Mood Enhancing Fragrance Compounds
Fragrance compounds profoundly impact emotions, memories, and overall mental well-being. They activate the olfactory system and interact with neurotransmitters, significantly influencing brain activity. Essential oils and aromatic plants have been utilized for centuries to promote relaxation, elevate spirits, and restore balance, with scents like lavender and rosemary demonstrating notable therapeutic benefits.
The article explores the science of fragrances, dealing with biochemical processes responsible for the perception of scents and their direct links to the brain’s limbic system, which plays a key role in emotions and memory. It highlights the psychological effects of fragrance, including emotional triggers that evoke nostalgia, the benefits of aromatherapy in enhancing mood, and the role of scents in neuro-marketing strategies to influence consumer behavior.
Additionally, the article addresses how fragrances can influence mood, encourage relaxation, and even boost cognitive performance. Beyond merely enjoyable aromas, these fragrance compounds hold significant potential for improving mental health and overall quality of life. It emphasizes the importance of fragrance as a vital resource for emotional well-being, highlighting its value and the need to recognize its benefits.
Understanding Mood-Enhancing Fragrance Compounds
Fragrance is more than just a source of sensory enjoyment; it can evoke emotions, spark memories, and affect mood. For centuries, people have turned to aromatic plants and essential oils to promote relaxation and emotional stability. Recent studies have uncovered the biochemical and neurological processes contributing to these effects. Both natural and synthetic mood-enhancing fragrances provide therapeutic advantages, such as alleviating stress and reducing anxiety. This article explores the science behind these scents, identifies effective options, and discusses their applications for mental health and well-being.
Mechanism of Action
The brain processes fragrance when aromatic molecules interact with olfactory receptors in the nose, triggering G-protein pathways that activate ion channels, causing membrane depolarization.
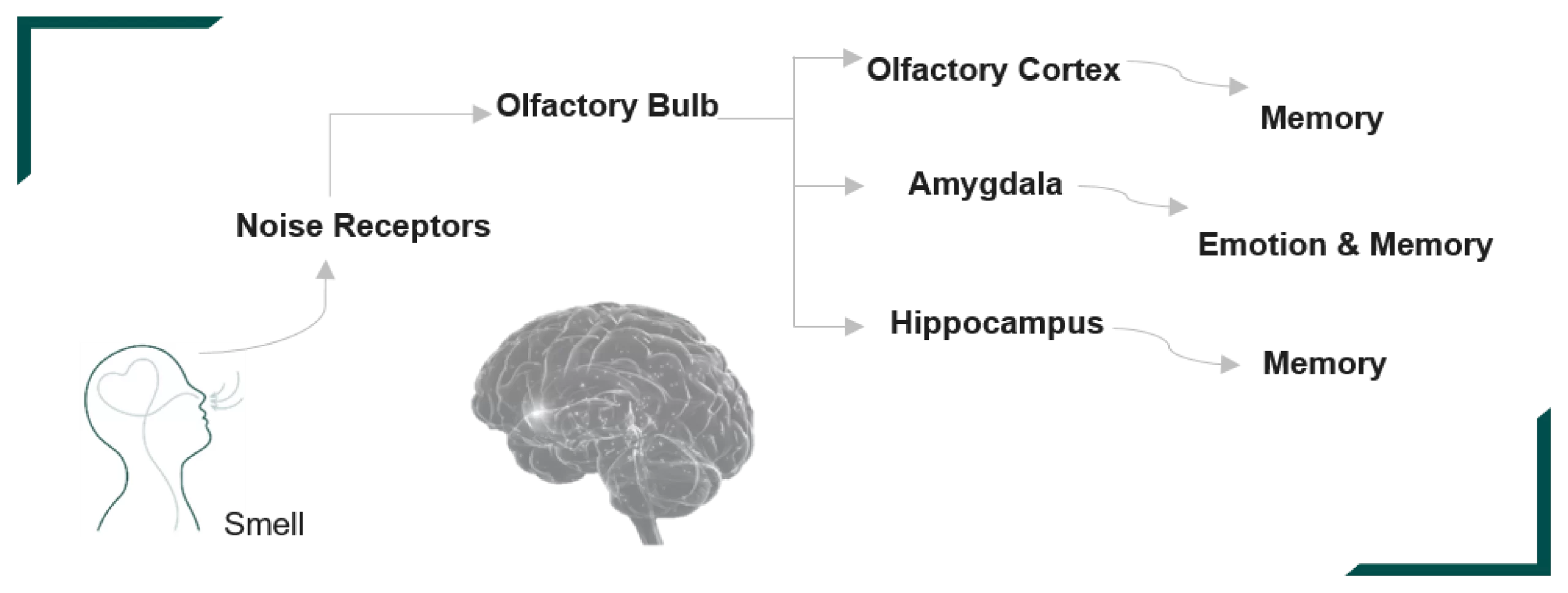
Signals travel to the olfactory bulb and cortex, connecting directly to the limbic system (amygdala and hippocampus), vital for emotion and memory. The piriform cortex supports odor recognition memory, while the periamygdaloid and entorhinal cortex link scent to emotional and memory processing through connections with the amygdala and hippocampus.
