Present and Future of Wi-Fi Technology
Wi-Fi technology has evolved greatly since its introduction and has become the most prevalent wireless communication technology. From its origination, the Wi-Fi standards have continuously advanced with the introduction of new protocols such as 802.11n, 802.11ac (Wi-Fi 5), 802.11ax (Wi-Fi 6), and 802.11be (Wi-Fi 7).
The Wi-Fi 6 was rolled out in the year 2020 with magnificent features such as Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA), Multi-User Multiple Input Multiple Output (MU-MIMO), trigger-based random access, spatial frequency reuse, and many more that make it more advanced and better than its previous Wi-Fi standards. The upcoming Wi-Fi standard Wi-Fi 7 is planned to launch in the year 2024.
The new Wi-Fi standards provide flexibility in combining them with 5G technology for easy user communication. The features of 5G resource development using unlicensed spectrum and the OFDMA technology to deal with unlicensed technology allow the integration of 5G services and Wi-Fi technology with the Wi-Fi 6 and future versions. The upcoming IEEE Wi-Fi 7 contains features such as multiple access point coordination and multi-link operation. These features can support communication technology at a much greater level.
Evolution of Wi-Fi Technology
The First Wi-Fi standard was released in 1997 for consumers; with the advancement in technology standards, Wi-Fi technology continues an impressive evolution launched over 25 years ago. Research institutions are working on upgrading the new standards with increased bandwidth, low latency, and more connected devices. They are also focusing on achieving high-cost efficiency and incorporating many other features. The figure below shows the timeline for the evolution of Wi-Fi technology standards.
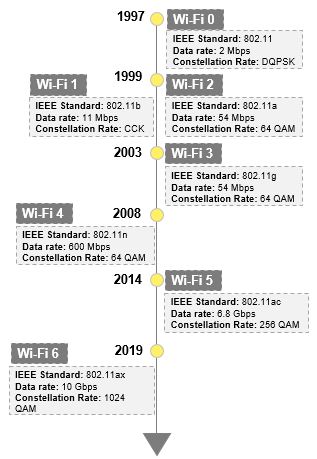
Figure 1: Evolution of Wi-Fi standards with advancement in the years
Wi-Fi 6 & 5G Technology Convergence
Earlier, Wi-Fi technology was used as a local area network primarily for indoor networks such as home, workplace, enterprise, etc., and cellular technologies were used as a wide area network primarily for long-distance networks. With the advancement in Wi-Fi and cellular technologies, converging both technologies to achieve higher speeds, lower latency, and increased capacity is possible.
The 5G and Wi-Fi 6 complement each other with common features like frequency spectrum, OFDMA, MU-MIMO, authentication protocols, target-wake-up-time, etc. This similarity allows seamless Wi-Fi and 5G integration into a common system to deliver a converged set of services for specific use cases, such as voice calling IoT networks and others. For example, initially, Wi-Fi technology had no role in voice calling. However, with advanced cellular technologies like 4G and 5G, it became possible to share resources and seamlessly integrate the networks for voice calling without any loss in quality.
Additional Information About Wi-Fi 6 & 5G Technology Convergence
5G technology is developed while considering its integration with Wi-Fi technology. Operators can provide 5G services using unlicensed spectrum while using Wi-Fi technology as a radio access network (RAN). Orthogonal frequency division multiple access (OFDMA) enables Wi-Fi technology to benefit from scheduled uplink transmissions, which is particularly useful in a heavily congested environment.
The 5G Core Network definition of access-neutral functionality, combined with a common EAP authentication framework, is similar to that of Wi-Fi technology. This similarity allows seamless integration of Wi-Fi and cellular into a common system that can deliver a converged set of services over Wi-Fi and Cellular-based access networks.
With the several advantages of the convergence of 5G and Wi-Fi technology, it will also provide an opportunity to reduce the processing burden on the cellular network. The 5G technology allows the handset to connect for Wi-Fi calling using a null (unencrypted) IPsec tunnel to reduce the burden due to encryption/decryption of the data traffic on the cellular network. With the integration of Wi-Fi and 5G technology, these capabilities will create a great opportunity for providing higher data rates. It will keep the latency low and reduce power consumption due to the burden on the network for processing.
Future of Wi-Fi Technology (Wi-Fi 7)
With the advancement in technology, a high data rate and low latency will always be in demand. Therefore, experts expect the upcoming Wi-Fi versions to deliver higher data rates alongside low latency in transmission.
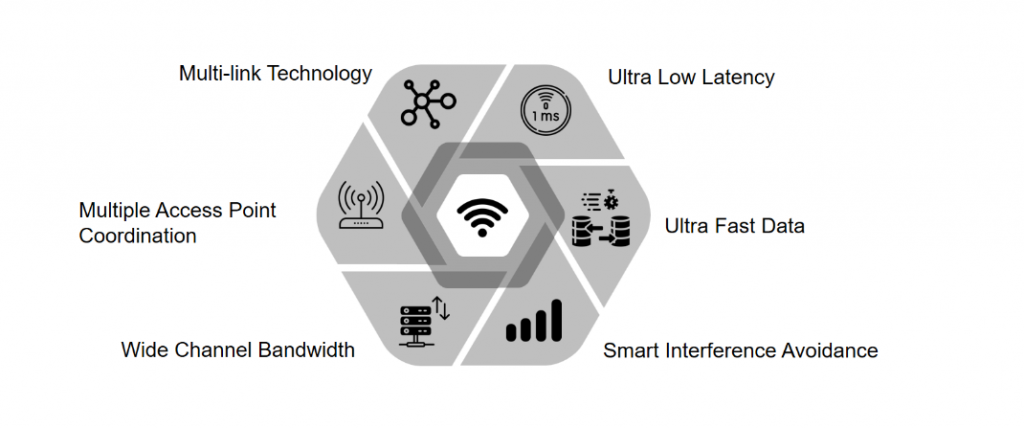
Figure 2: Proposed Feature of Wi-Fi 7
The new Wi-Fi 7 has the new proposed following features that seem to be promising and meet the demands of the future:
Multi-link technology
Wi-Fi 7 offers three channels: 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and 6 GHz. It also provides the multichannel option to utilize data rates efficiently. Multiple links can be switched to achieve maximum throughput.
