Nrf2, Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2-related Factor, Activators
Currently, the market is shifting toward developing skincare products focused on oxidative stress, yet it is also saturated with antioxidant claims.
Here, Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2-related Factor 2 (Nrf2) activation serves as an upstream, fundamental mechanism for cytoprotection. Nrf2, encoded by the gene NFE2L2, serves as a central transcriptional regulator of cellular defense mechanisms against oxidative stress.
Nrf2 exerts its protective function by binding to antioxidant response elements (AREs) in the promoters of target genes, thereby inducing the transcription of a broad array of cytoprotective enzymes and proteins involved in detoxification, redox homeostasis, and oxidative stress mitigation.
Nrf2 shifts from merely managing symptoms to actively altering fundamental cellular defense mechanisms.
However, several challenges exist in harnessing Nrf2’s market potential: high cost, steep learning curve, uncertainties of the market landscape, and R&D complexities.
The main question is how companies can turn Nrf2 activation into a profitable product, given high R&D costs and other significant barriers.
In this regard, the article explores Nrf2 activators, their mechanisms of action, key innovations, and the technical barriers that hinder commercialization among CPG players.
How Nrf2 Works?
It is important to distinguish Nrf2 from Nuclear Respiratory Factor 2 (NRF-2), also referred to as GA-binding protein alpha (GABPA), which mainly plays a role in regulating mitochondrial biogenesis and cellular energy metabolism through its interaction with peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha (PGC1α).
Under normal conditions, Nrf2 remains in an inactive state through its cytoplasmic association with Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (Keap1), which facilitates its degradation. Upon exposure to oxidative stress, this interaction is disrupted, allowing Nrf2 to escape degradation, accumulate in the cytoplasm, and translocate into the nucleus.
Once in the nucleus, Nrf2 binds to antioxidant response elements (ARE) within the promoter regions of target genes, thereby initiating the transcription of a broad array of cytoprotective and detoxification genes. The molecular mechanism underlying this regulatory cascade is illustrated in Figure 1.
