Humanoid Carebots: The Next Generation of Nursing
Advances in technology have overhauled almost every industry in the world, and healthcare is one of those industries. The most thrilling invention of the era in the healthcare domain is humanoid nurse robots (HNRs). These highly intellectual machines are going to make the work of healthcare workers easier in taking care of patients through vital signs monitoring, medication dispensing, and even administering comfort. This article will cover the domain of humanoid carebots from their inception to possible application in future healthcare.
What Are Humanoid Nurse Robots, and How Do They Work?
These humanoid nurse robots are not only robots but have been fashioned and taken on the appearance of human beings; they look and behave like human beings. They walk, talk, and can even express emotions. Humanoid carebots represent one of the most innovative forms of robotics and have been programmed to execute health-related jobs, including measuring vital signs, dispensing medications, and providing companionship. These robots are embedded with cameras, sensors, and AI technology to aid them in communicating, collecting data, and providing most medical operations. The main objective behind these robots is to make patient care effective and of high quality while taking some stress off the shoulders of healthcare providers.
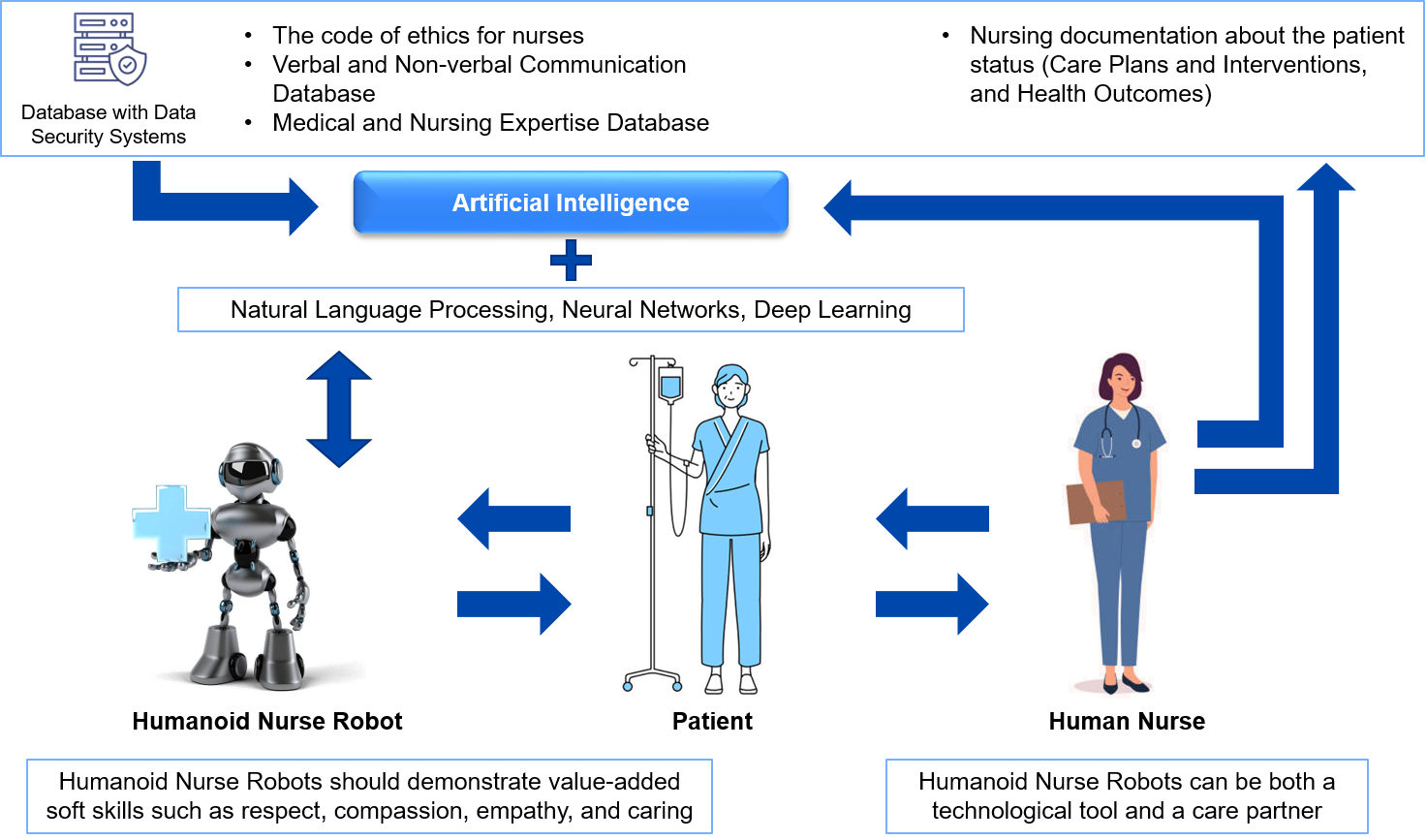
Figure: Relationship between Humanoid Nurse Robot & Patient
- The development and design of humanoid nurse robots of the present and future calls for participatory dialog and trans-professional collaboration between healthcare professionals, technology engineers, and care stakeholders.
- Nursing professionals can deliver critical inputs with empirical value at the point-of-care. Specifically, HNRs can develop through the nurses’ integration of knowledge, clinical expertise, nursing documentation, and care competencies, covering significant and reliable information about patients’ status, care plans and interventions, and medical outcomes.
- This information can be gathered and systematized using a framework and database. Consequently, a natural conversation would be possible between HNRs and humans, i.e., patients and their families, provided the databases are well-integrated with AI. This permits HNRs to communicate competently and respond appropriately and precisely to patients while cautiously considering the all-inclusive situation comprising the patient’s condition, the psychiatric database, and the healthcare setting.
Benefits of Humanoid Nurse Robots
One must be struck by the current prominence of humanoid carebots in today’s healthcare world. Imagine walking into a hospital setting and being greeted by a sociable robot willing to help patients and staff alike. What advantages make these robots so valuable and beneficial to hospitals, clinics, and nursing homes?
Following are the incredible benefits they bring along:

