Natural Food Coloring: Benefits, Challenges, and Future Trends
Enhancing the quality and safety of our food holds paramount significance for the well-being of humanity. From ancient times, humans have continuously refined their dietary practices, evolving hunting methods, and domesticating animals and plants. They have preserved food through physical means and introduced molecules to elevate flavors and prolong shelf life. Moreover, throughout history, numerous ingredients have fulfilled essential roles in diverse food items, ensuring an accessible, nutritious, flavorful, visually appealing, and secure food supply. The pivotal roles of food additives (precisely natural food coloring) and technological advancements have been instrumental in achieving these objectives over the years.
Natural food coloring use in the food industry is fundamental, allowing loss reduction, quality increase, shelf life extension, new formulation development, and standardization. Thus, meeting the increasingly challenging market demands. Used in all types of foods, additives are becoming increasingly prevalent and important in human nutrition. Despite the controversy caused by conflicting results from many studies involving these compounds and different government interpretations, they are subject to strict regulation. Today, hundreds of additives are added to food globally, while many others have been banned over the years.
Know More About the Growing Need For Natural Colorants
With an increasingly competitive market, reducing production costs and monetizing existing products is essential while ensuring food safety and quality. Since coloring and preserving additives are among the most important ones in the food industry, improving the appearance and preservation of foodstuffs, several studies have focused on finding new solutions and/or improving existing alternatives. Finding compounds with both capacities (colorant and preservative) and exhibiting bioactive functions can be a promising solution.
However, to obtain benefits such as antioxidant or antimicrobial activity, the concentration of the compounds commonly used as dyes is usually high, not meeting the requirements of the admissible daily intake (ADI). Research and development of new molecules through new chemical approaches, with the modification of natural molecules already known, so that they can develop a better and double performance (colorant plus preservative), may be a path to be followed by the scientific community to circumvent the difficulties and monetize the use of these additive molecules in the food industry.
The global natural food colors market is forecast to reach about 2.5 billion dollars by 2025.
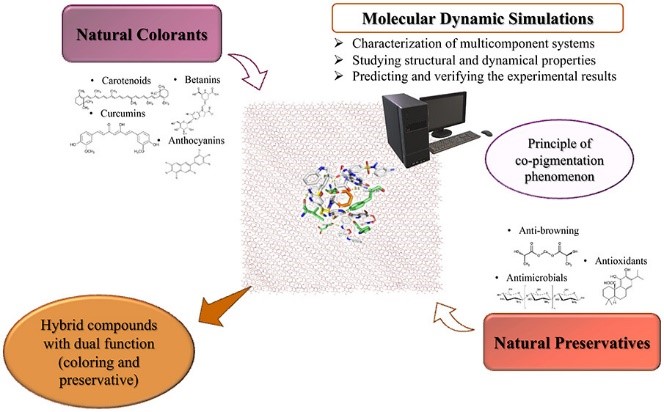