Multiple Access Point Coordination
Wi-Fi 7 provides coordination between multiple access points. When the device connects to an access point, it relays information to other access points. This helps reduce transmission power for interference reduction. The modulation scheme used in Wi-Fi 7 is 4096 QAM, which allows it to serve multiple users simultaneously.
Wide Channel Bandwidth
Wi-Fi 7 offers a 320 MHz channel bandwidth for transferring data, while Wi-Fi 6 offers a channel bandwidth of 160 MHz
Ultra Low Latency
In Wi-Fi 7, multiple links can be accessed in parallel. Due to this ability, the new Wi-Fi technology offers very low latency compared to its previous versions. The Wi-Fi 7 offers a latency of less than 5 milliseconds.
Ultra-Fast Data Rate
The Wi-Fi 7 technology offers 16×16 MIMU technology. It also provides 4096 QAM modulation schemes and a higher spectrum to achieve a high data rate. The upcoming Wi-Fi 7 technology is expected to provide a data rate of up to 46.1 Gbps.
Smart Interference Avoidance
In Wi-Fi 7, utilizing a smart solution called Preamble Puncturing prevents spectrum interference. Preamble Puncturing allows avoiding the portion of the spectrum and allocates contiguous channels within that spectrum.
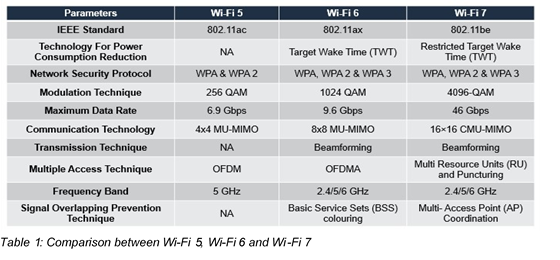
Difference Between Wi-Fi 7, Wi-Fi 6, And Wi-Fi 5
Wi-Fi standards are constantly updated with time, and keeping up with the updated standards can be challenging. With each release, developers modify the Wi-Fi standards, enhancing their specifications and increasing usability. Wi-Fi 5 (802.11ac) was a leading standard for several years, but it was dethroned with the release of Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax). The release of Wi-Fi 7 (802.11be) is also on its way.
Recent Development
Many measures and developments have been made to advance Wi-Fi technology in recent years. Some of them are mentioned below:
- Wireless Broadband Alliance (WBA) and Next Generation Mobile Networks (NGMN) collaborated
In September 2019, WBA and NGMN created a RAN Convergence White Paper to address the limitations of streamlined integration between Wi-Fi and cellular access with the cellular operator core.
- Wi-Fi Alliance advocates for a common QoS approach across wired, Wi-Fi, and 5G networks
Meanwhile, in September 2022, Wi-Fi Alliance released a paper advocating for adopting a consistent quality of service approach across Wi-Fi and 5G networks based on Wi-Fi CERTIFIED QoS Management and Wi-Fi CERTIFIED Multimedia (WMM®) programs.
- MediaTek announced its flagship processor with Wi-Fi 7
In January 2022, MediaTek announced its new flagship processor, Dimensity 9200, with Wi-Fi 7 support. The new processor has a performance boost and is more efficient than its predecessor.
- Virgin Media announced its first Wi-Fi 6 broadband router
In October 2021, Virgin Media announced its first Wi-Fi 6 broadband router, which provides supported devices with a connection having a data rate of 2.5Gbps and enables multi-gigabit rates.
- Skyworks developed a partnership with Broadcom to provide advancements in next-generation Wi-Fi devices
Also, in December 2022, Skyworks developed a partnership with Broadcom to deliver unprecedented power efficiency for next-generation Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 6E devices.
- Intel Corporation collaborated with its newly acquired Rivet Networks for the development of Wi-Fi technologies
Moreover, in May 2020, Intel Corporation collaborated with its newly acquired Rivet Networks to develop the Killer AX1650 Wi-Fi solution, which offers Wi-Fi 6 technology and provides immersive entertainment and gaming experiences.
Conclusion
Wi-Fi technology has evolved according to the demands for increased data rates and very low transmission latency. Several technologies in common, between 5G technologies and Wi-Fi 6, show the possibilities of integrating these technologies. Recent Wi-Fi standards have seen numerous advancements. Ongoing research and work are shaping future technologies. Several alliances have been formed to integrate Wi-Fi technology with 5G technologies.
In addition, the companies are also focusing on exploring new features of Wi-Fi 7, such as Multiple Access Point Coordination, multi-link operation (MLO), etc., and constantly working to bring these capabilities into existence. Upcoming technologies focus on blending cellular networks and Wi-Fi seamlessly. Advanced Wi-Fi is expected with high data rates, low latency, and simple integration. These Wi-Fi advancements enable easy deployment and integration into upcoming mobile tech. The integration emphasis leads to improved Wi-Fi: high data rates, low latency, and smooth mobile integration.
Let's Take the Conversation Forward
Reach out to Stellarix experts for tailored solutions to streamline your operations and achieve
measurable business excellence.