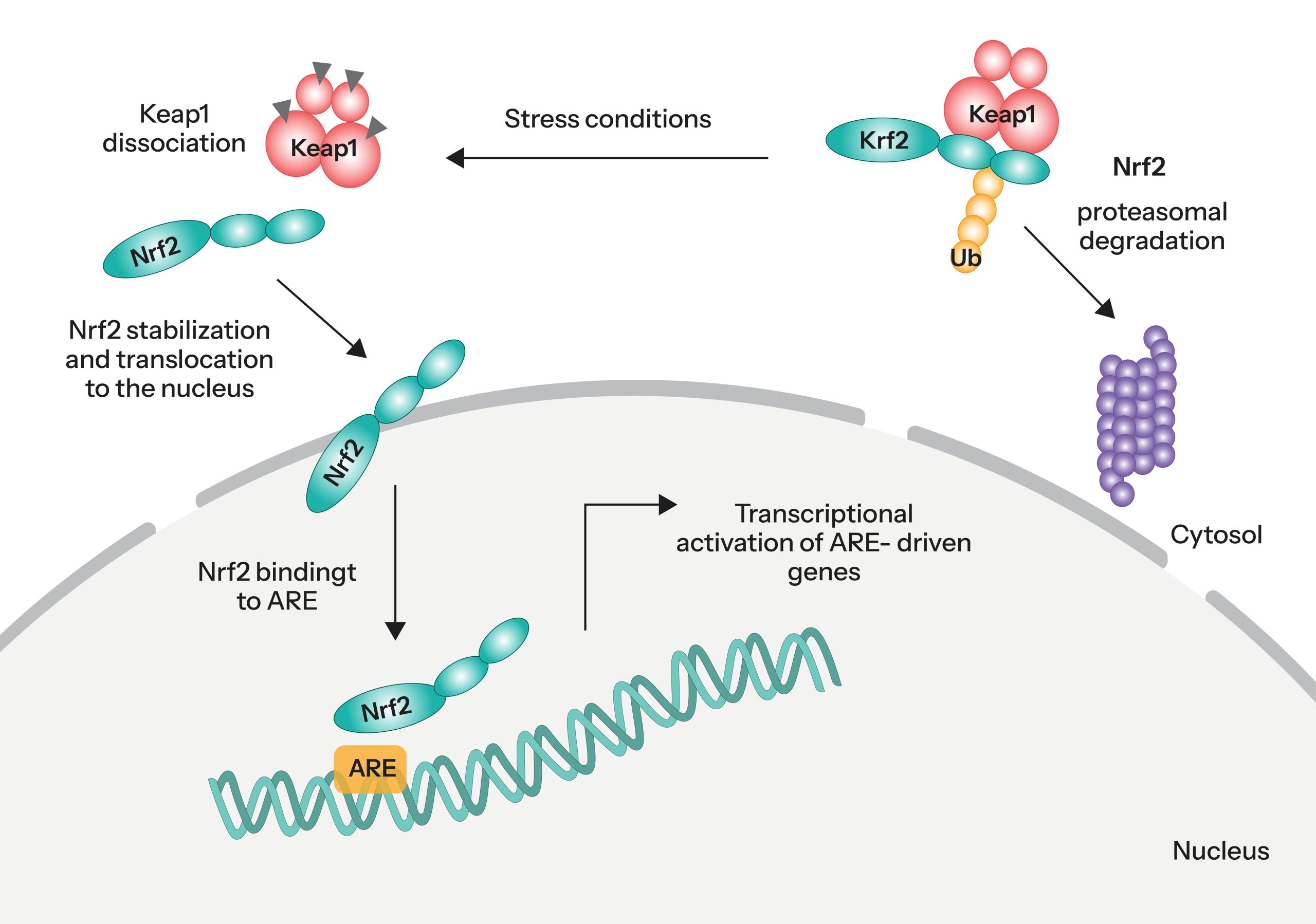
A diverse array of compounds activates the Nrf2 signaling pathway through distinct mechanisms. Electrophilic agents such as curcumin and sulforaphane activate Nrf2 by covalently modifying cysteine residues on KEAP1, thereby disrupting its ability to target NRF2 for proteasomal degradation.
Additionally, peptide mimetics like LDEETGEFL-NH₂ and small molecules such as benzenesulfonyl-pyrimidone inhibit the Nrf2–KEAP1 protein–protein interaction, stabilizing Nrf2 and promoting its translocation into the nucleus.
Notably, certain compounds, including Tideglusib, have been shown to activate Nrf2 independently of KEAP1, suggesting alternative regulatory pathways.
Despite these variations in acting mechanism, the majority of known NRF2 activators exert their effects via modulation of KEAP1, underscoring their central role in Nrf2 pathway regulation.
Functions of Nrf2 Activators/ Nrf2 Activation Pathway
Nrf2 orchestrates the expression of genes involved in redox homeostasis, glutathione biosynthesis, detoxification, drug excretion, and heme metabolism.
Apart from translation regulation, Nrf2 plays an important role in the following areas:
- Nrf2 inducers have demonstrated neuroprotective effects, particularly in the context of neurodegenerative disease-associated brain lesions.
- Nrf2–ARE aids in reducing inflammation-driven diseases, including autoimmune disorders, rheumatoid arthritis, asthma, emphysema, gastritis, colitis, and atherosclerosis
- Activation of Nrf2 by sulforaphane has been shown to reverse hyperglycemia-induced biochemical dysfunction in endothelial cells, suggesting its role in preventing diabetes-related complications.
- Nrf2 has been characterized as a tumor suppressor that confers resistance to reactive oxygen species (ROS) and inhibits cancer progression.
Nrf2 activation has shown promise in reducing cellular aging marked by skin deterioration, leading to ongoing research and commercial interest in finding compounds that can boost Nrf2 signaling to fight against age-related skin issues and hair loss. The functions are summarized in the figure.
