Non-invasive Treatments Revolutionizing Cancer Care
The latest advances in non-invasive cancer treatments enable patients to defeat cancer without the trauma, scar, infection, and lengthy recovery periods. The non-invasive treatment options ensure less chemotherapy and radiation, shorter hospital stays, faster recovery, and less need for reconstructive surgery. More targeted approaches to non-invasive cancer treatments lead to better outcomes than traditional surgical methods.
Benefits of Non-invasive Cancer Treatment
Non-invasive cancer treatments ensure multiple benefits compared to traditional invasive methods like surgery. Some key advantages of non-invasive cancer treatments are listed below.
- Less Pain and Quicker Healing: Numerous non-invasive approaches are more pleasant to patients because they do not involve any injections or surgical procedures, which improves the treatment process. Patients also tend to heal faster and with fewer side effects in most non-invasive procedures than invasive ones. Certain therapeutic regimes, such as those involving the application of topical ointments, allow the patients to self-manage the condition at home, thus making it more comfortable than visiting the patient’s center repeatedly for further care.
- Targeted Therapy and Preservation of Healthy Tissues: Aiming at the preservation of healthy tissue, non-invasive procedures such as Cytotron therapy concentrate only on cancerous cells to inhibit growth and spread. In this instance, the RFQMR system produces modulated FRBs that alter the activities of certain proteins localized within the cancer cell. The focused ultrasound is used after MRI imaging to precisely guide and destroy the tumor tissues while keeping the surrounding normal tissue safe (MRgFUS).