Top Humanoid Nurse Robots Changing the Healthcare Industry
- Moxi (Diligent Robotics):
An advanced robot designed to assist healthcare teams. Equipped with advanced sensors, cameras, and deep AI algorithms, the autonomous robotic assistant can roam independently around healthcare facilities, interact with people, and perform non-patient-facing tasks like laboratory specimen delivery and supply or collection of soiled linens.
- Robear (Riken and Sumitomo Riko Company Limited):
A robotic bear can assist in caring for elderly patients by lifting them from a standing position or floor, transferring them to a wheelchair, carrying them from point A to B, and turning patients in bed.
- Robot Dinsow Mini (CT Asia Robotics):
It is designed with embedded voice recognition, voice command, face recognition, and AI features that enable the robot to learn more about the elderly person’s voice, face, behavior, and lifestyle. Furthermore, the robot is designed to aid those people who have Alzheimer’s disease and promotes the elderly for the exercise of brains.
- Paro Therapeutic Robot (Paro Robots):
The robot has five kinds of sensors consisting of temperature, tactile, light, audition, and posture sensors, with which it can observe people and their environment. It has been reported that Paro reduces the stress of patients and their caregivers, stimulates communication between patients and caregivers, and psychologically affects patients. Further, it also improves relaxation, motivation, and the socialization of patients with each other and with caregivers.
- Pepper Robot (Aldebaran):
With Pepper’s camera and personalized healthcare solutions, medical staff can track their patients, provide timely feedback, set up appointments, and more. Telepresence allows patients’ families to video call Pepper, offering social bonding.
- Grace (Hanson Robotics):
The robot is equipped with sensors, including a thermal camera to detect a patient’s temperature and pulse, to help doctors diagnose illness and deliver treatments. Grace, who specializes in senior care, speaks three languages, including English, Mandarin, and Cantonese, and can socialize and conduct talk therapy.
The following ecosystem includes big entities/ SMEs, universities, and start-ups in the domain of humanoid nurse robots. These players are driving innovations and paving the way for the widespread adoption of these robots in healthcare settings.

Driving Factors of Humanoid Nurse Robots
The market-driving factors of humanoid carebots are primarily based on the growing demand for healthcare automation and the need to improve patient care and health outcomes. They possess leading sensing and manipulation capabilities, help support repeated tasks, etc. The following represent some of the essential aspects that boost the humanoid carebots market:

- Increased Adoption of Robotic Nursing Assistant Devices: Increased pressure on healthcare services has increased the adoption rate of robotic nursing assistant devices worldwide. Such devices automate routine tasks and have ensured better patient safety along with better patient care experience.
- