Smart Pill Technologies Offer New Hope for Diagnosis and Drug Delivery
The healthcare sector is undergoing a shift toward technology-driven innovation, particularly in drug manufacturing, delivery, and diagnostics. Recent advancements have greatly aided doctors. One such technology that has gained attention is the smart pill in the medtech industry.
Smart pill technologies integrate ingestible medication with miniature electronics, scripting the evolution of medical science by assisting in diagnosis and treatment and monitoring a range of ailments. A smart pill incorporates wireless communication, sensors, and drug delivery systems, providing real-time solutions in a non-invasive manner that enables personalized medicine for various diseases.
The blog delves deeper into smart pills, exploring their impact, transformation, advantages, challenges, applications, and the road ahead, among other topics.
Understanding the Smart Pills Concept
The term ‘smart pills ‘is self-explanatory, as it bifurcates from the traditional pills that are ingested. They are packed with technology that diagnoses the human body through microelectronics and sensors, unlike conventional pills, and interact with the body’s systems to monitor health conditions and parameters, such as pH, temperature, and biomarker presence. The information is then sent to devices connected wirelessly, such as smartphones.
Market Size of Smart Pills
The global smart pills market is poised for substantial growth, with an estimated average market value of $4.87 billion in 2024, expected to expand to approximately $11.47 billion by 2030. This growth is driven by increasing advancements in smart pill technology, rising demand for non-invasive diagnostic and monitoring solutions, and expanding applications in the healthcare sector. The market is anticipated to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 15.56% during the forecast period, reflecting the sector’s strong potential and increasing adoption worldwide.
Common Types of Smart Pills
- Diagnostic Pills: These pills are used for non-invasive diagnostics, such as imaging the gastrointestinal tract or detecting early biomarkers of diseases like cancer or diabetes.
- Therapeutic Pills: These are designed to deliver medication directly to targeted areas of the body, improving treatment efficacy and minimizing side effects.
- Monitoring Pills: These pills continuously monitor vital signs or disease markers and transmit this data to healthcare providers or personal devices.
Key Technologies Behind Smart Pills
The development of smart pill technologies relies on several critical technologies, each contributing to the pill’s functionality:
Microelectronics and Sensors: Smart pills incorporate miniaturized sensors to measure parameters such as pH, temperature, or pressure within the patient’s body. These sensors collect real-time data, which is then relayed to be processed by onboard microelectronics. The smart pill sensors are tiny, measuring in the millimeter range. They are designed to function within the human body without causing any side effects.
Wireless Communication: It plays a crucial role in smart pill technologies once they are ingested. Wireless communication collects and transmits data to external devices, such as wearable devices like smartphones, smartwatches, smart glasses, or medical monitoring systems. Bluetooth and Near Field Communication (NFC) are commonly used protocols for data transmission. It enables real-time data transmission to healthcare providers, allowing for remote monitoring of a patient’s condition.
Power Systems: To address the issue of devices that can remain inside a human body for hours to days, several methods of power generation are being explored, including energy harvesting from the body’s movements, wireless charging, and miniature batteries. These systems are designed to last the entire duration of the smart pill’s use while being small enough to fit inside the pill.
Biocompatibility and Materials The materials used to construct smart pills must be biocompatible, meaning they must not cause adverse reactions within the body. Researchers are developing bioresorbable polymers and other materials that dissolve or are absorbed by the body after the pill has performed its task. This ensures that no foreign objects are left behind once the pill’s job is complete.
Artificial intelligence is being used to analyze the vast amounts of data generated by smart pills. AI algorithms can process information in real-time, providing healthcare providers with insights into a patient’s condition and enabling them to make informed decisions. These technologies could allow for early diagnosis, automatic treatment adjustments, or personalized medication regimens.
Current Applications of Smart Pills
Medical Diagnostics
Smart pills are being used for non-invasive diagnostic purposes. One of the most well-known examples is the PillCam, a capsule-sized camera that captures images of the gastrointestinal tract. This technology eliminates the need for traditional, invasive endoscopy procedures. Similarly, smart pills equipped with sensors can detect biomarkers related to diseases, such as cancer, allowing for earlier and more accurate diagnoses.
