Solid State Batteries: Current and Future Prospects
Battery technology has evolved from lead-acid to lithium-ion battery, with advancements in the 1970s and early 1990s. Current research focuses on improving energy density and safety features, while solid-state batteries are under development. These advancements have revolutionized portable devices, electric vehicles, and renewable energy storage systems, transforming various industries. Solid-state batteries (SSB) are crucial in the industry for their safety, energy density, and fast charging capabilities. They are stable, resistant to overheating, and enable smaller, lighter devices with longer battery life. Their eco-friendly composition aligns with sustainability goals, driving technological advancements, transportation, and renewable energy.
How Solid State Batteries Work?
Solid-state batteries employ solid electrodes and electrolytes, eliminating liquid or gel electrolytes found in traditional batteries. The solid electrolyte, often made of ceramic or polymer, allows for the direct flow of ions between the electrodes, enhancing safety and energy density. Lithium ions move from the anode to the cathode through the solid electrolyte, releasing energy during discharge. They possess high ionic conductivity, chemical stability, electrochemical stability, and interfacial compatibility. They are also cost-effective and compatible with existing battery production technologies, ensuring long-term reliability. Interfacial compatibility reduces resistance at the electrode-electrolyte interface.
In charging, the process reverses. This design prevents issues like leakage and thermal runaway, enhancing battery safety. Solid-state batteries promise higher energy density, faster charging, and longer lifespan, making them vital for electric vehicles, portable electronics, and renewable energy storage, revolutionizing the future of energy technology.
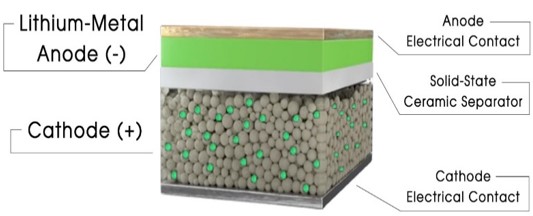
Figure 1: Solid-State Battery
- Solid Electrolyte: Solid-state batteries replace the liquid or gel electrolyte found in conventional batteries with a solid electrolyte. This solid material, often a ceramic or polymer, serves as a medium for transporting ions, such as lithium ions, between the battery’s electrodes.
- Ion Migration: Lithium ions (or other relevant ions, depending on the battery chemistry) migrate through the solid electrolyte during the charging and discharging process. When discharging, lithium ions move from the anode to the cathode, releasing energy in the form of electricity. During charging, this process reverses, with lithium ions moving from the cathode to the anode, storing energy.
- Electrodes: Solid-state batteries employ traditional cathode and anode materials similar to those used in lithium-ion batteries. These materials facilitate the electrochemical reactions that occur during charge and discharge cycles.
Comparison with Lithium-ion Batteries
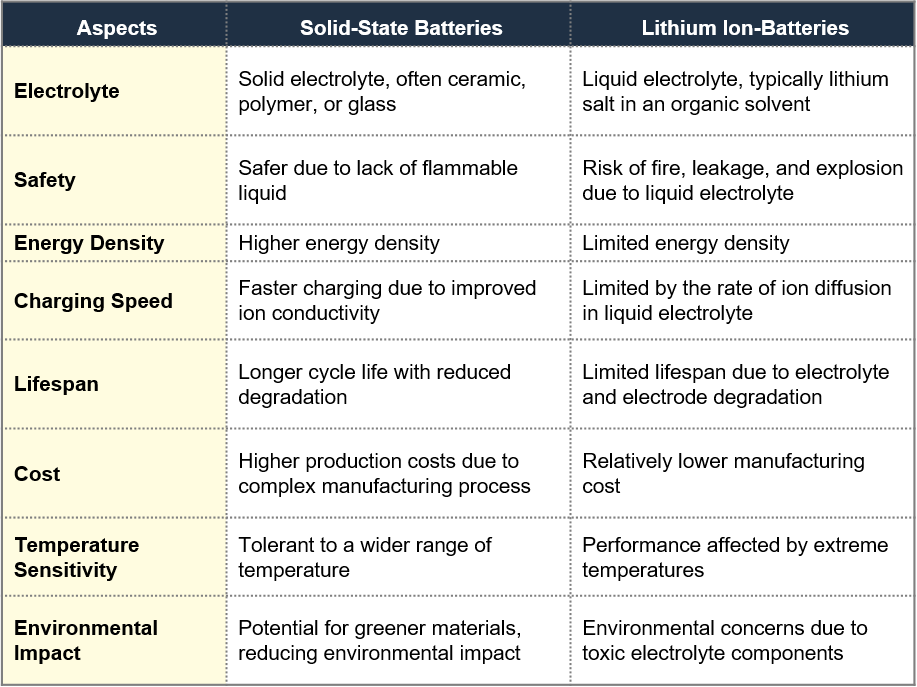
Table 1: Solid-Sate Battery v/s Lithium Ion
Types of Solid-State Batteries
- Polymer Electrolyte Solid State Batteries (PESSBs) are advanced energy storage devices using solid polymer electrolytes. They offer superior safety, stability, and a wider operating temperature range. They cater to diverse applications like portable electronics and electric vehicles and have the potential for higher energy density, longer cycle life, and faster charging. As research progresses, PESSBs are promising contenders in battery technology, addressing challenges and driving innovations in various industries.