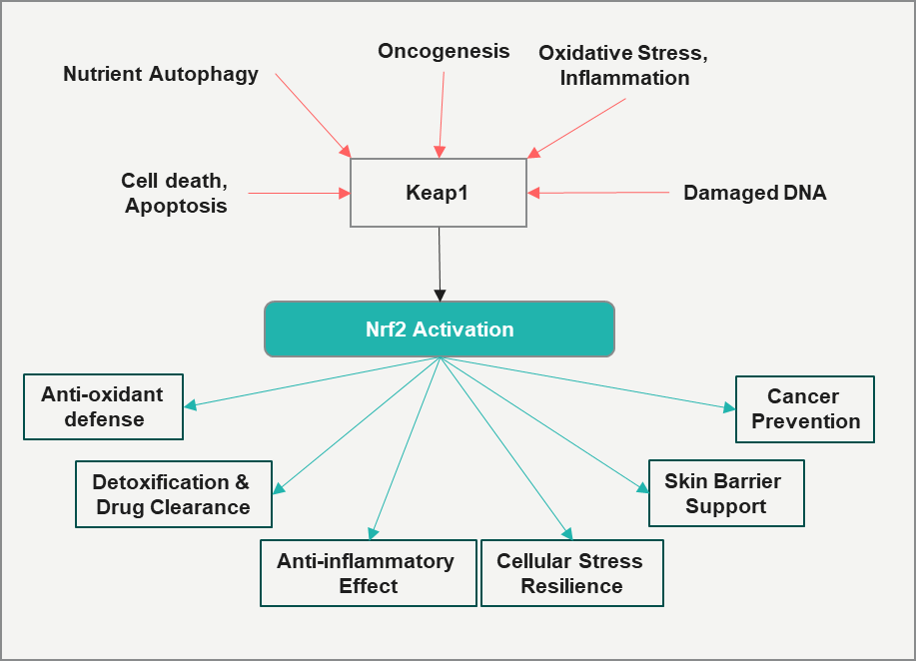
“Considering Nrf2 functions, the most commercially lucrative applications for Nrf2 modulation could be eradicating inflammation-driven skin aging or improving detoxification pathways.”
What are the Major Pain Points for Industry Players in Scaling and Commercializing?
- Developing Nrf2 activators or compounds requires high R&D costs. It needs advanced research infrastructure, including cutting-edge molecular biology labs, expertise in animal models, and extensive clinical trial experience.
- New entrants often lack awareness of the scientific basis and mechanisms behind Nrf2 activators, the technologies or ingredients that boost Nrf2 activity, and the competitive landscape of established players in this field.
Nrf2 Activators – Ingredient Innovations
Emerging interest from biotechnology firms, start-ups, and academic researchers has focused on identifying natural or synthetic compounds capable of enhancing the expression and activity of Nrf2 to improve cellular functions
The focus is especially on reducing oxidative stress and cellular aging. The following are examples listed below.
Sulforaphane (SFN)
Sulforaphane, a sulfur-rich isothiocyanate derived from cruciferous vegetables, interacts with Keap1 to release Nrf2 from cytoplasmic sequestration. Restoration of Nrf2 activity by SFN has been shown to protect against age-related muscle and cardiac dysfunction. Additionally, dietary supplementation with SFN ameliorates skin aging in the mouse models via activation of the Keap1-Nrf2 pathway.
Walnut Peptide
The peptide LPLLR (LP-5) from walnuts activates Nrf2/Keap1 signaling and suppresses NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated inflammation. Another peptide, WEKPPVSH, similarly attenuates oxidative stress and inflammatory responses through Nrf2-dependent mechanisms.
Salvianolic Acid B (Sal-B)
Sal-B, a potent antioxidant isolated from Salvia miltiorrhiza, protects against UVB-induced skin photoaging in mice by activating Nrf2 signaling pathways.