- Improved Diagnostics and Treatment Planning: The technology implies the analysis of tumor-derived material in body fluids, which can be of potential help in early diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment planning for ovarian and endometrial cancer. It includes circulating tumor cells (CTCs), circulating nucleic acids (DNA, RNA, microRNA), and extracellular vesicles (EVs).
Advancements in Non-invasive Cancer Treatment
Non-invasive methods for treating cancer are dashing into an age of transformation in cancer care because these techniques would allow early diagnosis, increasingly personalized care, and improved quality of life. More investigation and clinical trials are required to understand the safety and efficacy of these treatments compared to the traditional mode of treatment.
Non-invasive methods for treating cancer are dashing into an age of transformation in cancer care because these techniques would allow early diagnosis, increasingly personalized care, and improved quality of life. More investigation and clinical trials are required to understand the safety and efficacy of these treatments compared to the traditional mode of treatment.
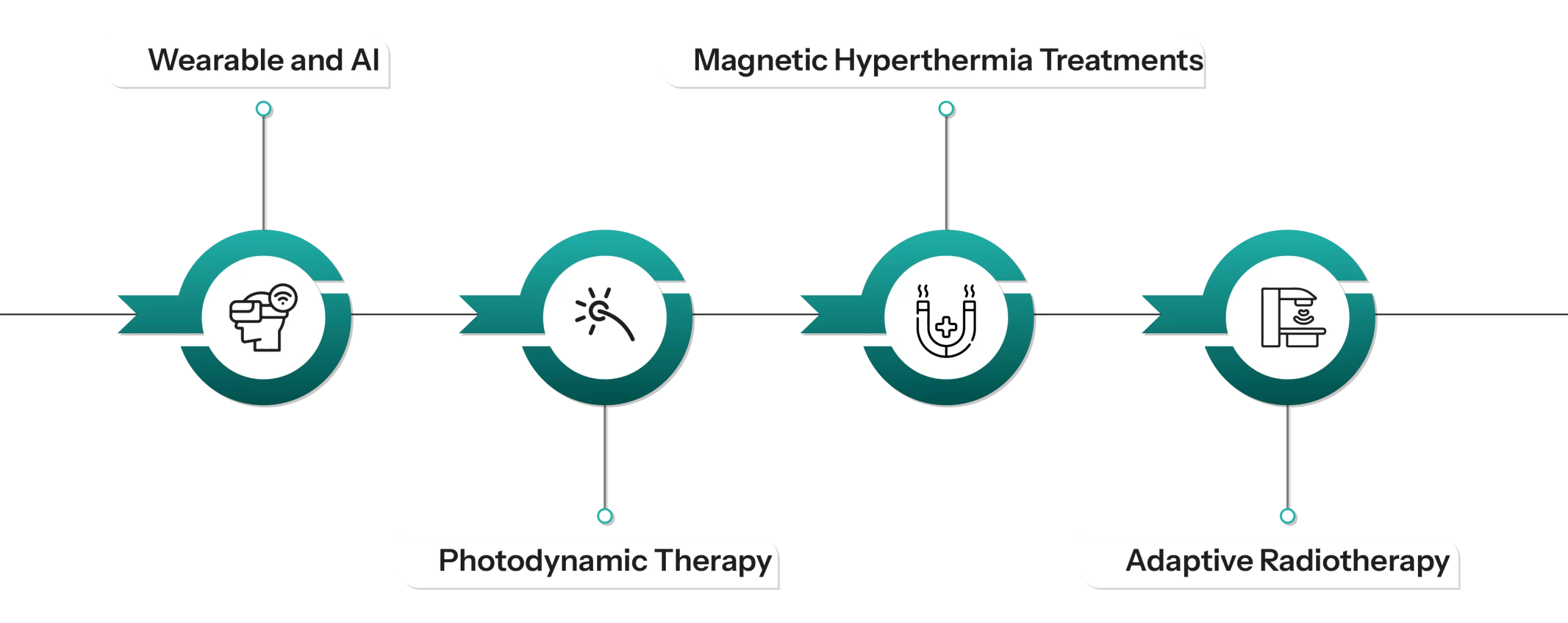
Figure 1: Advancements in Non-invasive Cancer Treatment
