Wearable Technology In Healthcare: Benefits, Challenges, Types
Wearable technology in healthcare has experienced a remarkable surge in popularity in recent years. Embodied within this surge lies the astounding progress made in biosensor technology, resulting in heightened precision and accuracy. Moreover, the continuous advancements in battery technology have led to the development of compact sizes, enabling seamless integration into wearable medical devices. Such enhancements, coupled with an overall increase in performance, have endowed users with the invaluable ability to access and interpret accurate healthcare data. Consequently, individuals are now empowered to assume an active role in their personal healthcare, embracing the responsibility that comes with informed decision-making and self-care.
Defining Wearable Healthcare Technology
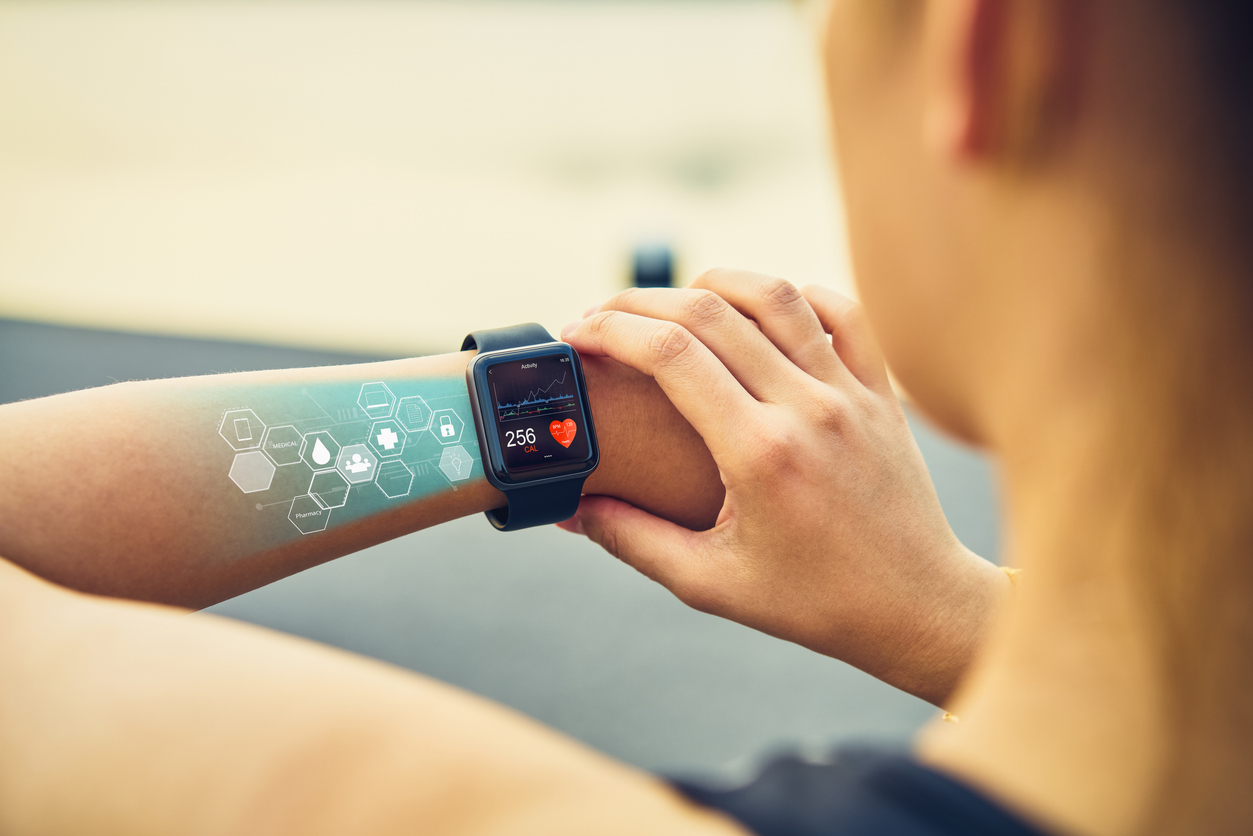
Wearable technology encompasses a diverse array of electronic devices crafted to elegantly adorn the human physique, exemplified by gadgets such as smartwatches. Within the realm of healthcare, these wearable marvels serve a pivotal role by diligently gathering and tracking users’ personal health and exercise data. The brilliance lies in their ability to seamlessly transmit this vital information, in real-time, to healthcare practitioners and medical experts, ensuring timely and accurate insights into a patient’s well-being. The global wearable technology market was valued at USD 96.50 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 15.47%, as per Stellarix’s survey and analysis from 2023 to 2027. In 2027, the value is estimated to grow to USD 198.09 billion.
