How Telehealth is Changing Healthcare in 2025
Telehealth is one boon that emerged from the COVID-19 pandemic, which hit the world in 2020-21 and significantly disrupted lifestyles. The modern-day healthcare delivery system has taken the world by storm, offering a patient-centric model that is data-driven and provides sophisticated care.
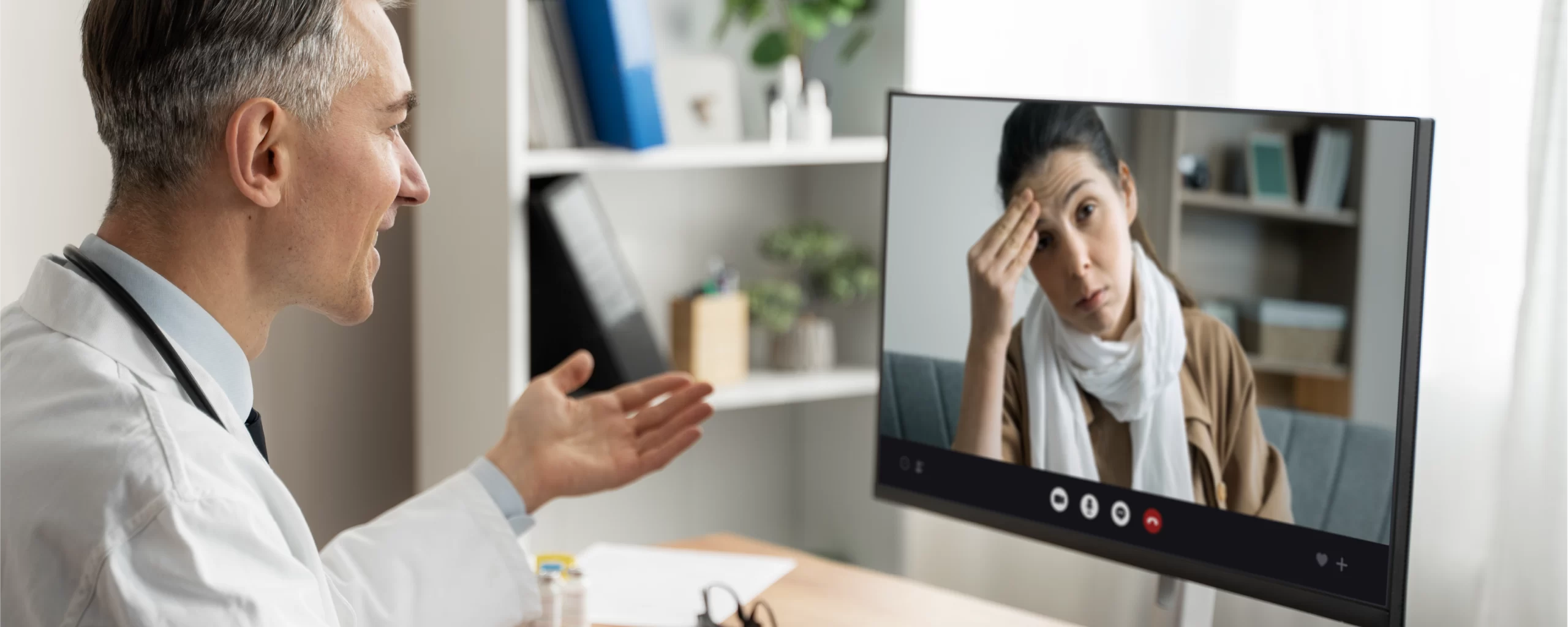
Moreover, telehealth is an integration of various platforms, creating an ecosystem that encompasses digital therapeutics, remote diagnostics, virtual consultations, and AI-powered decision-making support to assist healthcare specialists.
The adoption of telehealth has been swift, and the need for sustainable and scalable solutions and care models, technological innovation, and the requirement for accessible patient care, as well as expectations for positive change, have served as catalysts.