- Wearables and AI: Wearable devices and artificial intelligence are making inroads into oncology for diagnosis, therapy, and patient self-management. The technology uses big data processing, self-learning, real-time acquisition, and personalized health for intelligent treatment platforms.
- Photodynamic Therapy: Photodynamic therapy provides non-invasive treatment for subcutaneous tumors targeted on oral, head, and neck cancers. The aim behind developing this photosensitizer procedure is to enhance the sugar receptor target on tumor cells to reduce the glucose consumption of tumor cells.
- Magnetic Hyperthermia Treatments: The technology is used to develop nano-bacteria magnets, which are prepared with anisotropic magnetic nanocubes disposed in E.coli. The nanoparticles are delivered to the tumor, and a magnetic field is provided to the nanoparticles to generate heat in the cells.
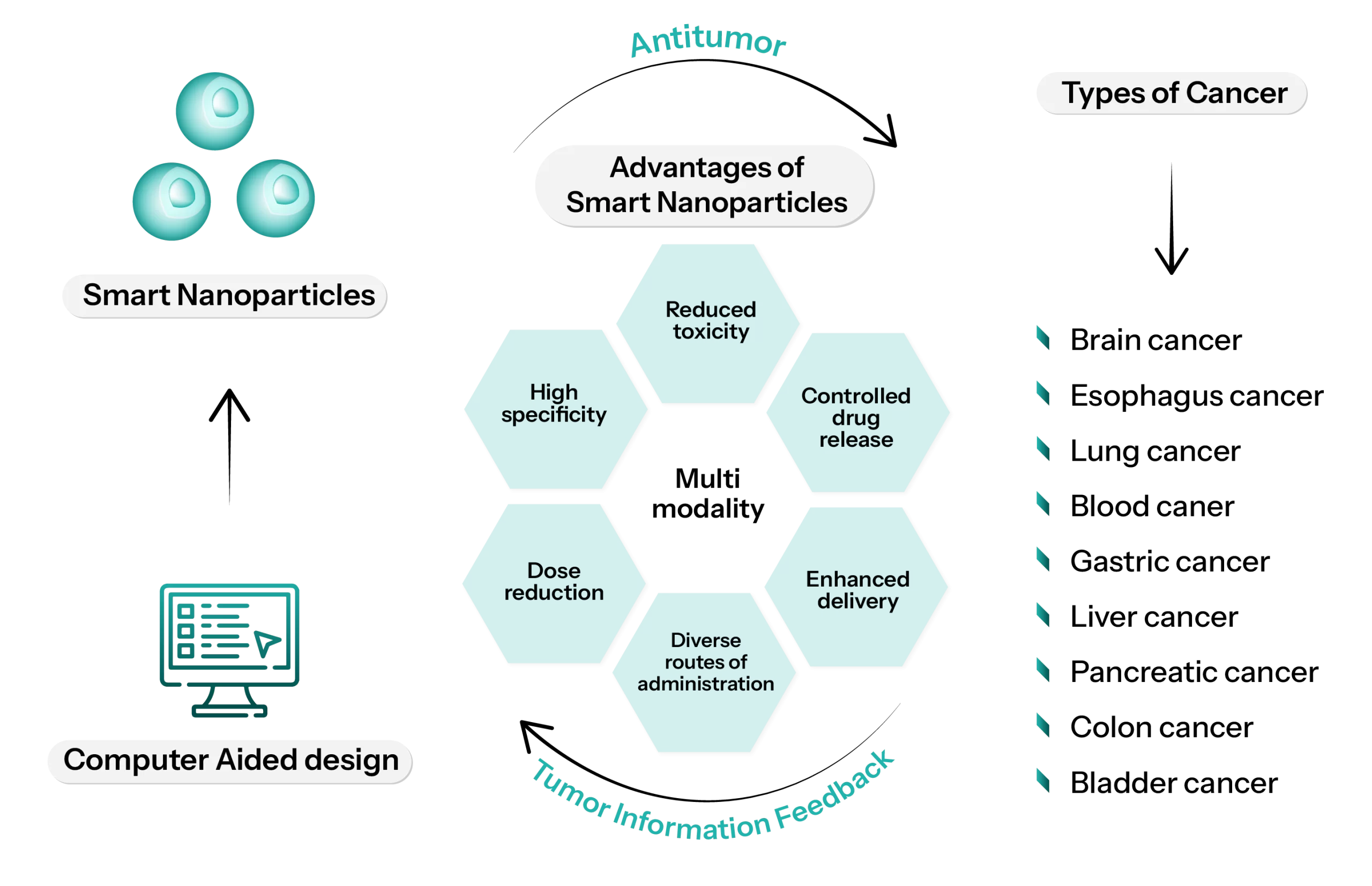
Figure 2: Schematic Illustration of Smart Nanoparticles for Cancer Treatment
- Adaptive Radiotherapy: MRI-guided radiotherapy is another advanced technique wherein real-time imaging can be done during treatment, and the treatment plan altered by any changes in the system. This enhances the precision of the treatment and minimizes the side effects.
Growth Drivers for Non-invasive Cancer Treatment
The global non-surgical cancer treatment market is experiencing growth on account of the increasing cancer population, technological developments, growing awareness programs, rising preference for non-invasive techniques, and improvements in genomic and molecular biology.