Figure 1: Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Natural Colorants
How Are Natural Food Colorants Obtained?
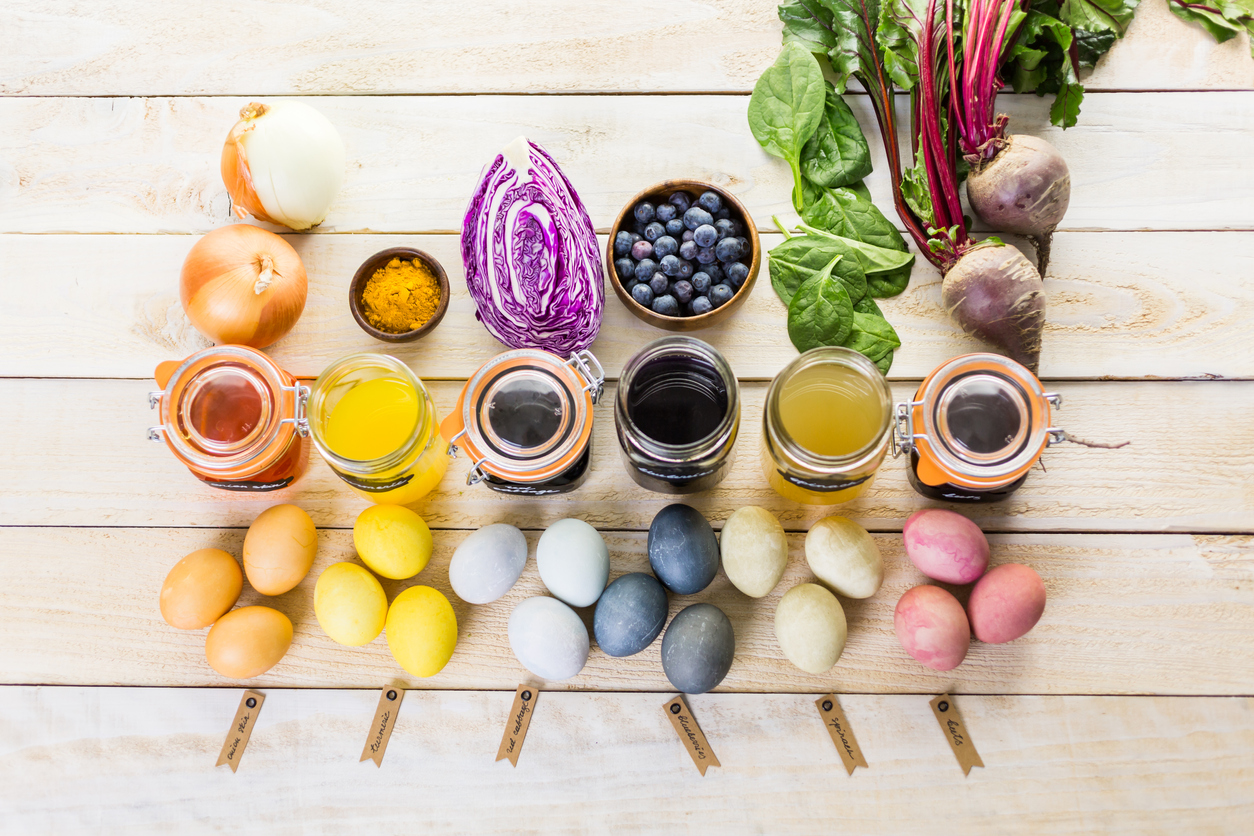
Natural food colorants are obtained from fruits, vegetables, and minerals and are generally considered safer than synthetic colorants. In the United States, the FDA has approved a specific list of food ingredients that can be used as colorants. Among the natural food colorants approved by the FDA are annatto extract, beet juice, beta carotene, black/purple carrot, blue fruit juice color, blue shade vegetable juice colors, blue spirulina extract, butterfly pea powder, calcium carbonate, caramel color, elderberry, fruit juice, grape juice, hibiscus fruit, paprika, and purple carmine. Most natural colorant extracts are derived from plant tissues, and many are insoluble in water. Moreover, this necessitates the addition of an emulsifier to achieve an even distribution throughout the food product. Natural food colorants can be produced at home using strawberries, raspberries, beets, tomatoes, carrots, paprika, sweet potato, saffron, and turmeric.
New FDA Approvals
In a move to replace synthetic dyes, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has added three more natural color additives to its list. They are:
- Butterfly Pea Flower Extract: The extract is renowned for its pH-sensitive properties and vibrant purplish-blue color. It is gaining popularity as a dairy alternative and in health beverages.
- Galdieria Extract Blue – The species of red algae (Galdieria sulphuraria) provides a bright blue stable hue suitable for beverages, confections, and snacks.
- Calcium Phosphate – It is not the pigment, but calcium phosphate improves stability and pigment dispersion in food matrices.
The approval indicates the biologically derived color sources and open avenues are gaining momentum toward formulation experimentation, precisely for heat-processed or high-acidity products.
Phase‑out timeline for petroleum-based dyes –
Petroleum-based dyes, such as Red No. 3, are slated to be revoked by the FDA by the end of 2026. Moreover, California is aligning with the thought and may ban Red 3 by 2027. The change presents opportunities for innovation and regulatory pressure for organizations or businesses seeking clean-label formulations.
Importance of Natural Food Colorants
Natural food colorants are essential for several reasons, including:
- Health Benefits: Natural colors have a variety of health benefits, including antioxidant, anti-cancer, and anti-inflammatory properties
- Masking Unpleasant Attributes: Food colorants are paramount in food production as they serve the critical function of concealing undesirable attributes or augmenting the inherent qualities of food products.