Interestingly, the global market for medical wearables is forecast to grow from 20.1 billion U.S. dollars to 83.9 billion U.S. dollars between 2021 and 2026.
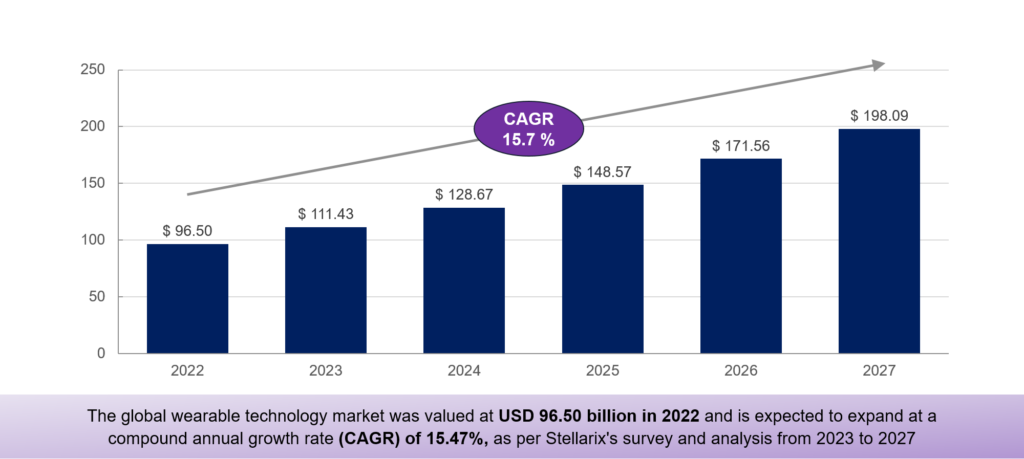
Figure: Wearable Technology In Healthcare Stats
Challenges for Wearables in Healthcare
Accurate and Reliable Data Collection
Collecting data accurately and reliably poses a significant obstacle for wearable technology. Despite their potential to offer valuable insights into our well-being and daily routines, inaccuracies can compromise their effectiveness. Achieving precision hinges on crucial factors, including sensor calibration, proper placement, and using high-quality algorithms for data analysis.
Inherent Limitations of Sensors
Ensuring precise data collection is a prominent hurdle in the realm of wearable technology. These innovative devices heavily depend on sensors to capture a wide range of physiological signals, including heart rate, sleep patterns, and step count. Nevertheless, these sensors often encounter inherent limitations that impede their accuracy. Issues such as motion artifacts, signal interference, and suboptimal device placement can introduce errors and compromise measurement precision. To tackle this challenge, wearables manufacturers must consistently allocate resources to research and development, aiming to enhance sensor technology, refine signal processing algorithms, and implement rigorous calibration procedures. By investing in these areas, they can strive to deliver more reliable and precise data, thereby maximizing the potential benefits of wearable devices for users.
Lacks some features
Just because a wearable is jam-packed with interesting features doesn’t necessarily mean it has everything you want. Research before purchasing a device to ensure it has all the features you need. Otherwise, you may be disappointed.
Dwindling Ergonomics
Comfort and ergonomics are most necessary in the healthcare sector. However, the biggest issue with healthcare devices is long-term usage. They tend to heat and sometimes hang. Thus creating an issue for the user.
User Privacy, Security, Cyber Risks, and Hacking
Privacy and security risks are increasing due to frequent global advancements in information and technology. Privacy breaches have become common, and personal data leaks are often in the news, which scares users. Also, due to the Internet’s connectivity, the perils of hacking and phishing are increasing.