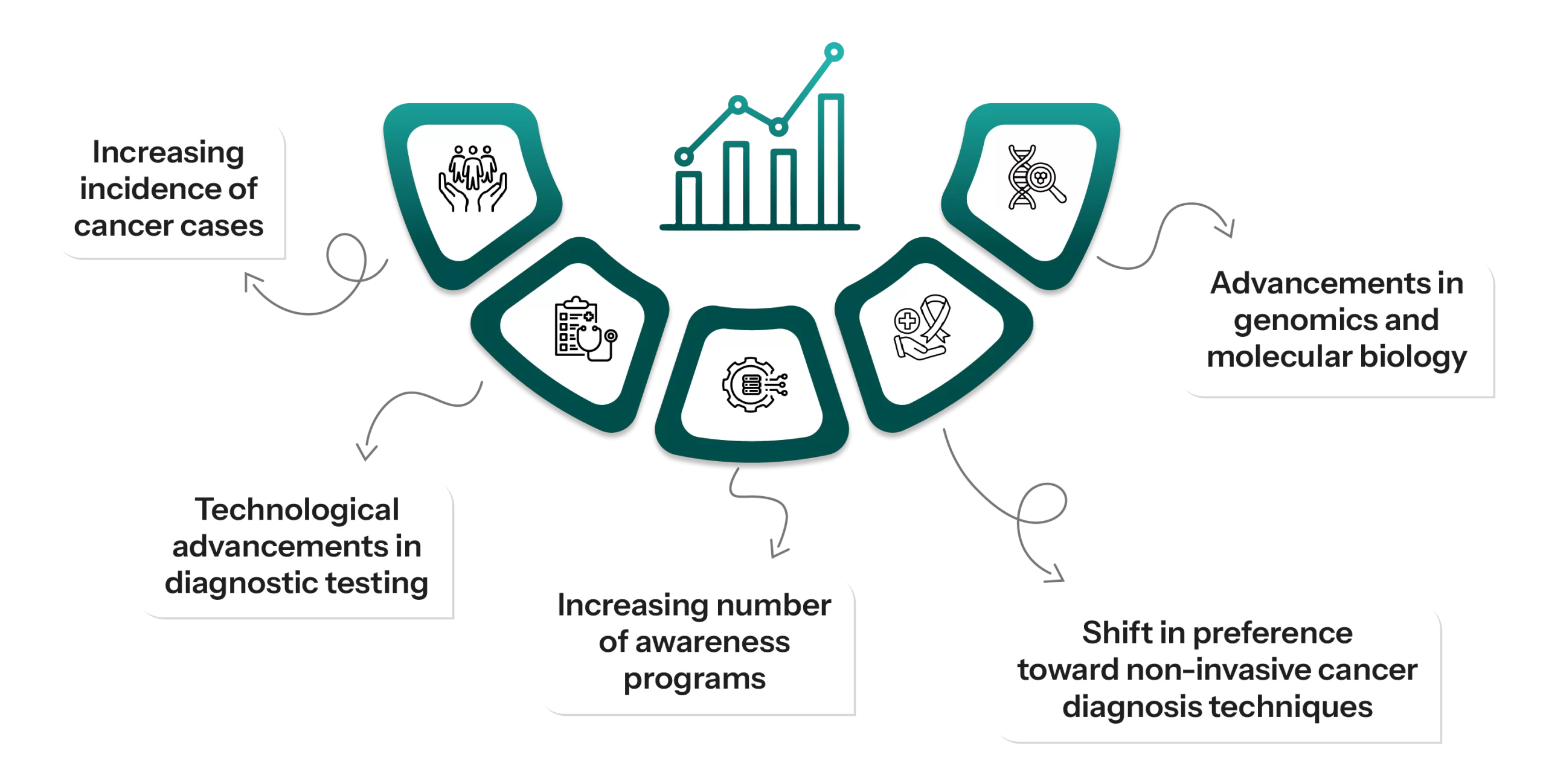
Figure 3: Growth Drivers for Non-invasive Cancer Treatment
- Rising Incidence of Cancer Cases: The increase in the number of cancer-diagnosed patients has been a significant factor propelling the growth of the market for diagnostic non-invasive cancers around the globe.
- Technological Advancements in Diagnostic Testing: The rapid upsurge of new and innovative diagnostic methods that include both deep learning-enabled artificial intelligence and volumetric imaging technology is expected to positively impact the growth of the market. For instance, Hologic, Inc. announced that commercial access was made available to the Genius Digital Diagnostics System in Europe to enable the detection of cervical cancer cells and precancerous lesions.
- Expanding Awareness Campaigns: Rising initiatives by major players to create awareness about cancer screening are one major reason driving the expansion of the need for diagnostic items.
- Change in the Approach Towards Non-invasive Cancer Diagnosis Techniques: Non-invasive cancer diagnosis techniques are preferred much more than traditional invasive diagnosis techniques. It is because patients are uncomfortable with invasive imaging techniques, and there are better ways to treat these patients.