- Inorganic Solid State Batteries: ISSBs are advanced energy storage devices that use solid inorganic materials as electrolytes, offering enhanced safety, stability, and energy density. They eliminate the risk of leakage and fire, making them ideal for high-safety applications like electric vehicles and aerospace. ISSBs can withstand a wide range of temperatures, offer rapid charging, and have a longer lifespan, making them crucial for emerging technologies like electric transportation, renewable energy systems, and portable electronics.
- Sulfide-Based Solid-State Batteries: SBSSBs are solid-state batteries using solid sulfide electrolytes, offering superior safety and energy density. They eliminate leakage and fire risks, are suitable for electric vehicles and portable electronics, and provide high energy density, longer lifespan, and faster charging.
Materials Used
- Solid Electrolyte Materials: Solid electrolyte materials are crucial in solid-state batteries, enabling ion conduction without liquid electrolytes. Materials like Lithium Phosphate (LiPON), Lithium Lanthanum Zirconate (LLZO), and Polyethylene Oxide (PEO) are used, with LiPON offering stability and conductivity in thin-film batteries. LLZO offers high ionic conductivity and stability for high-power applications. Polymer electrolytes are lightweight and flexible, while Lithium Sulfide (Li2S) offers good ionic conductivity at lower temperatures.
- Cathode & Anode Materials: In solid-state batteries, cathode materials such as lithium transition metal oxides (LMO, NMC, NCA), sulfur, and phosphates provide high energy density and stability. Sulfur and Selenium offer impressive theoretical energy densities, while Prussian blue analogs show potential for fast ion diffusion. Anode materials include lithium metal, which is known for its high energy density but is hindered by dendrite formation. Lithium titanate ensures exceptional cycle life and safety, while silicon and germanium offer high capacity, although they suffer from volume changes. Carbon-based materials, like graphite, are being adapted for solid-state batteries.
Impact of Materials on Battery Performance
The choice of materials significantly influences solid-state battery performance. Electrolyte materials impact ionic conductivity, stability, and interface compatibility, crucial for rapid ion transport, longer lifespan, and reduced resistance at interfaces. Cathode materials affect energy density and voltage, with higher specific capacities contributing to increased overall energy storage. Anode materials impact energy density, and cycling stability mitigates issues like dendrite formation.
Challenges & Solutions
Challenge
- Ionic Conductivity: Many solid electrolytes exhibit lower ionic conductivity than their liquid counterparts, restricting power output.
- Thermal Expansion: Mismatched thermal expansion coefficients between components can cause mechanical stress and reduced battery life.
- Electrode Compatibility: Ensuring stable interfaces between electrodes and solid electrolytes is challenging, impacting overall performance.
Solution
- Material Engineering: Research focuses on developing new solid electrolytes and electrode materials with high conductivity and stability.
- Nanotechnology: Nanostructured materials enhance ionic conductivity and reduce mechanical stress, addressing both conductivity and thermal expansion issues.
Solid State Batteries: Safety & Reliability Issues
Challenge
- Dendrite Formation: Lithium dendrites can form, leading to short circuits and safety risks.
- Thermal Runaway: The SSB can experience thermal runaway events less frequently than liquid electrolyte batteries.
- Mechanical Durability: Brittle electrolytes are prone to mechanical stress, affecting the battery’s longevity.
Solution
- Thermal Compression: Brown University demonstrated in December 2025 that the thermal compression resulting from heating one side and cooling the other side of the electrolyte could suppress dendrite formation.
- Densifying Argyrodite Solid Electrolyte: In October 2025, the University of Oxford demonstrated that densifying argyrodite solid electrolyte to 99% density paved the path for 9 mA/cm2 lithium plating without dendrite formation.
- Space Charge Layers: The University of Texas discovered that space charge layers between solid electrolytes increase ionic conductivity.
- Advanced Coatings: Protective electrode coatings prevent dendrite formation, enhancing safety.
- Thermal Management: Innovative thermal management systems mitigate the risk of thermal runaway, ensuring safer operation.
Manufacturing Issues
Challenge
- Complexity: Precise manufacturing processes are required, which leads to increasing production complexities
- Scalability: Scaling up production while maintaining quality and reducing costs remains a challenge
Solution
- Advanced Techniques: Automation and advanced manufacturing techniques streamline production, reducing complexity and costs.