Water Proofing
Wearable healthcare products are mostly marred by moisture, water, and sweat. Devices go dysfunctional when they come in contact with water or any liquid. So, wear them during any physical activity, wash your hands, or do other tasks. Hence, the lack of waterproofing ruins the experience and correct reading.
Interoperability Challenges
Patients using healthcare devices must share data with their doctors and health specialists. However, not all devices are compatible, which creates problems when integrating and sharing reports.
Mostly Expensive
These devices aren’t for the faint of heart or those on a tight budget. The cost of wearable technology can range from a few hundred pounds to several thousand, depending on the features and brand.
Incompatible With Phone
If you purchase your generic wearable from an e-commerce website, there’s a chance it may not be compatible with your phone. For the device to work properly, it needs to be able to sync with your phone. If it can’t, then it’s essentially a glorified paperweight.
Can Cause Distraction
One of the common complaints about wearable technology is that it can be distracting. It can be very tempting to check your email or social media accounts when you’re supposed to be focusing on something else besides offering health-related information or tips. This is especially true for devices that allow you to access the internet or receive notifications.
Requires Power Management
One of the biggest complaints about wearable technology is that it requires frequent charging. This can be a real pain, especially if you’re using your device to track your sleep patterns or monitor your heart rate during a workout.
Tough to Operate
Not only are these devices likely to be inaccurate, but they can also be difficult to operate. This is often the case with smartwatches and other devices that have many features crammed into a small space. Learning how to use all the different features can take some time.
Easily Breakable
It can be damaged or broken depending on where this wearable is worn. Whether it’s an active lifestyle or everyday wear and tear, these devices can break easily and often at the most inopportune time.
Advantages
Proactive Monitoring of Patients’ Health
Wearable technology plays a vital role in healthcare by facilitating the monitoring of patients’ well-being. By continuously tracking patient activity and data, wearables provide valuable insights to healthcare providers, enabling a deeper understanding of patients’ conditions and more effective disease management. Devices like anklets and watches offer valuable applications in care settings like hospitals and nursing homes.
Reducing Healthcare Risks
Utilizing wearable technology devices to enhance patient safety is an excellent strategy for mitigating risks in healthcare. For instance, a wearable device that records calorie intake can be integrated into meal plans for patients struggling with weight loss or dietary requirements. Such technology also helps prevent patients from exceeding their physical limitations or encountering accidents while engaging in various activities, including medication administration.
Proactive Approach
Wearable devices offer valuable data and automated analytics, enabling nurse practitioners to diagnose issues more efficiently and intervene promptly. This proactive approach helps prevent readmissions and mitigate potential negative consequences.
Personalized Care
Hospitals are increasingly adopting wearable technology for broader purposes. Some establishments employ wearables to establish seamless connections between patients and caregivers, delivering more personalized care. Furthermore, wearables serve as auxiliary communication tools within hospital settings, benefiting residents and visitors alike.
Promoting Health and Well-being
Wearable technology empowers patients to improve their sleep quality, enhance memory functions, and achieve better physical fitness. Moreover, these devices enable doctors to monitor their patients’ health remotely, freeing up valuable time and ensuring overall well-being.
Reduced Anxiety and Stress
Equipped with wearable devices, healthcare staff can monitor vital signs such as heart rate and blood pressure, providing timely assistance and support whenever necessary, alleviating anxiety and stress levels among patients and caregivers.
Enhanced Accuracy in Patient Data
The presence of wearable devices allows hospitals to improve data accuracy by tracking the number of visitors each patient receives and their duration of stay. This valuable information can be leveraged to enhance care planning and delivery, leading to more effective and tailored patient outcomes.
Improved Communication
Through real-time feedback during patient interactions, wearable devices facilitate a better understanding for nurses and other medical professionals regarding their patients’ physical health requirements. This enhanced communication fosters improved care provision and patient support.
Wearable Technology: Devices Available
Blood Pressure Monitors
Effortlessly obtain your blood pressure reading directly on your smartphone by placing the monitor on your right or left arm. These convenient at-home blood pressure cuffs can connect to your phone, allowing you to store and track your blood pressure and pulse data for easy monitoring.