- Developments in the Field of Genetics and Molecule Biology: This concurrence has led to the subsequent development of effective and more targeted therapies using non-invasive diagnostic methods, making this sector one of the key components globally in the fight against cancer.
Restraining Factors of Non-invasive Cancer Treatment
While non-invasive cancer therapies have various benefits, great access challenges persist, and resolving these issues is going to be key to enhancing the outcomes of cancer patients all over the world. The key challenges that affect the non-invasive cancer market and play the role of blockers are discussed below:
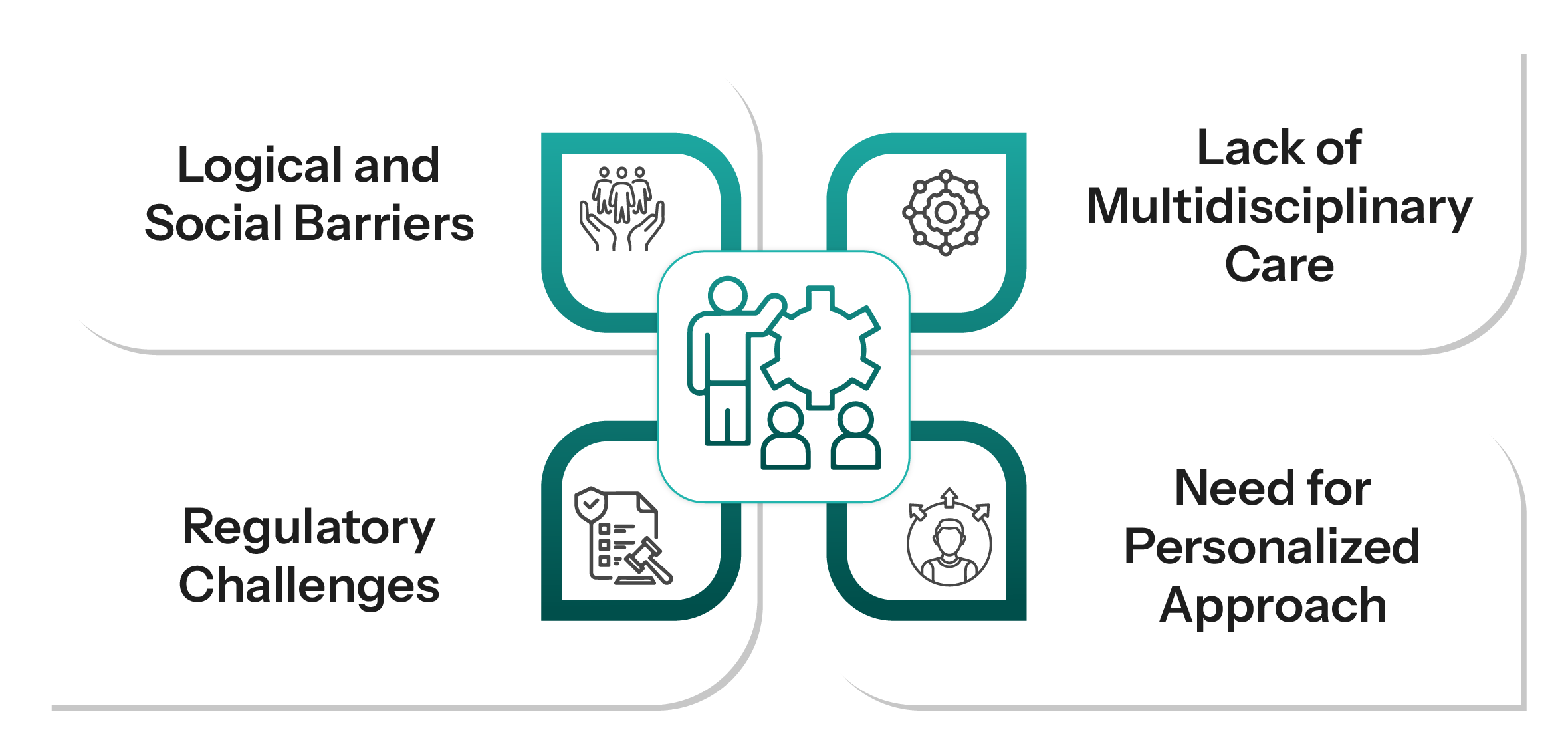
Figure 4: Restraining Factors of Non-invasive Cancer Treatment
- Absence of Integrated Approach: Integrated care includes the provision of continuity of care, the application of correct treatment regimens, and the control of complications. Also, systems should be capable of timely diagnosis, avoiding loss to follow-up, providing additional therapy referrals, and educating the patient on the illness and the reason for treatment.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Presently, there is no accepted guidance established by the FDA for the approval of cancer treatment nanotechnology products. Each situation is reviewed separately, which is long and poses challenges in bringing products into the market. This is likely to be difficult now with the advent of many functional capabilities of nano platforms.
