Molecular Ingredient/Reverse food engineering used in the domain of food is a technology that will help to identify cheap and sustainable alternatives over the conventional expensive functional ingredients. This will not only reduce the burden of overproduction of specific ingredients due to increasing food demand but also generate the use of underutilized ingredients and sustain a better environment for the future population.
Molecular Ingredient Engineering
Molecular ingredient/Reverse engineering of food ingredients involves identifying specific ingredients on a molecular level responsible for delivering distinct functional benefits in the particular product. This information is then processed to identify sustainable alternatives. With the help of these shortlisted sustainable ingredients, the food product is redesigned with the same functional benefit. Such products include beanless coffee, cocoa-free chocolates, and peanut butter without peanuts.
The mission of this food sector is to meet the food demands of the world population while decreasing the negative impact of overproduction on the environment and increasing access to safe, sustainable food sources for people around the world.
Market of Molecular Engineered Ingredient
Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, the supply of raw materials used to develop specific products was limited and irregular.
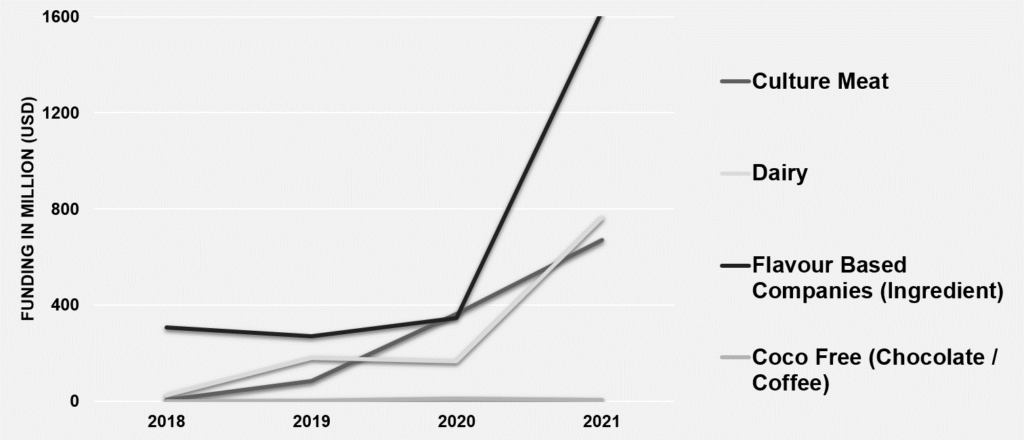
Hence, this pandemic dramatically accelerated the investment in molecularly engineered ingredients. Investors are mainly focusing on streamlining molecular ingredients trend sets in different domains like cultured meat, dairy proteins, cocoa, chocolate, and other ingredients that can lead to sustainability and supply chain resilience.
Investors have inclined more toward molecular-engineered ingredients in the last couple of years. A few companies are filing patents for the same, such as Good Meat and Supermeat- The Essence Of Meat Ltd. This indicates that there will be rapid growth in this sector.
Reverse Food Engineering: Cocoa-free Chocolates
Millions of hectares of rainforest had to make place for cocoa plantations during the last decade. Naturally, cocoa trees grow underneath huge rainforests. Industrial cocoa, however, is often planted directly under the sun to increase yield and profits. Many researchers came forward with their novel findings to avoid difficulties with traditional chocolate manufacturing, such as overexploitation of the land and oppressive labor conditions.

Cocoa Cell Culture Chocolate
Researchers from the Zurich University of Applied Sciences first succeeded in multiplying cocoa cell cultures and using them to produce chocolate. The alternatively made chocolate looks like ordinary milk chocolate. For this chocolate, the cells of cocoa fruits from Puerto Rico were propagated in a multi-stage process. It took more than half a year until the chocolate was ready. With cell cultures that the researchers have created, it is now possible to produce any number of chocolates without resorting to natural fruits. The researchers are currently working on transferring the production process to large bioreactors. The chocolate should be available for sale in stores in about two years.
QOA Cocoa-free Chocolate
QOA is the world’s first 100% cocoa-free chocolate alternative. It is based on natural ingredients that are carefully fermented and roasted. QOA uses precision fermentation technology.
California-cultured 100% Real Chocolate
California Cultured selects cacao varieties with the best organoleptic properties, takes a handful of cells, and keeps them growing infinitely. It uses cell culturing with a proper set of plant nutrients and fermentation of cocoa cells, followed by traditional roasting steps, to create a rich flavor. Fermented cell-cultured cocoa nibs were used to develop a variety of cocoa products.