Psychology of Fragrance
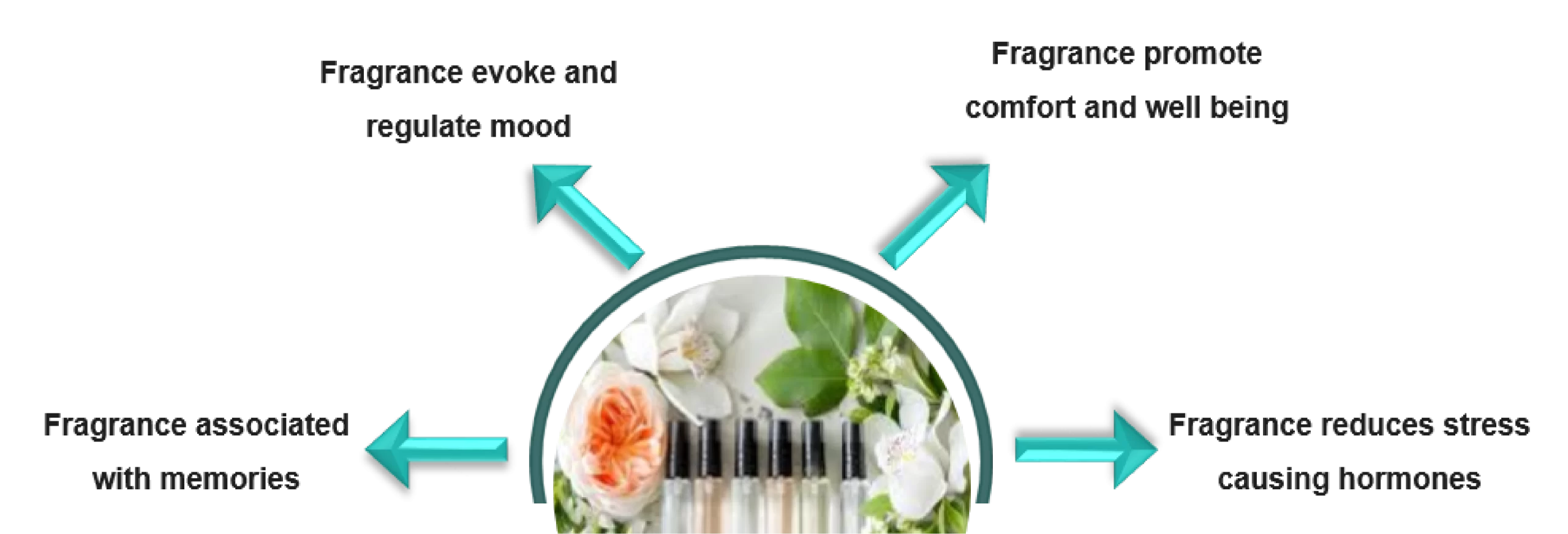
The psychology of fragrance explores the influence of scent on human emotion, behavior, and memories. In this section, we highlight the different emotions, moods, and experiences fragrances can evoke.
- Emotional Triggers: The sense of smell is closely tied to the brain’s limbic system, which governs emotions and memories. As a result, certain fragrances can instantly take us to specific moments or places, evoking the associated emotions connected to those experiences. For example, the smell of fresh-baked cookies may bring back childhood memories, eliciting warmth and nostalgia.
- Aromatherapy: Aromatherapy is the use of fragrance, specifically essential oils, to enhance well-being and influence mood. For example, Lavender is often used for its calming effects, while citrus scents can energize and uplift.
- Neuro-marketing: The impact of fragrances on the brain is an important area of research, with the potential to influence consumer behavior and decision-making. Understanding how scents affect the brain and elicit emotional responses can help companies craft more effective marketing strategies and design products that deeply resonate with consumers. For example, the scent of vanilla has been shown to enhance feelings of pleasure and relaxation, making it a popular choice for products aimed at promoting calm and well-being.
