Next-Generation Probiotics for Human
Next-generation probiotics (NGPs) are a novel class of helpful bacteria that are being created to improve human health through various therapeutic uses. Their growth is powered by developments in biotechnology and microbiome research, which have deepened the understanding of microbial interactions and their possible health advantages.
NGPs are intended for specific therapeutic interventions, unlike traditional probiotics, which are mostly used for nutritional purposes. They can be designed to treat particular diseases, such as diabetes, cancer, inflammatory bowel disease, obesity, etc. However, research involving human participants is still lacking despite the fact that many NGPs exhibit significant promise for the prevention and treatment of many chronic diseases. Consequently, regulatory bodies rarely approve these microorganisms. Furthermore, several obstacles prevent their broad market acceptance, such as the requirement for suitable techniques for cultivating and preserving these oxygen-sensitive microbes.
Understanding Next-Generation Probiotics
Traditionally, probiotics have included lactic acid-producing bacteria (LAB) such as Lactobacilli, bifidobacteria, and other species, typically sourced from fermented dairy products and fecal microbiota. As understanding the gut microbiome and its functions grows, new strategies and probiotic taxa emerge. However, a significant portion of the microorganisms in the human gut remains unidentified, as many are anaerobic bacteria that are challenging to cultivate. Advances in microbiology, particularly polymerase chain reaction (PCR) targeting the 16S rRNA gene, next-generation sequencing (NGS), and bioinformatics, have recently enabled precise identification and detection of various gut bacteria that could serve as next-generation probiotics (NGPs). NGPs have more physiological advantages than standard probiotics since they produce folate, serotonin, indoles, and short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) like butyrate, propionate, and acetate, all of which are important for controlling the physiological phenotype of the host.
Market Overview
The global next-generation probiotics market was valued at approximately USD 168.1 million in 2022 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 11.2%, reaching USD 393.9 million by 2030.

Factors Influencing the Growth of Probiotics and Solutions
1. Harsh Conditions of Gut: Nucaps® is a European company based in Navarra, Spain, specializing in innovative encapsulation technology for the industrial production of Nano capsules and Bio capsules designed for bioactives and probiotics. Their patented bioavailable capsules, which are composed of natural proteins and devoid of preservatives, improve the stability, effectiveness, and protection of the active ingredients while providing personalized solutions for better bioactive performance.
2. Sensitive to Oxygen Change: Researchers from the University of Gothenburg co-isolated Faecalibacterium prausnitzii with Desulfovibrio piger to boost its growth and function. They then “trained” the oxygen-sensitive bacteria in a favorable electrochemical environment, creating more oxygen-tolerant strains. By combining bacterial training and natural symbiosis, this approach forms live biotherapeutic items that may help avoid ailments associated with lower levels of Faecalibacterium prausnitzii.
3. Commercial Scale Production: IFF has developed advanced process capabilities for producing next-generation Akkermansia muciniphila, utilizing small-scale, high-throughput, and high-information tools combined with their large-scale manufacturing expertise from lab to pilot to industrial scale. Their efforts are backed by significant team investments, state-of-the-art facilities, and certifications. According to IFF, they will comply with EU Novel Food Regulations and pursue GRAS (Generally Recognized as Safe) status in the U.S. for this product.
Health Benefits and Potential NGP Candidates
Probiotics promote individual health through various mechanisms, including modulating the immune system, supporting epithelial cell and gut barrier integrity, producing antimicrobial substances, maintaining microbiota stability, and influencing the modulation and selection of bile acids.
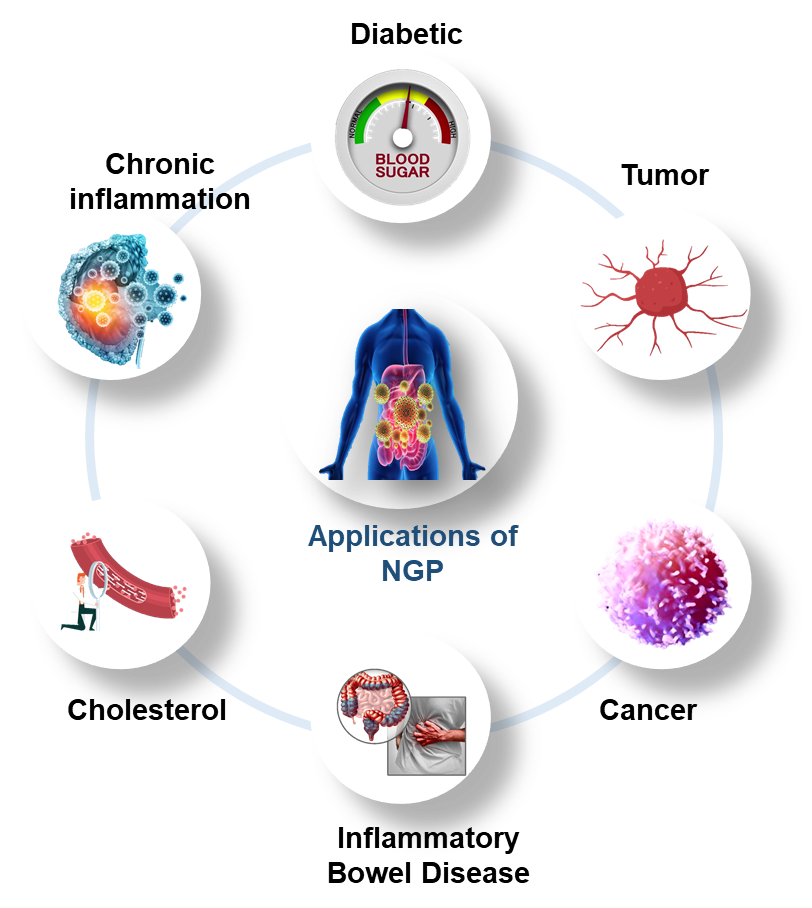
Proposed Next Generation of Probiotics Candidates
- Faecalibacterium prausnitzii
- Akkermansia muciniphila
- Bacteroides acidifaciens
- Bacteroides uniformis
- Clostridium butyricum
- Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron
- Christensenella minuta
- Prevotella copri
- Parabacteroides goldsteinii
Techniques for Enhancing Probiotic Viability
- Spray drying
- Extrusion
- Emulsification
- Electro spraying
- Freeze-drying
Regulatory Aspects
In the U.S., probiotics classified as Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) can be sold without prior approval, but newer strains must be registered as new dietary ingredients (NDIs). The FDA requires clinical trials for therapeutic use. The EU regulations are more stringent; requiring marketing authorization, and live biotherapeutics must undergo extensive testing. Similar ideas are followed by Russia and other areas, which modify laws to incorporate next-generation probiotics (NGPs) into food and medicine systems.
Caelus Health, a European company focused on developing next-generation microbiota-based products for preventing and treating cardio-metabolic diseases, particularly Type 2 diabetes and liver disorders, recently received a “No Questions Letter” from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). This letter pertains to their Generally Recognized As Safe (GRAS) notice for A. soehngenii (formerly known as E. hallii), confirming its safety for use.
Current Innovations
- Novel Strains: Recent research has identified Lactobacillus Plantarum JBC5, a strain found in fermented dairy products that may support longevity and healthy aging. The findings indicate that it boosts gut health, strengthens immune responses, enhances cognitive function, reduces inflammation and fat accumulation, and extends the lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans by 27.81%.
- Co-Culture Systems: These systems introduce innovative combinations of probiotic strains to boost metabolite production and growth efficiency by encouraging synergistic interactions. For example, co-culturing Faecalibacterium prausnitzii with Desulfovibrio piger has been found to significantly enhance butyrate production, a key compound for maintaining gut health.
Key Players and Their Innovations
A few of the key active companies on next-generation probiotics and their technologies are presented below:
- Genetic Modification: Zbiotics focuses on genetically modifying beneficial bacteria to improve their functions or introduce new capabilities. One application involves converting sugar into fibers by producing the enzyme levansucrase. Another aims to replicate the liver’s ability to break down acetaldehyde by using genetically modified Bacillus subtilis strains that produce a similar enzyme.
- Biotherapeutics Discovery Platform: Utilizing cutting-edge technology, top-tier expertise, and extensive experience in drug discovery, Creative Biolabs has developed a platform for discovering live biotherapeutics aimed at product development, pre-clinical studies, and production of live bio therapeutic drugs.
- Oxygen-free Manufacturing Facility: Pendulum specializes in advanced probiotics to improve metabolic health by targeting gut microbiomes with specific strains. These next-generation anaerobic strains are produced in a highly controlled, oxygen-free facility in the U.S.
- Artificial Intelligence: U.S.-based microbiome health startup Verb Biotics and Israeli computational biology firm Evogene have collaborated to create new probiotic strains that generate microbial metabolites with enhanced properties for precision health applications.
- Precision Biotic: Activated Probiotics offers a range of nine precision probiotics designed to provide targeted health benefits, such as relief from IBS, while supporting digestion, iron absorption, bone health, immune function, mood balance, and sleep quality. The company utilizes plant-derived microencapsulation technology to enhance the stability of its probiotics.
- Probiotic-rich Vegetables: Wonder Veggies has developed a cutting-edge technology that grows fruits and vegetables high in probiotics naturally. The patent-pending technique combines the health benefits of probiotics with the perks of fresh vegetables. When compared to other products, these vegetables offer a greater bioavailability and an ideal probiotic delivery mechanism.
Clinical Trials
- In a study sponsored by FitBiomics, researchers evaluated the effects of reducing fatigue and increasing energy levels in a diverse group of healthy adults compared to a placebo.
- The study, sponsored by Danisco, used metagenomic analyses to identify differences in the intestinal microbiota between lean and obese individuals. The findings aimed to support the development of Next Generation Probiotics (NGPs) to improve metabolic health.
- This study, sponsored by Texas Christian University, aims to evaluate the effects of consuming a Next-Generation synbiotic (a combination of probiotics and prebiotics) over 3 months. The research will assess changes in body weight, body composition, glucose sensitivity, psychological parameters, and gut and blood microbial composition.
Conclusion
In conclusion, next-generation probiotics (NGPs) mark a substantial advanced strategy for utilizing the positive effects of microbes on human health. These cutting-edge probiotics are designed for certain medical uses, focusing on long-term conditions like diabetes, obesity, and gastrointestinal issues. Overcoming obstacles to market adoption will require developing sophisticated methods for cultivating and stabilizing these microbes. The potential of NGPs to transform therapeutic interventions will become more apparent as research advances and more human studies are carried out, providing new opportunities to improve quality of life and health outcomes.
Let's Take the Conversation Forward
Reach out to Stellarix experts for tailored solutions to streamline your operations and achieve
measurable business excellence.