Liquiritigenin
Researchers at Qingdao University have identified liquiritigenin, a bioactive flavonoid derived from licorice root extract, as a potential anti-ageing agent for skin. The compound was shown to mitigate ultraviolet (UV)-induced skin ageing by inhibiting mitochondrial uncoupling and promoting the activation of Nrf2.
Bixin
Bixin, an apocarotenoid pigment from annatto (Bixa orellana), reduces epidermal oxidative DNA damage and inflammatory responses in murine models of skin photo damage through Nrf2 activation.
Resveratrol
Resveratrol, a polyphenolic compound found in grapes and red wine, prevents keratinocyte death in reconstructed skin models exposed to oxidative stress. Nrf2 activation was observed at concentrations from 20 µM to 100 µM.
Curcumin
Curcumin, the bioactive component found in turmeric (Curcuma longa), activates Nrf2 signaling in spinal cord astrocytes, reducing intracellular ROS levels and mitigating mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative damage.
Epigallocatechin Gallate (EGCG)
EGCG, a tea-derived polyphenol, prevents oxidative stress-induced senescence in human mesenchymal stem cells and provides neuroprotection by upregulating Nrf2/ARE signaling.
Fucoidan
The SCFC4 fraction of fucoidan, extracted from Sargassum confusum, promotes Nrf2-mediated antioxidant enzyme production in UVB-stimulated human keratinocytes, reducing oxidative stress. 23
Santamarine
Santamarine, a sesquiterpene lactone found in Artemisia scoparia and marine organisms, exhibits anti-photoaging effects in UVA-irradiated human dermal fibroblasts at 10 µM, stimulating Nrf2-dependent antioxidant gene expression.
Raspberry Extract
Raspberry extract has demonstrated protective effects against UVB-induced skin damage at a concentration of 750 µg/mL, mediated by Nrf2-driven antioxidant enzyme induction.
Dimethyl Fumarate (DMF)
DMF is a synthetic activator that has been approved by the FDA for the treatment of multiple sclerosis. It acts as Nrf2 activation, which is correlated with axon preservation and increased astrocyte activation.
The other synthetic Nrf2 activators include oltipraz, Bardoxolone-methyl, and omaveloxolone, which aid in the treatment of various diseases such as cancer and reduce inflammatory conditions.
Commercial Products
A growing number of cosmetic biotechnology companies have developed active ingredients targeting the Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2-related Factor 2 (Nrf2) pathway to enhance skin and hair resilience against oxidative and environmental stressors.
Below is a summary of select commercial products demonstrating Nrf2-mediated protective effects:
- MorinGuard® (Lipoid Kosmetik)
MorinGuard® is a cosmetic formulation enriched with moringin, a potent bioactive compound derived from Moringa oleifera. The product exerts dual protective effects by suppressing inflammation through NF-κB inhibition and enhancing antioxidant defense via Nrf2 activation.
- ALGAKTIV® Densidyl (Algaktiv)
ALGAKTIV® Densidyl is a microalgae-based solution designed to counteract stress-induced hair loss and premature graying. It contains Chlorella emersonii, rich in xanthophylls, and Spirulina maxima, a source of phycocyanin. The formulation activates Nrf2 signaling, thereby promoting follicular resilience and maintaining hair vitality.
- SantEnergyTM (Mibelle)
SantEnergy™ is a polyphenol-rich extract derived from Eriodictyon californicum (Yerba Santa). It revitalizes UV-damaged hair follicles by stimulating Nrf2-dependent antioxidant pathways, contributing to improved scalp and hair health.
- Pterovita® (Circe Scientific)
Pterovita® contains pterostilbene, a stilbenoid extracted from blueberries. The formulation supports skin defense against photoaging, regulates melanin synthesis, enhances hydration and elasticity, and modulates inflammation. These effects are mediated in part through the Nrf2 pathway activation.
- Protandim® Nrf2 Synergizer (LifeVantage)
Protandim® is a patented nutraceutical developed by LifeVantage, comprising a synergistic blend of botanical extracts including ashwagandha, green tea, milk thistle, bacopa, and turmeric. The product enhances Nrf2 expression and has been shown to reduce cellular oxidative stress by approximately 40% within 30 days in human studies.