Key Terms of Telehealth
Telehealth underpins several key features and properties that ensure the delivery of optimal health services to patients. Here’s the following:
- Teletriage: Clinical protocols, combined with digital assessment tools, enable the remote identification of symptoms, determining the urgency and level of care required by patients. It minimizes frequent visits to the ER while prioritizing critical cases.
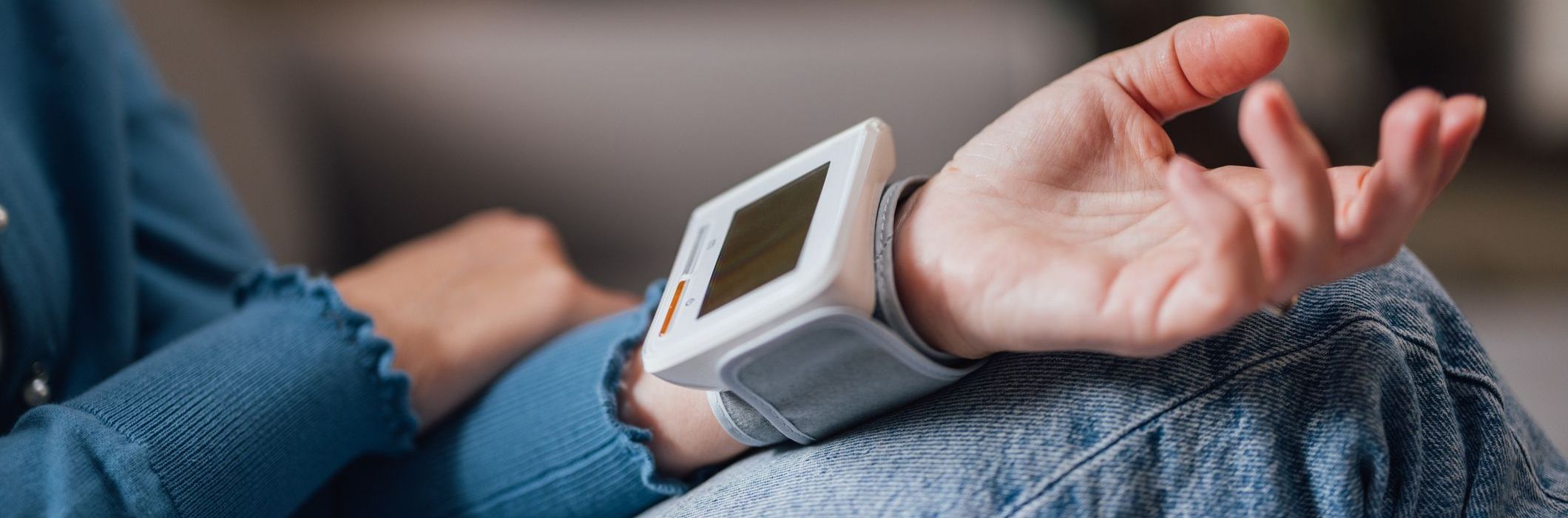
- Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM): This technology utilizes connected devices, such as glucose meters, blood pressure monitors, and pulse oximeters, to collect and transmit real-time physiological data from patients with various health issues or diseases. RPM enables the rapid detection of anomalies, proactive care delivery, and effective management of chronic diseases.
- AI-Assisted Telemedicine: The clinical effectiveness is bolstered by artificial intelligence, with chatbots assessing symptoms, aiding radiological interpretation, recommending diagnostic tests, and using data analysis to flag critically ill patients.