- Scale-Up Research: Research into large-scale production methods ensures scalability without compromising quality
Current Research & Innovations
- Manufacturing Developments: Several new developments have emerged in the manufacturing processes of solid-state batteries:
- Nissan opened a prototype solid-state battery production facility and aims to launch EVs with batteries by 2028 while reducing battery pack costs by 65%
- Toyota & Idemitsu Kosan announced the construction of a large-scale lithium sulfide plant that is scheduled to be completed by June 2027
- Interfacial Coating: Innovative coatings on electrodes and electrolytes help to prevent reactions and enhance compatibility.
- Shanghai Isai Battery Technology Co., Ltd. is developing a coating roller for solid-state lithium batteries containing copper powder, graphite powder, neutralizing agent, and conductive adhesive, which enhances battery anode energy, tensile strength, and long service life.
- Toyota Motor provides a liquid coating for solid-state batteries comprised of phosphoric acid and lithium compounds that reduce battery resistance.
- Additive Manufacturing: 3D printing technologies are explored for precise manufacturing, enabling complex and customized designs for solid-state batteries.
- Beijing University of Technology is working on a method for preparing a solid-state lithium-ion battery using 3D printing. The process involves preparing positive, negative, and composite electrolyte inks, printing layer by layer on a glass substrate, and photo-curing simultaneously.
- Quantum Machine Co., Ltd. is developing automatic solid-state battery manufacturing equipment, including a cathode deposition device, a negative electrode deposition device, a solid-state electrolyte molding device, a stacking crimping device, and transmission devices.
Application of Solid State Batteries
- Electric Vehicles & Transportation: Solid-state batteries are poised to revolutionize the electric vehicle industry with their enhanced safety, higher energy density, and faster charging capabilities. They offer a longer driving range, reduce charging times, eliminate electrolyte leakage and thermal runaway risks, and can be designed in lightweight configurations. Additionally, their longer cycle lives reduce maintenance costs and increase the overall safety of electric vehicles.
- Consumer Electronics: Solid-state batteries are ideal for consumer electronics due to their extended battery life, faster charging, slim design, and portability. They can be customized for wearable devices, offer longer wireless earbuds and headphone usage, and enhance gaming experiences. They also reduce battery replacement frequency and ensure consistent performance in remote controls and IoT devices.
- Renewable Energy Storage: Solid-state batteries are revolutionizing renewable energy storage systems by improving efficiency, safety, and reliability. They stabilize the grid, store excess energy, and integrate with solar panels for a consistent power supply. Moreover, they serve as backup power for businesses, facilitate energy storage in microgrids, and enable fast charging stations for electric vehicles. They are also used in research laboratories for energy storage and analysis.
Solid State Batteries: Key Players & New Entrants

Figure 2: Important Players and Leading Startups
Prieto Battery’s
Its solid-state technology uses a unique three-dimensional copper foam design for high energy density, resulting in longer-lasting, more powerful batteries. This technology ensures rapid charging without compromising safety, eliminating liquid electrolytes and reducing leakage and thermal incidents. It is suitable for electric vehicles and consumer electronics and represents a significant step towards safer, greener, and more efficient energy storage solutions.
QuantumScape
It specializes in solid-state lithium-metal batteries. Their technology replaces the traditional liquid electrolyte in batteries with a solid ceramic electrolyte. This innovation enhances safety by eliminating the risk of electrolyte leakage and enabling the use of a lithium-metal anode, boosting energy density significantly. The solid-state design allows for faster charging, longer lifespan, and improved overall performance compared to conventional lithium-ion batteries. QuantumScape’s breakthroughs represent a promising step toward safer, more efficient, and higher-capacity energy storage solutions, with potential applications in electric vehicles and renewable energy systems.
BrightVolt
It is a leading solid-state battery company specializing in flexible, ultra-thin batteries. Their batteries are adaptable to various form factors, making them ideal for wearables, IoT devices, and medical implants. They prioritize safety, reliability, and customization, making them inherently stable. Their innovative and scalable technology contributes significantly to the advancement of flexible electronics and energy-efficient devices.
Ilika
It is actively involved in the research and development of thin-film solid-state batteries for various applications, including the Internet of Things (IoT), industrial sensors, and medical devices. Ilika’s solid-state batteries are known for their small form factor, high energy density, and ability to operate in extreme environmental conditions. The company has been working on miniaturized, high-performance batteries designed to meet the power requirements of emerging IoT devices and other portable electronics.
Basquevolt
It is an emerging company that develops solid-state lithium batteries for electric vehicles, heavy transport, renewable energy, and electronic devices. Their technology offers efficiency, longer life, and less wear and tear than liquid batteries. Basquevolt aims to create sustainable materials and battery cells for mass deployment in electric transportation, stationary energy storage, and advanced portable devices.