- Mood Enhancement and Regulation: Different fragrances influence the brain differently, and some fragrances can control and regulate mood, promote relaxation, and reduce anxiety. For example, Jasmine has uplifting and euphoric properties, often used to inspire optimism, confidence, and emotional warmth. Its sensual aroma is also linked to relaxation and enhanced mood.
- Memories and Recall: Scents are powerful memory triggers. Researchers suggest that olfactory cues can evoke memories more vividly than visual or auditory cues, making them valuable in therapeutic settings. The brain can form associations between specific scents and experiences, leading to conditioned responses. For instance, rosemary has been thoroughly studied for its ability to enhance memory and boost cognitive function. Its scent stimulates the brain, increasing alertness and improving memory retention. Research suggests that exposure to rosemary can enhance both prospective memory and long-term recall, making it a valuable tool for improving memory capabilities.

Fragrance Compounds
These fragrance compounds in essential oils, perfumes, or ambient diffusers are powerful tools for influencing emotional states. Their ability to evoke feelings of calm, joy, focus, or relaxation makes them valuable in mood-enhancing applications across personal care products, wellness practices, and aromatherapy. Below are some commonly known fragrance compounds used for mood enhancement.
Beta-damascenone
This volatile compound is commonly found in various essential oils, mainly rose, and has gained attention for its potential mood-enhancing properties.
| Smell | Rose |
| Effect | Calming and Stress relieve |
| Source | Clove, Grapes, Plums, Lychee, Apples, Raspberries, Apricots |
| Mood Impact | Calming and Stress Relief |
The aroma of β-damascenone, with its distinctive floral and fruity notes, notably impacts mood. Research indicates that pleasant scents, like β-damascenone, can trigger positive emotional responses by engaging the brain’s reward pathways. This activation can lead to the release of neurotransmitters such as dopamine, which is linked to feelings of pleasure and well-being. As a result, exposure to enjoyable fragrances can help elevate mood and enhance emotional states.
Regulatory Aspect:
Research Institutes for Fragrance Materials (RIFM) is in the process of completing comprehensive safety assessments.
Safranal
Safranal is a key aroma compound in saffron. It belongs to the monoterpenoid chemical group and is derived from picrocrocin, the precursor found in saffron.
| Smell | Floral Undertones |
| Effect | Anxiety reduction, Mood enhancement |
| Source | Saffron, Rose, Cinnamon, Clove |
| Mood Impact | Safranal may exhibit antidepressant-like effects. It has been shown to influence neurotransmitter systems positively. |
It exhibits antidepressant properties and increases the serotonin level in the brain; serotonin is a neurotransmitter associated with feelings of well-being and happiness, and the ability of safranal to potentially elevate mood through dietary supplementation is significant.
Regulatory Aspect:
The comprehensive safety assessments of safranal have not yet been established.
Eugenol
It is a naturally occurring ingredient found in several types of essential oils, such as clove, cinnamon, and nutmeg. Eugenol is a phenol, an organic hydroxy compound of benzene bearing a single substituent.
Research indicates that eugenol can trigger autonomic nervous system (ANS) responses linked to emotional states.
| Smell | Spicy |
| Effect | Stimulating and invigorating |
| Source | Lemongrass, Nutmeg, Ginger, Basil, Cloves, Cinnamon |
| Mood Impact | Its stimulating properties offer a sense of warmth and revitalization. It uplifts mood and enhances mental clarity. |
When participants inhaled eugenol, researchers noted changes in heart rate, skin conductance, and breathing patterns. These physiological reactions indicate that eugenol may affect mood by influencing the body’s stress response systems.
The emotional response to eugenol varies depending on the individual’s experiences. A study shows that dental patients without anxiety associated eugenol with positive emotions like happiness and surprise, whereas anxious patients connected it to negative feelings such as fear and disgust. This demonstrates how personal experiences can shape reactions to specific scents.
Regulatory Aspect:
- FDA considers eugenol GRAS, which is commonly used in foods, air fresheners, cosmetics, and perfumes
- EU identified a potential skin sensitizer that has the potential to cause a skin reaction
- The Research Institute of Fragrance Materials has completed an official safety assessment for eugenol and concluded it is a weak skin sanitizer; it has determined that the concentration is not expected to cause sensitization
Alpha-Pinene
Alpha-pinene, a monoterpene found in pine trees and various essential oils, is known for its refreshing scent and potential mood-boosting effects. Its influence on mood is linked to several mechanisms interacting with the brain and body.
| Smell | Pine |
| Effect | Memory-enhancing and Uplifting |
| Source | Dill, Fennel, Citrus Fruits, Bay Leaves, Coriander Seed, Angelica |
| Mood Impact | Alpha-pinene has been associated with improved mood, mental clarity, and memory enhancement. |
Studies have shown that alpha-pinene can enhance parasympathetic nervous system activity, fostering relaxation. One study found that exposure to alpha-pinene significantly increased heart rate variability (HRV), a marker of parasympathetic dominance. This physiological response is associated with reduced stress and a sense of comfort, positively impacting mood.