Drug Delivery and Personalized Medicine
Smart pills are also revolutionizing the way we administer medications. These pills can be designed to release drugs at specific times or locations in the body, optimizing therapeutic effects. For example, some smart pills are engineered to release medication in response to changes in pH or temperature, targeting diseases in specific organs or tissues. This approach not only improves the effectiveness of treatments but also minimizes side effects.
Monitoring Chronic Conditions
For patients with chronic conditions such as hypertension, diabetes, or cardiovascular diseases, adherence to medication schedules is crucial. Smart pills can help monitor patient adherence by sending reminders to take medication and notifying healthcare providers if doses are missed. Additionally, smart pills can continuously monitor health parameters, such as blood glucose levels or heart rate, and transmit this data in real-time to doctors or caregivers.
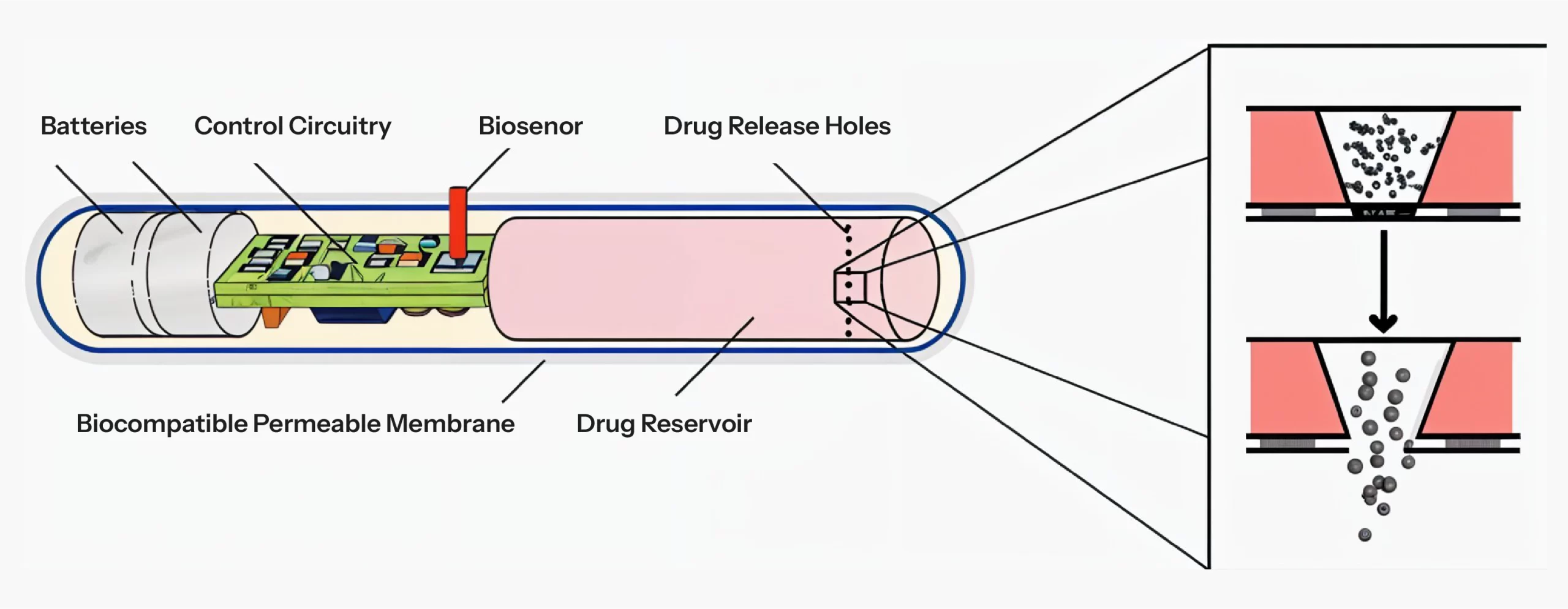
Figure 1: Smart Pill Implant from ChipRx (50) (Source)
Benefits of Smart Pills
Enhanced Precision and Personalization
Smart pills enable personalized treatment regimens, where medications are delivered to the right location at the right time, based on an individual’s unique health data. This precision not only enhances the effectiveness of treatments but also reduces the risk of adverse drug reactions.