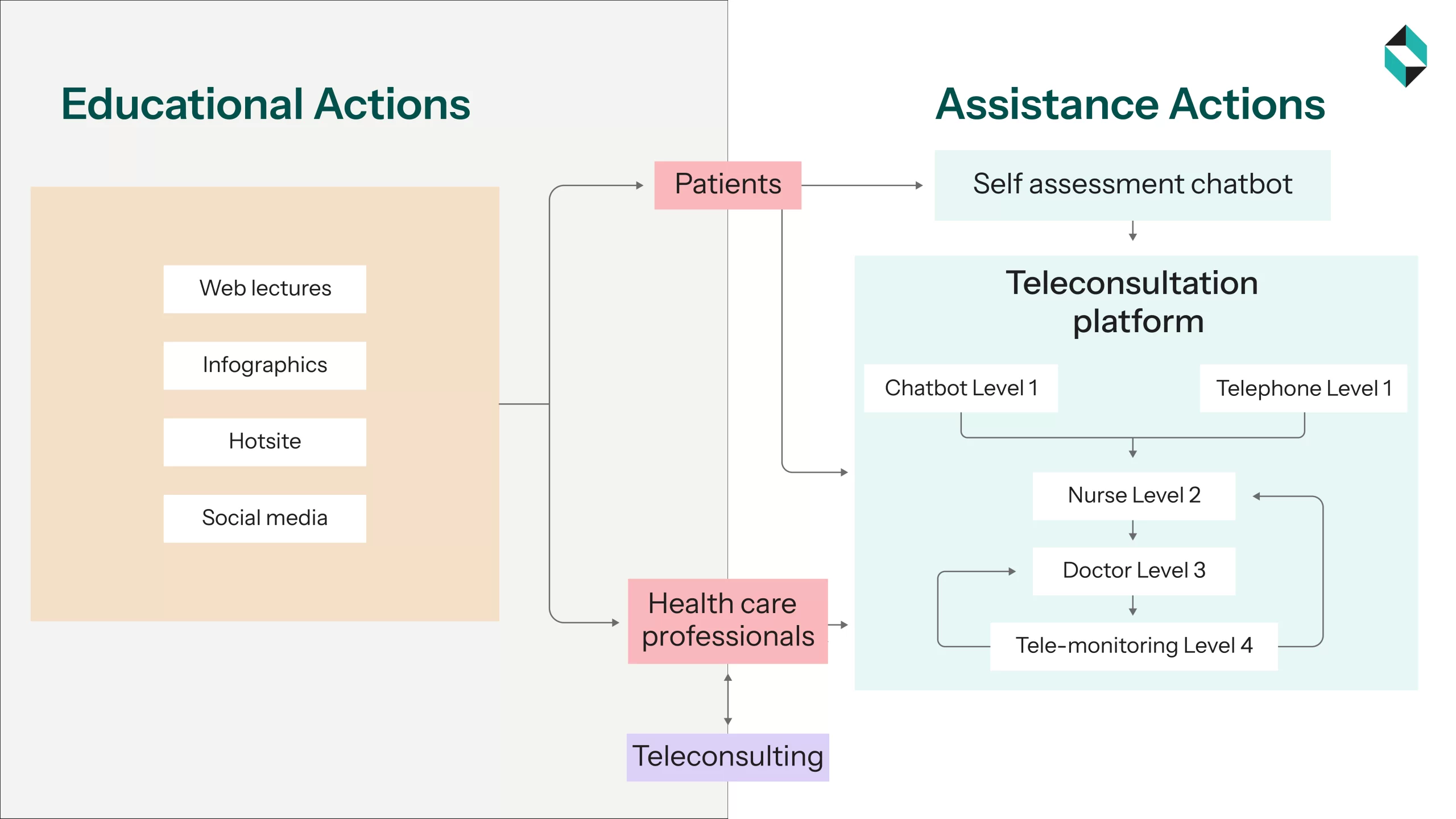
- Teleconsultation: It enables real-time communication between doctors or healthcare personnel and patients via various secure digital channels. It supports complex care coordination for regular and necessary check-ups.
- Digital Therapeutics: It provides software-based treatments that incorporate the management or prevention of chronic or critical conditions, and diseases through evidence-based procedures. They include distinct tools for ailments like musculoskeletal disorders, diabetes, and mental health. Moreover, they are typically prescribed in conjunction with traditional medications.
