Energy Security in 2025: Balancing Sustainability with Economic Stability
The energy security phenomenon is the requirement of the hour, with its consistent availability across the globe and affordability. It has risen as a cornerstone of global stability in 2025. As nations take on climate change, geopolitical volatility, global population increase, and rapid technological advancements balancing sustainability goals with economic resilience has become a grave challenge that needs to be addressed for the growth of the world.
Current State of Energy Security
Global Energy Landscape
The rising demand and urgent requirement for sustainable practices are pushing a significant transformation in the global energy landscape. Interestingly, as per projections, the global energy demand can grow by approximately 7 percent, driven by a hike in energy consumption post-pandemic in several nations in 2025. Key players shaping the future of energy security include:
- China: With its ambitious Energy Law set to mandate that renewables supply 40% of its energy by 2030, China is leading the charge in transitioning to cleaner sources. The country is investing heavily in solar and wind technologies, positioning itself as a dominant force in the renewable sector.
- United States: The U.S. has become a leader in liquefied natural gas (LNG) exports, leveraging its vast shale reserves to stabilize global markets. This shift enhances domestic energy security and positions the U.S. as a critical player in global energy supply chains.
- European Union: The EU’s REPowerEU plan aims to reduce dependency on Russian gas by 66% through the expansion of renewable energy sources and investments in hydrogen technologies. This strategy underscores the importance of diversifying energy sources to enhance security.
Recent Developments
Recent geopolitical events have had profound impacts on energy security:
- Technological Innovations: Advances in technology are reshaping the energy sector. For instance, artificial intelligence (AI) is used for predictive maintenance in power plants, while innovations in renewable technologies, such as perovskite solar cells, improve efficiency and reduce costs.
- The European Union has undertaken a significant shift in its energy strategy to offset its reliance on Russian gas.
The Role of Renewable Energy
1. Transition to Renewables
The transition to renewable energy is no longer a choice but a necessity for achieving long-term energy security:
- Solar and Wind Energy: The costs of solar and wind technologies have plummeted over the past decade, with solar panel prices dropping by 89% and wind turbine costs decreasing by 70% since 2010. By 2025, solar farms in sun-rich regions like Morocco are expected to produce electricity at an astonishingly low cost of $0.015 per kilowatt-hour (kWh), making renewables increasingly competitive against fossil fuels.
- Small Modular Nuclear Reactors: These are also called micro reactors, which have a huge potential in catering to the energy demands of future generations while offering low-carbon power. They have the potential to improve grid stability by engaging with energy sources such as solar and wind.
- Hydrogen Economy: Green hydrogen production—generated using renewable energy—is rapidly scaling up globally. Projects like Australia’s $50 billion Asian Renewable Energy Hub aim to supply green hydrogen to Japan and South Korea, demonstrating the potential for hydrogen to play a pivotal role in future energy systems.
- Case Study- Germany’s Energiewende: Germany’s ambitious Energiewende initiative has successfully reduced coal consumption by 45% since 2022 through investments in offshore wind farms and biogas plants. This transition highlights how policy frameworks can effectively drive the shift towards renewables while enhancing energy security.
2. Economic Implications
The economic benefits of transitioning to renewable energy are substantial:
- Job Creation: The renewable sector now employs approximately 38 million people globally, significantly outpacing job growth in fossil fuel industries. As countries invest more in clean technologies, job opportunities continue to expand across various sectors, including manufacturing, installation, and maintenance.
- Price Stability: Countries that diversify their energy portfolios with renewables experience fewer price shocks compared to those reliant on fossil fuels. For example, Denmark’s investment in wind power has led to greater price stability and reduced reliance on imported fossil fuels.
Balancing Sustainability Goals
The Energy Trilemma
The concept of the “energy trilemma” highlights the need to balance three critical pillars:
- Sustainability: Achieving net-zero emissions by mid-century requires significant investment in renewable technologies and infrastructure upgrades. Reports indicate that trillions of dollars will be needed globally. For example, some analyses point to the fact that to reach net-zero emissions by 2050, annual investments into clean energy technologies need to reach amounts of nearly 5.7 trillion USD per year by 2030.
- Affordability: Ensuring that all populations have access to affordable energy is essential for social equity and economic development.
- Security: Maintaining a reliable supply chain is crucial for preventing disruptions that can lead to economic instability.