- Need for Personalized Approaches: Knowledge of the cancer cell physiology, the environment of the tumor, systemic drug pharmacokinetics, and those of delivery vehicles is critical in the successful invention of new chemotherapeutic agents.
- Economic Constraints: Expensive advanced treatments such as CAR-T or proton therapy limit their availability to a wider percentage of patients and health systems. Furthermore, varying insurance coverage for non-invasive procedures may limit patient access as well.
Also Read Cancer Therapy: Innovations, Challenges, and Hope
Recent Innovations in Non-invasive Cancer Treatment
A list of recent innovations in terms of novel technologies for non-invasive cancer treatments.
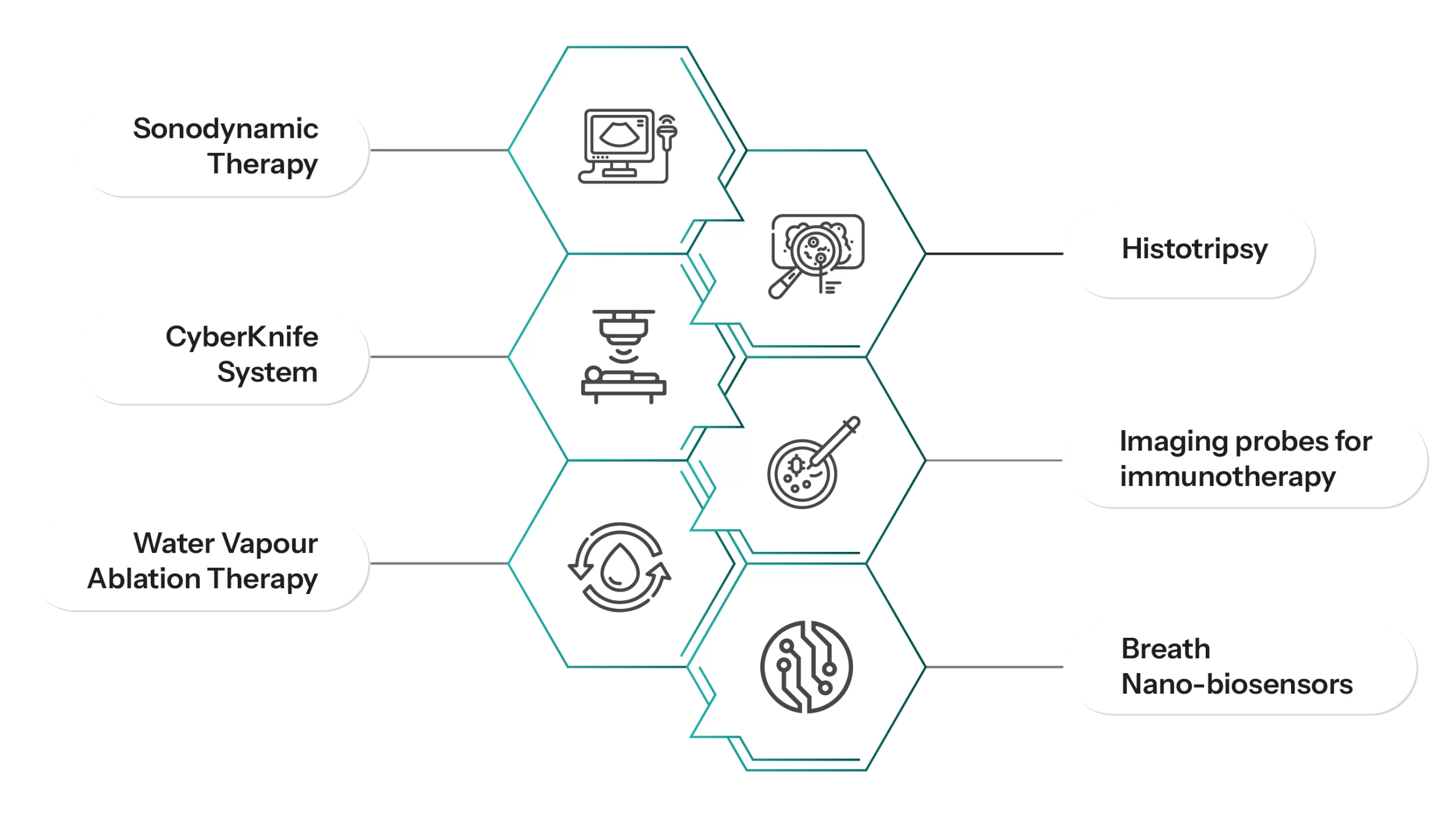
Figure 5: Recent Innovations in Non-invasive Cancer Treatment
- Sonodynamic Therapy: In this treatment, an ultrasound activates the sonosensitizer that produces reactive oxygen species (ROS) to kill cancer cells. The piezoelectric sonosensitizer utilizes ultrathin iron-doped bismuth oxychloride (BOC) nanosheets with rich oxygen vacancies and a bovine serum albumin coating on the surface. E.g. Sonalasense
- Histotripsy: It uses focused ultrasound waves to target and break tissues without harming nearby healthy tissue. This approach ensures efficient procedures and minimal recovery times. It can also be done without disrupting chemotherapy or other cancer treatments. E.g. Histosonics
- CyberKnife System: A non-invasive, painless form of radiation therapy that uses image-guided robots to accurately target and destroy tumor cells and other lesions through high-energy multi-beam radiation. The CyberKnife System delivers radiation directly to the tumor, ensuring pinpoint accuracy, without distressing the surrounding healthy tissues and organs. E.g. CyberKnife System
