Future of Collaborative Robots- Intuitive & Intelligent
Collaboration between humans, robots, and industries is getting mainstream. From the first robotic arm, Unimate of 1961, to the present-day UR30 from Universal Robotics, there has been a profound technological shift in robotics. Unlike robots, collaborative robots are lightweight, possess advanced sensors, are capable of using a hand-guided approach, and are embedded with AI and intelligent end effectors. Today, cobots have found workability in almost all industries. This blog will elucidate how the future of cobots is bright, given the rapid need for automation and increased manufacturing.
Surging Demand for Collaborative Robots
With over 3.4 million operating robots, some 517,000 new industrial robots were set up in 2021 alone. Out of them, 39,000 / 7.5% were cobots. Mobile cobot demand is high, and its market is expected to reach $7 billion by 2030. Material handling tasks, such as assembling, picking and placing, testing, welding, sorting, and positioning, had the biggest implementation among other cobot applications.
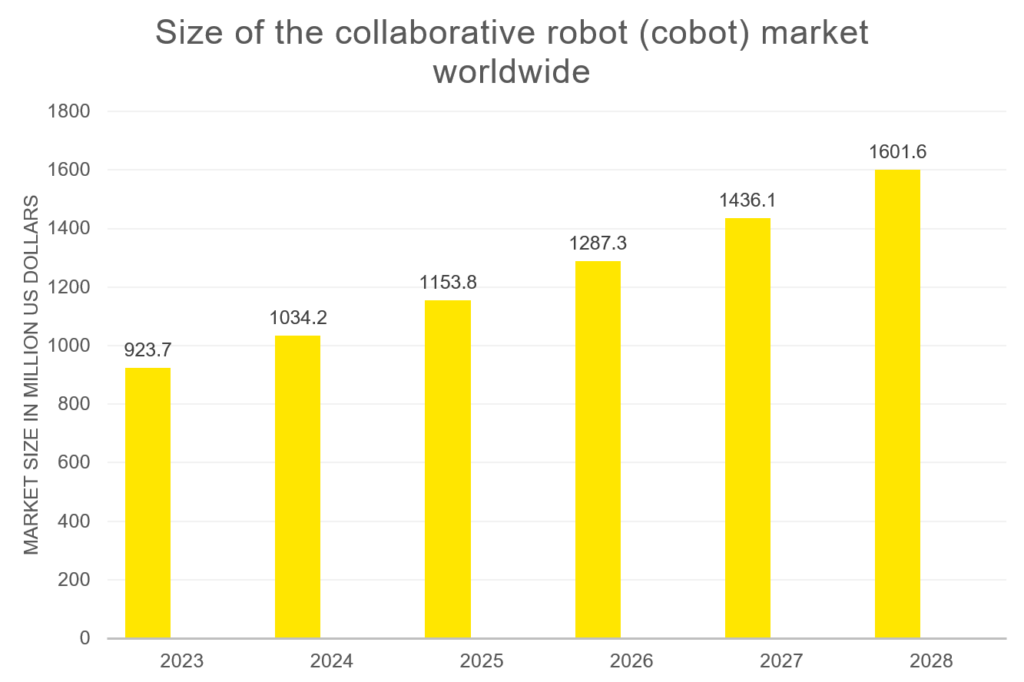
Source: Collaborative Robot Size Globally
Industry Guidelines for Collaborative Robots
Whether service robots, vision-guided robots, or new-age industrial mobile robots (IMRs), requisite cobot parameters must be well-applied. Moreover, cobots need precise force control/payload, rounded edges, advanced sensors to detect human skin/touch detection for collision prevention, force/speed limitations, and internal sensors for force detection.
Many manufacturers use the industry cobot controls to ensure human safety and keep accidents at bay. Cobots are developed for precise and unique automation tasks. Hence, the working and software of the cobot type differ; however, the core/minimum safety measures are integral for every commercial and personal cobot.
Types of Collaborative Robots
Cobots are quick to set up and reprogram and can be used to perform complex tasks. For classification’s sake, cobots can be distinguished by how they work in collaboration with humans. Cobots are employed with Power and Force Limiting (PFL) and Speed and Separation monitoring (SSM), joint sensing, skin sensing, hand-guided controls (HGC), and Safety-rated Monitored Stop (SMS). As cobot is an emerging field, a preliminary classification can also be based on usage: a) industrial and b) service.
Top Companies in the Cobot Space
Leading cobot companies include names like Universal Robots, FANUC, ABB, KUKA, Doosan Robotics, Neura Robotics, and Mitsubishi. Universal Robots had a Q3 (2023) revenue of $ 71m. Fanuc Corporation had a net income of 63,937¥ for April 1, 2023, to September 30, 2023. ABB Robotics Q3 revenue was $7,968 million, with an 8% growth from Q3 2022.
KUKA, the Germany-based robot/cobot-making company, saw revenues of €3.9 billion (2022), a 19% increase compared to the previous year. Mitsubishi Electric’s revenue reached 5,003.6¥ billion for the financial year April 2022-March 2023, a 12% increase year-on-year. Rethink Robotics, Locus Robotics, Yaskawa Motoman, Techman Robot, Omron, and AUBO Robotics are other key collaborative robot manufacturing companies. They have developed modern cobot solutions with varying payload capacities, advanced vision and flow sensors, compact design, and pre-integrated cobots.
Cobots Use in Various Industries
Cobots are used in many industries, such as manufacturing, healthcare, retail, food& beverage, agriculture, electronics, metal, mining, construction, plastic/polymer, chemical, and almost any other industry. Collaborative automation has great advantages like streamlining production, increased quality, and improved human/machine undertakings. On average, Cobots cost between 20,000/55,000 USD anyway, making them affordable for SMEs and large manufacturers. Unlike robots that are heavy, high-priced, single-task-oriented, and programmable only by experts, collaborative robots are sleek and smart. They occupy less space, are easy to move, and can be programmed for multiple tasks via mobiles/tablets/via guided hand movement. The greatest draw of working with cobots is that they are safe and instinctive robots.
Latest Research in Collaborative Robots Technology
Regular cobot implementation includes use in assembling and handling work. The latest cobots are being used in X-ray inspection/security, 3D vision-enabled surgeries, cobot prosthetic applications, and supernumerary robotics/soft robotic limbs (SRLs). Surgeons have been using collaborative robots with 3D sensors, helping them perform complicated surgeries easily. Amputees are using cobot prosthetics, thus allowing them an opportunity to interact with their surroundings/people in ways not previously possible. SRLs are being used in different use cases to help users free up their limb usage and add more dexterity to their current activities. Additionally, they can be attached to the user’s back, arms, legs, fingers, and head and embedded with physical sensors, bioelectric signals, control strategies, wireless Electromyography (EMG) signals, and other control mechanisms.
Standards and Regulations for Collaborative Robots
The risks of working with collaborative cobots are low, as they have built-in measures to work in close proximity to humans. A thorough Cobot Risk Assessment (RA) needs to be done for integration, setup, operation/function, and maintenance works. Many accidents often take place while performing maintenance. The various international standards for collaborative robot safety include ISO 10218-1, ISO/TS 15066, ANSI R15.08-1-2020, ANSI/RIA R15.606, and ANSI B155.1-2016. One can also refer to industrial robot safety and hazard measure standards (country-wise) like ISO 10218-1 and -2 and the Occupational Safety and Health Administration’s (OSHA’s) manual. Hybrid interaction modes, AI/ML, and advanced sensors are helping users and cobots work safely simultaneously.
Conclusion
One of the key next-frontier technologies is cobots, which are surely revolutionizing manufacturing. The efficient production process is a staple for any vibrant economy or business, and this is where Cobots offer excellent value addition. Moreover, business owners need to be smart about how they will incorporate cobots into their work processes.
There are still questions on how safe cobots will be, especially with Artificial Intelligence, and if they can think for themselves. Despite all the RA, other thoughts remain about the possibility of accidents in the near and far future, and if the cobots can truly replace human workers. The catch is that cobots can never replace humans. However, they act as assistants to support high-quality automated tasks and reduce human workload.
Let's Take the Conversation Forward
Reach out to Stellarix experts for tailored solutions to streamline your operations and achieve
measurable business excellence.