- Telementoring: It offers swift and smooth collaborations among clinicians for surgical mentoring, multidisciplinary case management, and rural diagnostics. The capacity gets amplified with its deployment in areas underserved or remote, allowing for global exchange of information and knowledge.
- Interoperability: This facilitates flawless exchange and integration of patients’ data across different systems, including wearables, EHRs, telehealth platforms, and health apps. It is important for patient-centered care and better coordination.
Latest Research, Discoveries, and Innovations
Hybrid Care Models
The hybrid care model is the byproduct of the pandemic. It’s a blend of virtual and in-person care. Virtual consultations for initial visits, medication adjustments, or mental health support are now the norm, complemented by face-to-face care for physical exams and procedures.
AI & Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence is deeply embedded across healthcare operations. AI tools are now used to:
- Predict ICU admissions,
- Interpret imaging scans (e.g., mammograms, chest CTs),
- Automate documentation and clinical coding,
- Support population health management.
Wearable Health Technology
Wearables have become mini-clinics on the wrist. Smartwatches and biosensors continuously track vital signs, activity levels, and sleep cycles. Advanced features, such as non-invasive glucose monitoring, blood pressure sensors, and stress indicators, empower patients to take charge of their health while enabling providers to intervene early.
Read our following blog for Wearable Healthcare Technology
Digital Twin Health Modeling
Digital twins, virtual replicas of a patient’s biological and behavioral state, allow providers to test treatment options in a risk-free simulated environment. Already in pilot use for cardiology, oncology, and orthopedics, digital twins are poised to revolutionize personalized medicine, drastically improving prediction accuracy and patient outcomes.
Personalized Medicine
By integrating genomics, lifestyle data, and real-time health metrics, providers can tailor treatments to individual patients. For instance, mental health apps now adapt therapy modules based on a user’s biometric data and mood history. Cancer treatments are being personalized based on tumor DNA sequencing coupled with wearable-derived activity data.
Sustainability and Societal Impact
Reduced Carbon Footprint
Telehealth contributes significantly to environmental sustainability by minimizing the need for patient travel and hospital energy consumption. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), widespread adoption of virtual care could lead to a 35-40% reduction in transportation-related healthcare emissions globally.
Efficient Resource Utilization
Remote care technologies reduce hospital congestion and streamline workflows. AI-assisted triage tools free up physicians for more critical care, while virtual ICUs allow for centralized monitoring of multiple hospital sites, improving clinical oversight and response times.
Improved Access and Health Equity
Telehealth eliminates geographic and economic barriers to care. It enables rural, elderly, and marginalized populations to receive timely consultations and continuous care. Programs like Project ECHO and startups like Intelehealth are actively closing the care gap in low-resource settings by equipping local workers with telemedicine toolkits.
Read our latest insight on Future of Elderly Care
Advantages
Enhanced Accessibility
Telehealth removes physical, geographic, and logistical barriers, providing flexible access to care, which is especially crucial for patients with mobility issues, full-time workers, or those living in medically underserved areas.
Early Detection & Prevention
With 24/7 data capture via wearables and RPM, clinicians can detect warning signs before they become critical, initiating preventive interventions that reduce emergency admissions and healthcare costs.
Patient Empowerment
Modern platforms come with dashboards, chatbots, trackers, and personalized feedback loops. These tools educate patients, help them monitor health metrics, and stay adherent to treatments.
Cost Efficiency
Telehealth reduces:
- Travel expenses,
- Missed workdays,
- Inappropriate ER usage,
- Redundant diagnostics.
Payers and providers are seeing ROI through reduced readmissions and optimized resource utilization.
Challenges
Cybersecurity
With the increasing number of digital touchpoints, data breaches are on the rise. Sensitive patient data is a high-value target. Solutions include end-to-end encryption, blockchain EHRs, and multi-factor authentication for both providers and patients.