- Attractive Appearance: Natural colorings help make foods more attractive
- Nutritional Value: Some natural colorings, such as beetroot and turmeric, are recognized to increase the nutritional value of the foods
- Consumer Demand: Consumers are increasingly demanding more natural and transparent ingredients in their food, including natural food colorants
Diseases Linked to Artificial Food Colorants
Artificial food colorants are commonly incorporated into processed foods, confectionery, sports energy drinks, baked goods, and pharmaceuticals. However, research indicates that these artificial food dyes may contribute to various health issues, including cancer, allergies, and heightened levels of hyperactivity in children. Some of the primary food dyes even contain benzene, a known carcinogen. For example, Red 3 has been shown to induce cancer in animal studies, and there is compelling evidence suggesting that several other food dyes possess carcinogenic properties.
Moreover, artificial food dyes have been associated with respiratory disorders such as asthma and bronchitis. Four specific colorants ( Red 40, Blue 1, Yellow {5, and 6}) have been associated with hypersensitivity reactions. Furthermore, the majority of artificial food colorings have raised significant health concerns, including inflammation, disruptions to the immune system, and the presence of cancer-causing toxic contaminants.
What are the Health Benefits of Using Natural Food Colorants?
Natural food colorants have several health benefits, including antioxidant, anti-cancer, and anti-inflammatory properties. Although most natural colors do not provide nutritional value to an end product. Some natural colorants, such as lycopene, a bioactive red-colored pigment naturally found in red fruits, provide antioxidant properties. They have interesting health benefits. Also, natural food colorants are often sourced from fruits, vegetables, and other plant-based sources. These sources may contain vitamins, minerals, and other beneficial compounds, enhancing the nutritional value of the food product. Additionally, natural food colors are generally considered safe for human consumption and less likely to cause adverse health effects than synthetic food colors.
Natural Colorants from Other Resources
Natural colorants can be obtained from various sources, including fruits, vegetables, plants, and minerals. Some examples of natural colorants from other sources are:
- Flowers
- Pepper
- Red beet
- Grapes
- Red cabbage
- Spinach
- Caramel
- Betalains
- Saffron
- Anthocyanins
- Carotenoids
- Auronidins: A novel family of coloring pigments known as auronidins may pave the way for producing more stable and intense natural, plant-based food and beverage colorants. Auronidins are water soluble and have a yellow/orange color when the pH is acidic.
- Vegetable Food Waste: The circular economy model has been expanding consistently, creating new businesses that open doors, like recuperating high-added value particles (e.g., dyes) from vegetable food wastes that might be applied as food additives (e.g., colorants).
- Agro-by-Products: The agro-by-products and their concentrates might be effectively integrated into groceries; for example, phenolic compounds from eggplant can possibly be utilized as a multifunctional food-added substance with antimicrobial, cell reinforcement, and food colorant properties.
Stability:
Encapsulation: Micro- and nanoencapsulation are useful platforms for preserving pigments from hazardous environmental conditions while allowing for regulated and targeted release. Moreover, emulsification, inclusion, coacervation, complexation, and nanoprecipitation are all methods for nanoencapsulating food components.
Oterra CapColors®, uses an encapsulation composition that enhances the usefulness and stability of natural color pigments.
Further, VIVAPIGMENTS® combines vegetable concentrates with rice protein. This results in a regular variety of powders and a normal variety of fluids for bright and stable natural colors.
Co-pigmentation: Co-pigmentation improves the stability and brightness of natural colors. There are two types of co-pigmentation methods: liquid and powder. Furthermore, the combination of co-pigmentation chemicals and the proper spray dryer process design can improve color fastness and stability.
Extraction:
Ultrasound: The recovery of natural plant pigments can be improved through ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE). An innovative green extraction method with numerous advantages is ultrasound treatment.
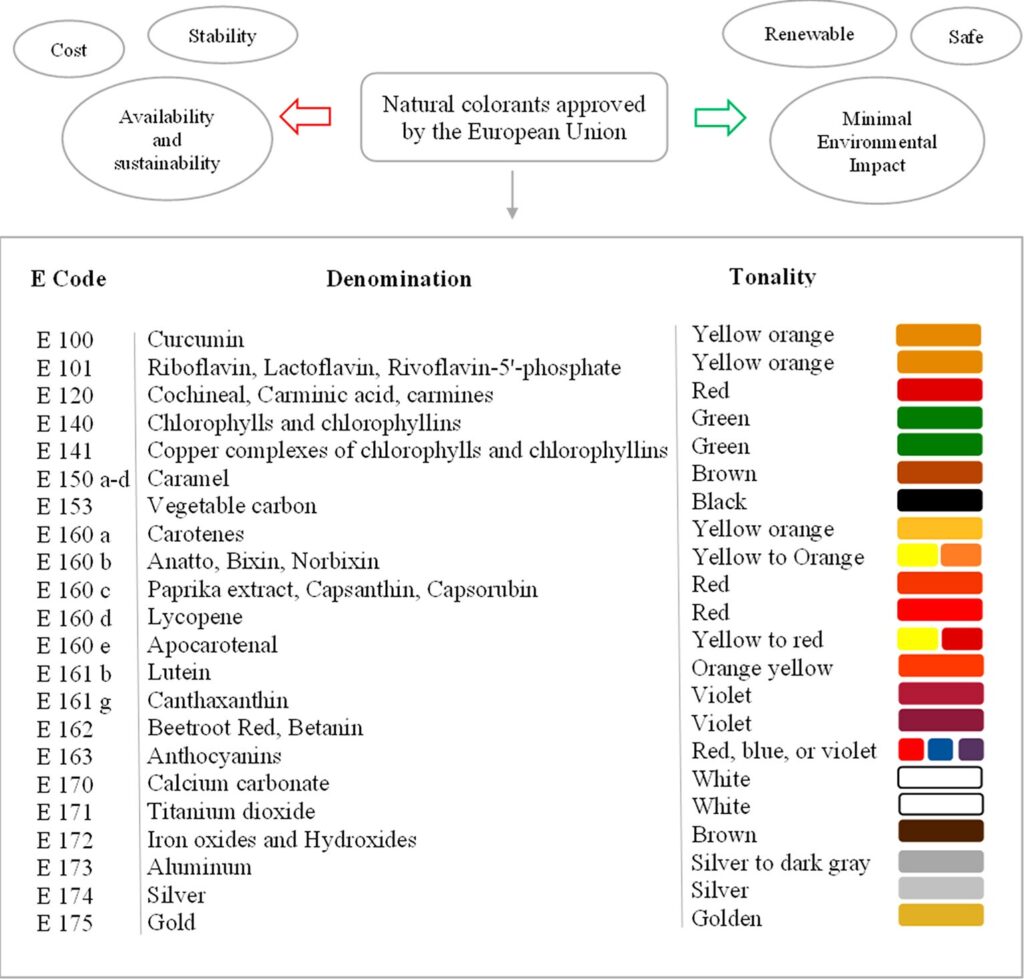
Source 2: Natural Food Colorants approved by the European Union
These natural colorants can be used in various food applications, including beverages, confectionery, dairy, bakery, and meat products. Encapsulation of natural colorants is also an emerging trend in the food industry. Also, this can improve the stability and functionality of the colorants.
Next-Generation Stabilization Techniques
Natural colorants face challenges with stability due to variations in light, heat, and pH. Some of the promising solutions yielded by R&D are:
- Protein–Inorganic Hybrid Nanoflowers: Scientists are focusing on leveraging nanotechnology to stabilize natural pigments, such as curcumin. Pigments are safeguarded from oxidation, UV damage, and thermal shifts by enzyme-based nanoflowers with metallic phosphate structures.
- Encapsulation and Nanoemulsion: These methodologies facilitate the controlled release of pigments, thereby improving the shelf life of processed foods. Microencapsulation can preserve carotenoids and anthocyanins using chitosan carriers, maltodextrin, and alginate, which are suitable for storage and cooking.
By converging these sustainable innovations into product development, companies can address formulation bottlenecks, allowing wider industrial adoption of plant-based colors.
Technological Applications
Natural colorants have various technological applications in food systems. Here are some of the technological applications of natural colorants in food systems:
- Bakery Products: Natural colorants are used in various bakery products, including cakes, bread, and cookies. For example, turmeric gives some cakes and bread a yellow color, while beet juice provides a red color for some cookies.
- Beverages: Natural colorants are used in various beverages, including fruit juices, sports drinks, and carbonated drinks. For example, beet juice is used to give a red color to some fruit juices, while spirulina extract is used to provide a blue color to some sports drinks.
- Confectionery: Natural colorants are used in various confectionery products, including candies, chocolates, and gummies. For example, carmine, a natural red color derived from insects, is used to give some candies and chocolates a red color.
- Milk, Dairy, and Dairy-Like Products: Natural colorants are used in various dairy products, including yogurt, ice cream, and cheese. For example, annatto extract gives some cheeses a yellow color, while beet juice provides a pink color for some ice creams.
- Meat and Meat Products: Natural colorants are used in various meat products, including sausages, ham, and bacon. For example, paprika gives some sausages a red color, while beet juice provides a pink color for some ham.
- Other Food Products: Natural colorants are also used in other food products, including soups, sauces, and dressings. For example, turmeric gives some soups and sauces a yellow color, while beet juice gives some dressings a red color.
Challenges With Natural Food Colorants
While natural food colorants have several benefits, some challenges are associated with their use in food systems. Here are some of the challenges with natural food colorants:
- Color Stability: Natural food colorants are often less stable than synthetic colorants, which can result in color fading or changes over time. This can challenge food manufacturers who must ensure consistent color in their products.
- Limited Color Range: Natural colorants may not provide the same range of colors as synthetic colorants, which can limit their use in certain food products.
- Cost: Natural colorants can be more expensive than synthetic colorants, making them less attractive to food manufacturers.
- Sourcing: Natural colorants are often sourced from specific fruits, vegetables, or minerals, subject to seasonal availability and price fluctuations.
- Processing: The extraction and processing of natural colorants can be complex and require specialized equipment, which can add to the cost and complexity of using natural colorants in food products.
Natural Food Coloring Brands and Suppliers:
- FoodRGB Inc.: A manufacturer and wholesaler offering a variety of natural food colorants, such as β-Carotene, Paprika Oleoresin, Beetroot Red, Radish Red, Cabbage Red, Spirulina Blue, and Curcumin.
- CAIF Naturally Sourced Solutions: A supplier specializing in natural food colorants, including annatto, beet juice, and turmeric.
- Deiman USA: Provides natural food colorants, including caramel color, annatto, and turmeric.
- Avalon Deco Supplies, Inc.: Offers natural food colorants like beet juice, spirulina, and paprika.
- RK Pigments: A supplier of various natural food colorants, including beet juice, spirulina, and paprika.
- Papagino Foods: Specializes in natural food colorants, including annatto, beet juice, and turmeric.
- Aldon Corporation: Supplies a variety of natural food colorants, including annatto, beet juice, and turmeric.
Different Types of Natural Food Colorants
Here are some different types of plant-based food coloring:
- Annatto: Derived from achiote tree seeds for yellow or orange food coloring.
- Turmeric: Obtained from turmeric plant roots, imparts a yellow hue to food.
- Beet Juice: Extracted from beetroots, provides red or pink food coloring.
- Red Cabbage: Derived from red cabbage leaves, it adds blue or purple tones to foods.
- Spinach: Obtained from spinach leaves, it imparts a natural green coloring.
- Caramel: Produced through the heating of sugar and used for brown food coloring.
- Paprika: Ground from paprika plant pods, used for red food coloring.
- Saffron: Derived from the saffron crocus flower stigma, it adds a yellow tint to foods.
- Chlorophyll: Extracted from the green pigment of plants, it provides a natural green color.
- Anthocyanins: Naturally occurring in various fruits and vegetables, including blueberries, blackberries, and red cabbage, used for red, blue, or purple food coloring.
Conclusion:
The future of natural food colorants or organic food coloring in the food industry holds great promise, driven by consumer preferences for natural and health-conscious food products. Given the flourishing market and health concerns, the demand for gluten-free food coloring and organic food coloring is growing. Moreover, here are some potential upcoming advancements in the utilization of natural food colorants:
- Enhanced Processing Techniques: The food industry is continually exploring novel processing methods and cutting-edge technologies to optimize the stability and effectiveness of natural colorants within food systems.
- Exploration of Novel Sources: Ongoing efforts are directed toward discovering fresh sources of natural colorants, particularly plant-based alternatives, and innovating extraction methods.
- Innovative Formulations: The development of inventive formulations and encapsulation techniques is poised to enhance the stability and functionality of natural colorants within food systems.
- Evolving Regulatory Standards: The regulatory landscape for natural food colorants is evolving, focusing on ensuring their safety and efficacy within food systems.
In summary, the outlook for natural food colorants in the food industry is promising, with ongoing research and development to elevate their stability, functionality, and safety within food products.
Let's Take the Conversation Forward
Reach out to Stellarix experts for tailored solutions to streamline your operations and achieve
measurable business excellence.