Reverse Food Engineering: Atomo’s Bean-less Coffee
The coffee industry is facing problems, such as the shortage of land for coffee growers and the large quantities of water needed for production. Temperatures are rising and, combined with erratic rains, are leading to lower crop yield. Atomo’s bean-less coffee is made from upcycled ingredients, e.g., sunflower seed husks and watermelon seeds, which undergo a patented chemical process to yield molecules that mimic the flavor and mouthfeel of the real coffee. The resulting grounds are brewed just like a regular cup of coffee. This coffee also has caffeine. Food scientist Jarret Stopforth and his partner, Andy Kleitsch of Atomo Coffee, had broken down all the compounds in coffee to determine their contribution to java’s taste and smell.
Cultivated Meat
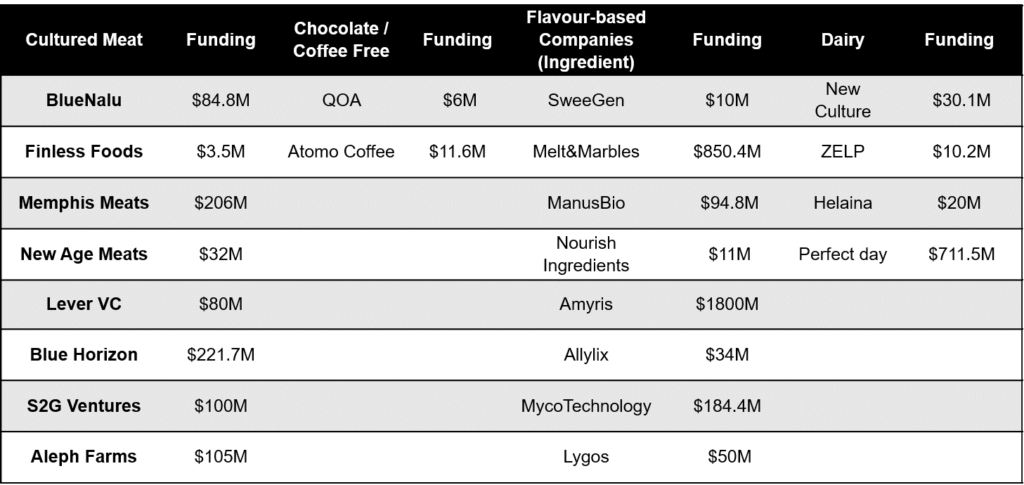
Cultivated meat is genuine animal meat produced by cultivating animal cells. It eliminates the need to raise and farm animals for food. Also, cultivated meat is made of cell types arranged in the same or similar structure as animal tissues. Hence, it replicates the sensory and nutritional profiles of conventional meat. Prospective life cycle assessments indicate that cultivated meat will use significantly less land and water, emit fewer greenhouse gases, and reduce agriculture-related pollution. A Few companies growing in this sector are Balletic Foods, BlueNalu, Finless Foods, Memphis Meats, and New Age Meats.
Reverse Food Engineering: CO2 into Edible Food Structure
Air Protein
It has created a meat substitute for elements found in the air around us. Air Protein uses the NASA-inspired concept of renewable energy and a probiotic production process (hydrogenotrophs) to convert elements such as carbon dioxide into nutrient-rich protein flour. Food and Agricultural Foundation (FAO) predicts farmers will need to increase food production by 70% with only a 5% land increase to meet the expected growing population of ten billion people by 2050. Air Protein flour can be made in just 04 days instead of months. Growth occurs through a proprietary probiotic production process where the hydrogenotrophs can consume CO2 and other elements to produce amino acids. Air-based meat is the next evolution of sustainably produced food without putting a strain on natural resources.
Solar Foods
It has developed a process to use renewable electricity and CO2 to produce a healthy ingredient that looks like wheat flour and contains 50% protein. The process uses solar power to split water through electrolysis in a bioreactor, creating hydrogen that can give microbes energy as they’re also fed carbon. The microbes produce food that has roughly 20-25% carbs, 5-10% fat, and 50% protein. Solein comprises whole cells that are 65-70% protein. The macronutrient composition of the cells is very similar to that of dried soy or algae.
Conclusion
The food industry has been reluctant to use reverse engineering. Still, now that there has been a change in many other domains, the food industry is attempting to shift production away from traditional ingredients and accept more sustainable and underutilized goods. Moreover, multi-criteria reverse engineering develops sustainable processes, looking at similar approaches in other sectors.