Regulatory Aspects:
- Alpha-pinene is GRAS-certified by the FDA for the use of flavoring substances and adjuvants
- The Research Institute of Fragrance Materials peer-reviewed the safety assessment and found it could potentially cause skin sensitization in a small fraction of people. It has set a limit on the concentration of its use
- The International Fragrance Association (IERA) has set a safe use standard for Alpha-pinene in household and personal care products based on this level
Iso E Super
Iso E Super can be derived from myrcene or OTNE (Octahydrotetramethyl Acetophenone). This versatile ingredient can be used in various products, including perfumes, laundry fragrances, and more. It’s known for its warm, woody, amber-like aroma.
Iso E Super stimulates the hypothalamus, an area within the limbic system that controls hormone regulation; the effect is stronger in women than in men.
Regulatory Aspect:
- The EU has identified Iso E super as a potential skin sensitizer. It may cause a reaction such as red, bumpy, or itchy skin.
- The Research Institute for Fragrance Materials (RIFM) is developing an official safety assessment for Iso E Super. The findings are currently under review and will be published after undergoing a thorough peer-review process.
- The International Fragrance Association (IFRA) has set standards for the acceptable concentration of iso E super.
AI Integration and Mood Enhancement
The integration of AI in mood enhancement is advancing quickly, fueled by the growth of machine learning models and emotional AI. These technologies analyze physiological, psychological, and behavioral data to provide personalized interventions to improve mood. In the fragrance sector, AI enables companies to sift through extensive consumer data to create emotional profiles associated with specific scents, helping perfumers understand how different aromas affect mental states.
Brands like Palmolive are utilizing AI to craft personalized scent experiences that aim to evoke specific emotions, such as happiness or relaxation, by employing predictive analytics and consumer feedback. This use of AI in fragrance development not only amplifies the emotional resonance of scents but also opens up possibilities for highly tailored, multi-sensory experiences. As this technology continues to progress, it has the potential to elicit more complex and nuanced emotional reactions.
Innovation
- AI & Mood Enhancement: The art of perfume-making is shifting toward mood-boosting fragrances, with brands using innovative technologies like AI to create scents that enhance well-being. Swiss firm Firmenich’s Focus by EmotiCode uses AI to develop perfumes aimed at improving concentration, blending neuroscience with perfumery to personalize emotional experiences through scent.
- Multifunctional Fragrance: Ôrəbella’s Ôrəlixir™ is a unique bi-phase formula that combines a nourishing base of hydrating snow mushroom and five oils for skin health and fragrance longevity. Its top phase features aromatherapy essential oils and premium fragrance components designed to elevate the wearer’s mood and aura.
- Functional Fragrance: Givaudan has introduced two innovative fragrances, Phytogaia™ and Thalassogaia™, inspired by the natural benefits of forests and oceans. Phytogaia™ contains phytoncides, molecules emitted by forest trees, which are known to reduce stress and fatigue. Thalassogaia™ mimics the composition of the marine environment, promoting a calming and soothing effect.
- Ingredients derived from Sea coral: The US company Human Pheromone Sciences has filed a patent for a sea coral-derived compound, provisionally labeled ER 303, intended for use in fragrances and cosmetics. This compound is designed to enhance mood by promoting feelings of personal well-being, positive social connections, and increased social attraction.
- Neuroscents: Charlotte Tilbury is launching a new fragrance collection designed to evoke various emotions using IFF’s advanced technology. The goal is to empower users by enhancing their mood with high-quality makeup or skincare.
Conclusion
Fragrance has always served a purpose beyond mere sensory enjoyment; it possesses a unique capacity to evoke emotions, spark memories, and affect or change mood. This happens through multiple pathways, mainly by activating the olfactory system and interacting with neurotransmitters. By integrating different essential oils, perfumes, and aromatherapy products featuring mood-enhancing scents into our everyday lives, we can take a holistic approach to enhancing mental health and achieving balance. As we continue exploring the complexities of scent and emotion, the potential for fragrance to transform our mood and enrich our lives remains promising and profound.
Let's Take the Conversation Forward
Reach out to Stellarix experts for tailored solutions to streamline your operations and achieve
measurable business excellence.