Natrion
It is bringing to market LISIC, a new plug-and-play solid-state electrolyte component that manufacturers can quickly integrate into their current production lines to reduce the risk of fire, increase durability, and allow the use of new high-energy-capacity chemistries for improved energy density.
Business Activities
Toyota
- In October 2025, Toyota signed a joint development agreement with Sumimoto Metal Mining to scale cathode materials production for solid-state batteries.
- The Japanese giant also received certification from Japan’s Ministry of Economy for all its solid-state battery development and production plans in 2024.
- Most importantly, it plans mass production of 450-500 Wh/kg energy density batteries offering 10-minute charging ability and a 40-year lifespan.
Mercedes-Benz
- The German automaker partnered with Factorial Energy using FEST technology.
- A Mercedes-Benz EQS equipped with solid-state batteries covered a distance of 749 miles in one stretch with 85 miles remaining.
Stellantis
- Stellantis and Factorial Energy validated automotive-sized solid-state cells with 375 Wh/kg energy density in April 2025. They achieved 18-mins charging, going from 15% to 90% with an operating temperature ranging from -30 degrees to 45 degrees C.
BMW
- IN 2025, BMW partnered with Solid Power and Samsung SDI for a trilateral collaboration. It also tested solid-state batteries in an i7 prototype.
Environmental Impact & Sustainability
- Reduced Environmental Footprint: SSBs can reduce EV carbon footprint by ~39% as compared to their liquid lithium-ion counterparts. They have longer lifespans and durability, reducing battery replacement frequency and electronic waste. They are often made from recyclable materials, promoting a circular economy. Their energy efficiency, particularly in electric vehicles and renewable energy storage, indirectly reduces greenhouse gas emissions and air and water pollution.
- Recycling & Disposal Consideration: Solid-state batteries are crucial for environmental sustainability due to their scarce materials and valuable components. Efficient recycling and proper disposal methods are essential to prevent contamination. Recycling processes should recover valuable materials like lithium and cobalt while ensuring safe handling of solid electrolytes. Establishing regulations and collaborating with manufacturers, recyclers, and policymakers is necessary to minimize environmental impact.
- Contribution to Green Technology: Solid-state batteries are crucial in green technologies, enhancing energy storage safety, reducing fossil fuel reliance, and promoting grid stability. They support portable green devices, ensuring longer usage without environmental harm. Their recyclability and longer lifespan reduce electronic waste, aligning with sustainable practices. Overall, solid-state batteries drive eco-friendly transportation and renewable energy integration.
Future Prospects
Market Growth
According to industry experts, in 2026, solid-state batteries cost between $400-800/kWh against lithium-ion batteries in 2024 that costed $115/kWh. Various automakers are aiming to bring costs between $65-85/kWh for commercialization purposes.
Commercialization Timeline
Based on recent developments, the commercialization timeline of solid-state batteries can thus be carved as:
- 2025-2027: Commercial deployment remains restricted to premium applications
- 2027-2028: Samsung SDI, Nissan, and Toyota are aiming for initial production
- 2028-2029: Market expansion as multiple manufacturers join the solid-state segment
- 2030+: Mass market adoption and cost leveling with lithium-ion batteries expected
Market Trends
- Widespread Adoption: Increased commercialization and wider adoption in electric vehicles, consumer electronics, and renewable energy systems as manufacturing processes become more efficient and cost-effective.
- Flexible Electronics: Developing flexible and thin-form solid-state batteries, enabling applications in wearable devices, flexible displays, and IoT sensors, fostering innovation in these sectors.
- Green Manufacturing: Focus on environmentally friendly manufacturing processes, align with sustainable practices, and reduce the ecological footprint of battery production.
Conclusion
Solid-state batteries signify a big leap from lithium-ion batteries. Their inherent high energy density, safety, and rapid charging potential position them as the future of various segments spanning EVs, renewable energy projects, consumer electronics, etc. As their market adoption increases, they will pave the path to a sustainable, safer, and compliant energy world.
As an innovation and strategy partner, we are helping market participants find answers to the following questions:
- How to overcome interfacial instability and dendrite formation for reliable, long-lasting performance?
- What partnerships are needed to accelerate the innovation pipeline and secure a competitive IP position?
- What’s a realistic timeline and total ownership cost for the integration of solid-state batteries as compared to the advancement of lithium-ion chemistries?
- Where should the initial commercialization be focused to validate the tech and ensure optimum ROI?
- How to adapt or reinvent gigafactory processes for stringent solid-state assembly requisites and moisture-sensitive materials?
- What kind of innovation in quality control and dry-room processing is required to reduce scrap rates and achieve >90% yield?
To navigate all relevant complexities, schedule a call with our experts.
Let's Take the Conversation Forward
Reach out to Stellarix experts for tailored solutions to streamline your operations and achieve
measurable business excellence.