- Imaging Probes for Immunotherapy: Affinity-based agents target immune cell markers, checkpoint molecules, and substrates, while activity-based probes are being developed for non-invasive assessment and prediction of tumor response to immunotherapy. E.g. IVISense
- Water Vapor Ablation Therapy: This minimally invasive procedure stops cancer cells without needing open surgery. It can be performed using the phase shift energy present in sterile water vapor to transfer thermal energy to cancerous tissue. E.g. Vanquish
- Breath Nano-biosensors: A promising noninvasive nano-biosensor for breath analysis integrated with artificial intelligence, machine learning, and IoT provides intelligence to nose-on-chip lung cancer nano-biosensors. The device is used for early detection of lung cancer, which is analyzed based on the breath biomarker, which includes volatile organic compounds and exhaled gases. E.g. Nose-on-chip Nanobiosensor
Ecosystem of Non-invasive Cancer Treatment
An ecosystem of Non-invasive Cancer Treatment, including key players, start-ups, and academics, is given below:
Figure 6: Ecosystem of Non-invasive Cancer Treatment
Future of Non-invasive Cancer Treatment
In the case of non-invasive cancer treatment, the prospects are quite good as the targeted, multifunctional, and personalized approaches influence the development of imaging, targeted nanomedicine, immunotherapy, and gene therapy. These advances will be important if these innovations are to be translated into the clinic and benefit cancer patients. These advances contribute to the future of non-invasive tumor treatment by improving the quality of life during cancer treatment, that is, non-invasively.
Let's Take the Conversation Forward
Reach out to Stellarix experts for tailored solutions to streamline your operations and achieve
measurable business excellence.