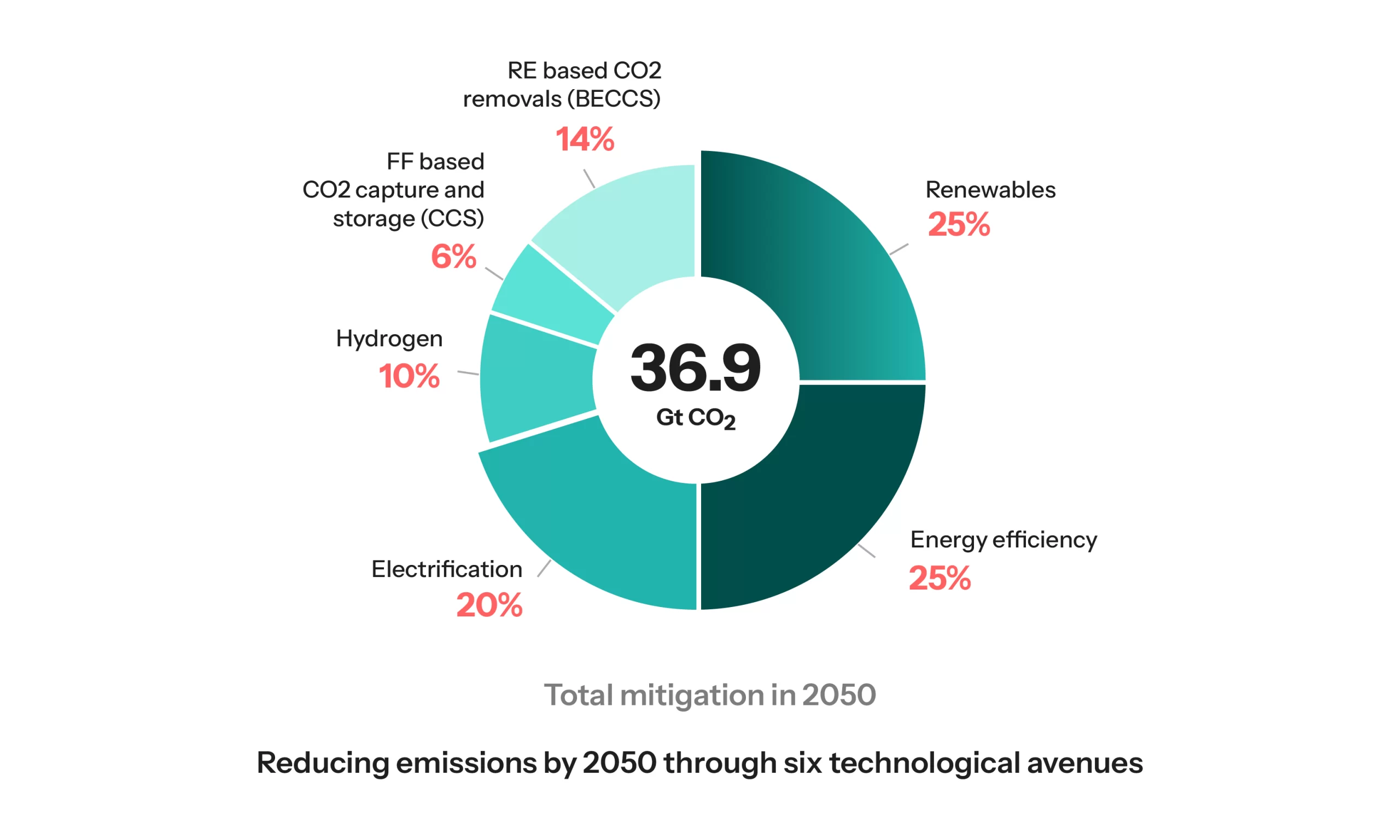
Example: India’s hybrid policy combines subsidies for rooftop solar installations with coal reserves to prevent blackouts while transitioning towards cleaner sources.
Policy Frameworks
Effective policy frameworks are vital for promoting sustainability while ensuring energy security:
- Global Agreements: The Paris Agreement’s “Global Stocktake” process reveals a significant emissions gap that must be addressed urgently through accelerated decarbonization efforts by all nations.
Economic Stability Considerations
Impact of Energy Prices
Energy prices have far-reaching implications for economic stability:
- 2022 Gas Crisis: European gas prices surged to €340 per megawatt-hour (MWh) during the crisis triggered by geopolitical tensions, leading many energy-intensive industries into recession due to skyrocketing operational costs.
- 2025 Outlook: While oil prices are projected to hover around $85 per barrel, falling costs associated with renewables provide a buffer against volatility and help stabilize economies reliant on imported fossil fuels.
Investment Trends
Investment trends indicate a clear shift towards clean energy:
Clean Energy Investments: Global investments will reach approximately $1.7 trillion in renewable technologies by 2025, with solar and wind capturing around 65% of total funding as investors increasingly recognize their potential for long-term returns.