Integrated Activewear
Experience the fusion of cutting-edge technology and activewear in various styles and sizes. Embedded sensors within the clothing emit gentle vibrations, providing real-time feedback to ensure the precise execution of yoga poses. By promoting balance and accuracy, this integration empowers you to achieve your fitness goals more effectively.
Wearable Health Watches
Among the most user-friendly fitness trackers, smartwatches have evolved with technological advancements. With the updated software, they monitor and store your health and fitness information seamlessly, enabling you to stay on top of your progress easily. For example, the Apple watch
Glucose Meters
Designed for diabetic glucose monitoring, these reading devices are positioned on the upper arm. Additionally, they utilize phone sensors to measure glucose levels. Moreover, by reducing the need for frequent finger pricking, they offer greater convenience and can be used continuously for extended periods. e.g., Abbott Freestyle Libre 2
ECG Monitors
Wearable ECG technology employs a single electrode sensor typically positioned on the underside of a smartwatch. By monitoring the heart’s electrical activity, these devices can detect atrial fibrillation (Afib), an abnormal heart rhythm. This innovation brings the benefits of ECG monitoring to your wrist, ensuring early detection and timely intervention when irregularities occur. e.g., Apple Watch.
Microfluidic Patches
A small adhesive patch, known as a microfluidic patch, is simulating a breakthrough in the wearable healthcare industry. It offers real-time and accurate analysis of bodily biomarkers, enhancing remote care through personalized health insights and reducing the need for invasive tests. It improves medication management for providers, enhances patient engagement, and solidifies diagnostic accuracy, making health monitoring more accessible.
EHR Integration
The integration of EHRs (electronic health records) and wearable health technologies can provide essential data through data generation and real-time insights to health systems. It can provide an overview of patients’ health while maintaining privacy and ensuring data accuracy. These wearables can enable tracking of several metrics, including calories, heart rate, steps, sleep quality, etc.
AI-Powered Robotic Prostheses
AI-powered robotic prosthesis devices use reinforcement learning to know the patient or the individual wearing them. Moreover, it continually adapts to changes and offers improvements to people by transforming their lives through the limb, empowering them to perform daily tasks with ease and comfort.
Also, check our latest blog on Smart Glasses: The Future of Wearable Technology
Top Startups in the Wearable Healthcare Technology Market
Several startups have found an opportunity to establish themselves and serve consumers in the wearable healthcare market with their technologically innovative devices.
- Anatomech: The company focuses primarily on physical rehabilitation and develops smart wearable devices that cater to home-based therapy, precisely for breast-cancer-related lymphedema. The bionic wearable from the startup utilizes patented actuators, providing relief from discomfort and swelling.
- Strados Labs: The startup developed the RESP Biosensor, which regularly monitors respiratory events and lung sounds. It assists in monitoring conditions such as asthma and COPD, and supports both home care and hospital care simultaneously.
- ABIORO: The company has developed an RX patch that is comfortable for patients and utilizes deep learning and biosensing to support remote patient monitoring by diagnosing arrhythmias.
- NNOXX: The startup develops wearables that monitor nitric oxide levels and muscle oxygen in real-time, offering trainers, athletes, and fitness enthusiasts actionable insights. The device can be integrated with various mobile apps.
- Optohive: The company is known for its wearable brain imaging technology, utilizing functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS). The modular system of the device allows non-invasive and comfortable brain monitoring for stroke recovery, neurorehabilitation, and neuroscience research.
Conclusion
Just like the metaverse in healthcare, wearable technology in healthcare is spiking quickly. Health wearable computing devices are going through discovery phases in their life cycle. However, a significant advancement that will propel the evolution of wearable devices is the advent of 6G technology. This next-generation network infrastructure will unleash greater bandwidth capabilities, unlocking many possibilities, such as real-time health monitoring and seamless multitasking with multiple applications running simultaneously. Also, the potential applications that can benefit from this powerful combination of healthcare wearables and 6G are boundless, opening up exciting avenues for innovation and transformative experiences.
Let's Take the Conversation Forward
Reach out to Stellarix experts for tailored solutions to streamline your operations and achieve
measurable business excellence.