldwide are dedicated to developing innovative solutions to overcome the endosomal barrier.
Stellarix Capabilities
Stellarix helps clients develop next-generation living-cell delivery systems to penetrate the intracellular space and overcome the endosomal escape barrier, a critical challenge. Using our multidisciplinary expertise—from RNA therapeutics to CRISPR systems and from nanocarriers to smart materials—we achieve optimized cytosolic delivery and improved therapeutic effectiveness.
Stellarix has distinguished capabilities pronounced in the following aspects:
- Endosomal Escape Technology Assessment – By evaluating pH-, redox-, peptide-, and multi-trigger systems, we decide which methods are the most effective.
- LNP & Nanocarrier Optimization – We improve membrane disruption, cytosolic release, and delivery efficiency with rational carrier design.
- Intracellular Trafficking Insights – We obtain the profile of uptake routes, endosomal maturation, and payload-release behavior for the targeted applications.
- Assay & Mechanism Validation – Helping escape efficiency testing and model development.
- IP & Technology Mapping – Spotting patent trends, white spaces, and key innovators in the endosomal escape landscape.
Stellarix serves as a source of power for leaders in life sciences and biotech to develop reliable delivery platforms that enable efficient escape, thereby opening the door to advanced therapeutics.
Let's Take the Conversation Forward
Reach out to Stellarix experts for tailored solutions to streamline your operations and achieve
measurable business excellence.