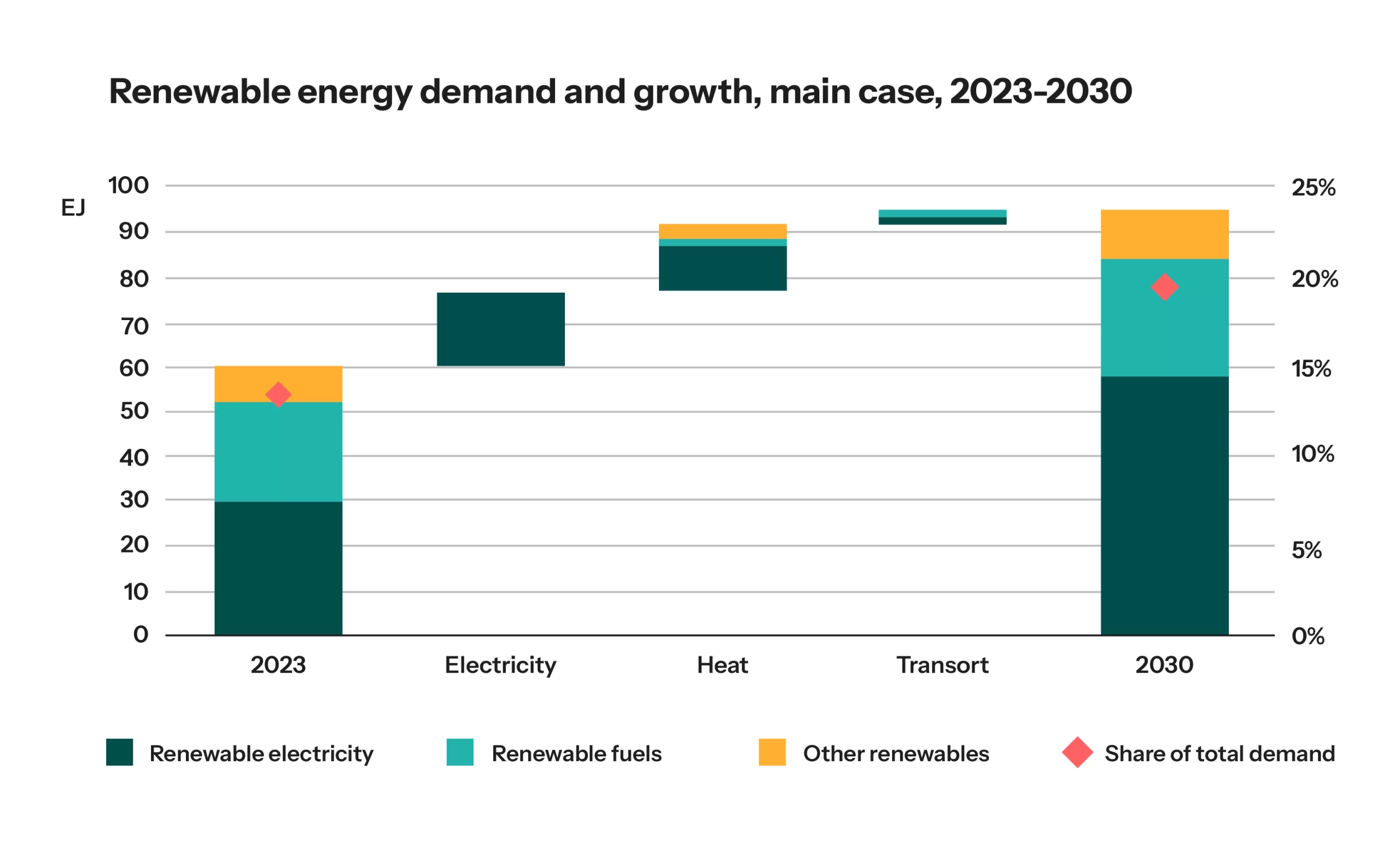
Addressing Emerging Threats
Cybersecurity Risks
The increasing digitization of energy infrastructure introduces new vulnerabilities:
- Threat Landscape: Ransomware attacks on critical infrastructure have become more common; for example, a ransomware attack on Brazil’s power operator costs an estimated $2.5 million per hour due to downtime.
- Mitigation Strategies: Implementing AI-powered anomaly detection systems can help identify potential threats before they escalate into crises. Additionally, blockchain technology can enhance grid decentralization and improve transparency within supply chains.
Climate Change Impacts
Climate change poses significant risks to existing energy infrastructures:
- Infrastructure Vulnerabilities: Extreme weather events—such as hurricanes or floods—can disrupt offshore wind farms or damage power lines, leading to supply interruptions.
- Adaptation Strategies: Countries like the Netherlands are investing in “Energy Islands,” which combine offshore wind farms with flood-resistant infrastructure designs that can withstand rising sea levels while generating clean power.
Future Outlook for Energy Security
Technological Innovations
Technological advancements will play a pivotal role in enhancing energy security:
- AI and Smart Grids: AI-driven predictive analytics optimize energy distribution across grids, reducing waste by up to 25%. Smart grids facilitate real-time data sharing between producers and consumers, enhancing overall efficiency.
- Battery Storage Solutions: Innovations such as solid-state batteries, with densities reaching up to 500 watt-hours per kilogram (Wh/kg), enable reliable storage solutions that support continuous access to renewable power even during periods of low generation.
Conclusion
In 2025, achieving robust energy security hinges on harmonizing sustainability with economic pragmatism. Nations must invest strategically in renewable resources while fortifying infrastructure against cyber threats and climate impacts. By prioritizing innovation, diversifying supply chains, and ensuring equitable access across populations, we can work towards a more secure future where both environmental sustainability and economic stability thrive hand-in-hand.
As emphasized by the World Energy Council, “The cost of inaction far outweighs the cost of transition.” It is imperative that we act decisively today to secure our collective future tomorrow.
Let's Take the Conversation Forward
Reach out to Stellarix experts for tailored solutions to streamline your operations and achieve
measurable business excellence.