Improved Medication Adherence
One of the main challenges in healthcare is medication adherence. Smart pills can help address this by notifying patients when it’s time to take their medicine and providing reminders through a smartphone app. Healthcare providers can also receive real-time alerts if patients miss doses, enabling timely interventions.
Non-Invasive Diagnostics
Smart pills enable non-invasive diagnostics, allowing doctors to perform tests and gather data without the need for invasive procedures. This is particularly beneficial for monitoring conditions such as gastrointestinal issues or detecting early-stage cancers.
Remote Monitoring
With continuous, real-time data transmission, healthcare providers can remotely monitor patients, making it easier to track disease progression, adjust treatments, and prevent complications. This is especially important for managing chronic conditions where regular monitoring is essential.
Challenges and Limitations
Privacy and Data Security
The use of smart pills raises significant concerns about the privacy and security of patient data. Since these pills collect sensitive health information and transmit it wirelessly, it is crucial to ensure that the data is encrypted and protected from unauthorized access.
Regulatory Approval and Clinical Trials
Obtaining regulatory approval for smart pills is a complex process. In the U.S., for example, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) must ensure that these devices are safe, effective, and reliable before they can be marketed. Furthermore, extensive clinical trials are necessary to demonstrate their efficacy in real-world medical settings.
Power and Longevity
Powering a smart pill for extended periods inside the human body is challenging. While solutions like wireless charging and energy harvesting are being explored, there are still limitations when it comes to maintaining battery life for long-duration monitoring or drug delivery.
Cost and Accessibility
The production cost of smart pills remains relatively high, which could limit their accessibility, particularly in low-income or rural areas. As the technology matures and becomes more affordable, however, it could become more widely available.
Ethical Concerns
As with any new technology, ethical concerns arise. Issues such as informed consent, data ownership, and the potential for misuse of health data need to be carefully addressed as smart pills become more common in healthcare.
Future Trends in Smart Pill Technologies
AI Integration
With the advancement in machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms, smart pills are becoming increasingly autonomous. AI can allow pills to make real-time adjustments to drug release or send alerts based on real-time health data, leading to more personalized and effective treatment.
Miniaturization and Enhanced Functionality
Future smart pills are likely to be even smaller, more efficient, and capable of performing additional functions. Researchers are exploring ways to integrate more advanced sensors, including those for detecting genetic mutations or environmental changes in the body, all within the size of a regular pill.
Bio-Printing and Smart Pill Development
3D printing could enable the development of personalized smart pills tailored to an individual’s specific health needs. Bio-printed pills could be designed with specific drug formulations and tailored to release medication based on a patient’s specific condition.
Integration with IoT Devices
Smart pills will likely be integrated into the broader Internet of Things (IoT) healthcare ecosystem. By connecting smart pills with wearable devices, healthcare providers will gain a more comprehensive view of a patient’s health, leading to improved treatment outcomes.
Global Expansion and Access
As smart pill technology becomes more affordable and scalable, it could expand to global markets, particularly in developing countries where access to healthcare is limited. Remote monitoring and diagnostics could significantly improve access to healthcare in underserved regions.
Nanotechnology (Nanochips)
Nanotechnology, especially in the form of nanochips, plays a critical role in the development of smart pills. Nanochips can be integrated into pills to enable real-time monitoring of a patient’s health, such as tracking vital signs, drug release rates, or even the pill’s journey through the digestive system. These tiny sensors can send data back to external devices, providing doctors with valuable insights into a patient’s condition.
Blockchain
Blockchain technology is being explored for smart pills to ensure the security and integrity of data. By integrating blockchain with smart pills, it’s possible to create secure, tamper-proof records of a patient’s health data, including the medication being taken, dosage, and adherence to treatment. This can also be used for managing and tracking pharmaceutical supply chains, ensuring that the correct medicine is delivered to patients, and preventing the distribution of fraudulent or counterfeit drugs.