Interoperability
Fragmented systems hinder seamless care delivery. Despite global efforts toward FHIR standards, many providers continue to struggle with integrating legacy systems, third-party applications, and cloud infrastructure.
Regulatory Landscape
Laws around telemedicine licensing, data storage, AI use, and cross-border care differ by country and state. Providers must navigate a rapidly evolving regulatory maze.
Digital Divide
A large portion of the global population still lacks access to stable internet, smart devices, or digital literacy. Bridging this divide is essential to ensure telehealth doesn’t deepen existing inequities.
Provider Training
Healthcare professionals require ongoing upskilling in digital tools, virtual communication, cybersecurity, and the interpretation of AI. Many institutions are integrating telehealth modules into medical curricula.
Leading Companies and Startups
Established Leaders
- Teladoc Health: Full-spectrum care, from primary to chronic disease management
- Amwell: Platform provider for hospitals and payers
- Doctor on Demand, MDLive: Broad reach, especially in behavioral health
Innovative Startups
- Intelehealth: Offline-first, mobile-optimized platform for underserved areas
- TytoCare: Home-based diagnostics that mimic clinic visits
- Huma, Kaia Health: Specializing in remote monitoring and digital rehab
Tech Collaborators
- Apple, Fitbit, Samsung: Driving innovation in consumer health tech
- Google Health, Microsoft Cloud for Healthcare: Providing AI, data infrastructure, and analytics
- Qure.ai, Butterfly Network: Leading in AI diagnostics and portable imaging
Specialty Areas and Use Cases
Telehealth is no longer limited to general consultations. It now permeates specialized care:
- Telepsychiatry: CBT, talk therapy, and medication management through secure platforms
- Teledermatology: Image uploads with AI-supported analysis for skin conditions
- Teleradiology: Remote reads for X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans with near-real-time feedback
- Telecardiology: Virtual consults, ECG uploads, and chronic cardiac monitoring
- Teleoncology: Second opinions, chemotherapy side-effect monitoring, survivorship care
- Telepediatrics & Telegeriatrics: Pediatric screenings and elderly care with caregiver integration
- Telepharmacy: E-prescriptions, remote medication adherence tracking
- Tele-ICU: Centralized, AI-supported ICU command centers monitoring multiple hospitals
Disease Applications:
- Chronic care: Diabetes, heart failure, COPD
- Acute care: Post-surgical follow-ups, COVID-19 management
- Preventive care: Wellness programs, lifestyle coaching
Future Outlook
The next decade will witness a profound shift from reactive to proactive care, powered by:
- AI-first triage and diagnostics
- Precision medicine based on real-time data and digital twins
- Interoperable platforms with embedded DTx
- Remote surgeries guided by AR/VR and robotic tools
- Policy frameworks that standardize cross-border telehealth
Telehealth will not just complement healthcare; it will redefine its delivery architecture, emphasizing value-based outcomes, environmental sustainability, and population health management.
Conclusion
Telehealth is emerging as the new standard in the healthcare industry, and 2025 has welcomed it by converging these advanced technologies to meet patients’ requirements, adhere to policies, and navigate the path for the healthcare system. Here are the following functions :
- Accessibility across income groups and regions
- Human-centred approach with data-driven technique
- Environmental and economically sustainable
- Proactive in promoting wellness and preventing ailments
However, the innovation needs to be dealt with responsibly, ensuring ethical AI implementation, equity, interoperability, and privacy remain intact and critical while adapting to telehealth, which can be the essential element in the healthcare industry.
Stellarix can help healthcare leaders and innovators reach the top of the chart with customized strategies tailored to their specific needs. Moreover, we can assist businesses relying on telehealth in scaling and embracing their full potential on a global scale.
Let's Take the Conversation Forward
Reach out to Stellarix experts for tailored solutions to streamline your operations and achieve
measurable business excellence.