- B-circadin TM (Clariant)
B-Circadin™, derived from Lespedeza capitata, a medicinal plant native to South Korea, has demonstrated efficacy in resynchronizing circadian gene expression in skin exposed to blue light. It also regulates aquaporin 3 and activates Nrf2 signaling, thereby protecting skin cells from light-induced stress.
- Depolluphane (Mibelle)
Depolluphane contains Lepidium sativum sprout extract and is formulated to combat pollution-induced oxidative stress in the skin. The product activates Nrf2, promoting the expression of detoxifying and antioxidant enzymes.
- Neøclair Pro™ (LipoTrue)
Neøclair Pro™, developed by LipoTrue, features epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) as its principal active. EGCG inhibits the aryl hydrocarbon receptor and upregulates Nrf2, facilitating skin detoxification.
What Technical Barriers Hinder the Widespread Use of Nrf2 Activators?
Safety – Hyperactivation
While Nrf2 activation holds promise for mitigating oxidative stress and promoting cytoprotection in conditions such as neurodegeneration, skin ageing, and cancer prevention, its therapeutic modulation presents significant challenges.
Major challenges are the risk of chronic, constitutive Nrf2 hyperactivation, which may inadvertently disrupt homeostatic biological processes. Recent findings demonstrate that sustained genetic activation of Nrf2 in mouse fibroblasts suppresses the expression of extracellular matrix components such as collagen and elastin, leading to compromised dermal integrity in aged mice.
Target Specificity
A critical consideration in the development of Nrf2-targeting compounds is the role of target specificity in balancing therapeutic efficacy with safety. Broad activation of Nrf2 can perturb redox equilibrium and metabolic networks, potentially impairing immune function and altering drug metabolism. Many electrophilic Nrf2 activators lack molecular precision and may concurrently engage other stress response pathways, thereby diminishing therapeutic selectivity.
Biomarker Identification
Another translational hurdle involves the monitoring of target engagement and pharmacodynamic responses in clinical settings. The absence of robust, validated biomarkers for in vivo Nrf2 activity complicates dose optimization and limits the ability to assess therapeutic outcomes.
R&D and Innovation leaders in this field need to consider this question: “How can next-generation activators achieve optimal signaling without disrupting essential cellular functions?”
Conclusion
Nrf2 activators are a promising group of compounds with broad therapeutic and cosmetic potential, as they can modulate oxidative stress, inflammation, and cellular resilience. To maximize the benefits of Nrf2 modulation, future research should focus on developing selective activators, reliable pharmacodynamics monitoring tools, and a better understanding of the tissue-specific and time-dependent dynamics of Nrf2 signaling. These efforts will be essential to ensuring safe, effective, and targeted use in the pharmaceutical, nutraceutical, and cosmetic fields.
In summary, the upcoming commercial frontier is defined by proof and precision: can your development process deliver selective activators that offer clinically proven, uniquely claimable advantages?
Stellarix as Solution Provider
Stellarix leverages its deep expertise and broad capabilities to provide tailored solutions that address critical pain points.
- Strategic Partnership Facilitation: Connect companies with contract research organizations (CROs), academic labs, and biotech incubators that already have advanced molecular biology facilities and animal model expertise, and provide solutions particularly for Nrf2 activation.
- Technology Scouting: Identify potential or novel or emerging Nrf2-related compounds, AI-based platforms discovering related compounds, or licensing opportunities to minimize the need for building infrastructure from scratch.
- Competitive Intelligence: Map the landscape of existing players, patents, and technologies to help new entrants understand the domain and position themselves strategically.
Get in touch with our CPG consultants for real-time, actionable insights into how market players are using Nrf2 activators to create viable commercial offerings, reshaping the future of nutraceutical, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic industries.
Let's Take the Conversation Forward
Reach out to Stellarix experts for tailored solutions to streamline your operations and achieve
measurable business excellence.