Digital Twins
Digital twins refer to the creation of a virtual model of a real-world object or system. In the context of smart pills, digital twins can be used to create a virtual model of a patient’s body and simulate the interaction of medications within that model. This can help predict how a pill will behave in a specific patient, optimize drug delivery, and improve personalized medicine.
Virtual Simulations
Virtual simulations can be utilized in the design and testing of smart pills. By simulating how a pill interacts with the body, researchers can optimize drug release mechanisms, bioavailability, and overall efficacy before conducting real-world clinical trials. These simulations can also help understand potential side effects or challenges the pill may encounter once it is inside the human body.
Machine Learning
Machine learning algorithms can enhance the capabilities of smart pills by predicting patient responses based on data gathered from the pills. The technology can personalize medication plans, monitor adherence, and even detect early signs of diseases by analyzing patterns in the data.
Biomaterials
The development of advanced biomaterials is also critical to the evolution of smart pills. These materials, such as biocompatible polymers or hydrogels, enable pills to interact safely with the body. Some smart pills can change shape or release drugs in response to certain environmental stimuli, such as changes in pH or temperature, offering more precise drug delivery.
Microfluidics
Microfluidics technology is helping to develop tiny, lab-on-a-chip devices that can be integrated into smart pills. These devices can monitor the patient’s body chemistry, provide feedback on digestion or drug metabolism, and enable controlled drug release. They could also facilitate real-time diagnostics through the pill itself.
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
Augmented reality and virtual reality technologies can be applied in the development of smart pills for training healthcare professionals and for patient education. Using AR/VR, doctors can visualize the effects of the pill inside the human body or simulate various health conditions to see how smart pills react in different scenarios.
Gene Editing (CRISPR)
While gene editing is still in the early stages of its integration with smart pills, it holds the potential for revolutionary applications. Pills could deliver CRISPR-based therapies that target genetic disorders at the molecular level. This could open new possibilities for treating diseases that currently have no effective treatments.
Key Players in the Smart Pill Industry
Several companies are at the forefront of developing smart pill technologies:
- Proteus Digital Health: Known for its digital medicine platform, Proteus has developed ingestible sensors that track medication adherence and provide real-time health data.
- Medtronic: Medtronic focuses on ingestible sensors for monitoring and diagnosing medical conditions, as well as advancing therapeutic smart pills.
- Capsule Technology: Specializes in capsule endoscopy and digital diagnostics, offering non-invasive methods for monitoring the gastrointestinal tract.
- IBM Watson Health: Known for integrating AI into healthcare, IBM Watson Health is exploring the use of artificial intelligence to enhance the data analysis capabilities of smart pills.

Figure 2: Prominent Medtech and Healthtech Giants in Smart Pills Market (Source: DelveInsight)
Olympus Corporation
Known for its medical technologies, Olympus develops endoscopic devices and advanced imaging systems, including the EndoCapsule, a smart pill for non-invasive gastrointestinal tracking. It provides doctors with valuable insights into the digestive system.
CapsoVision created the CapsoCam Plus, a capsule endoscopy system. It’s a smart pill that captures high-resolution images of the digestive tract, particularly useful for detecting diseases like Crohn’s and colorectal cancer, offering a less invasive alternative to traditional endoscopies
The Road Ahead: Potential Impacts on Healthcare
Smart pill technologies hold the potential to transform the healthcare industry completely. By enabling more precise diagnoses, personalized treatments, and continuous monitoring, smart pills will help improve patient outcomes, reduce healthcare costs, and empower individuals to take control of their health. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see widespread adoption, ultimately revolutionizing healthcare for the better.
Conclusion
The healthcare market has found a catalyst in Smart pill technologies. They are here to redefine the medical market by providing unmatched levels of precision, personalization, techniques, and remote monitoring. While challenges such as regulatory approval, privacy concerns, and cost remain, the potential benefits make this an exciting area for development. With continued innovation, smart pills could become a cornerstone of modern medicine, enabling more effective treatments and improved patient care.
Let's Take the Conversation Forward
Reach out to Stellarix experts for tailored solutions to streamline your operations and achieve
measurable business excellence.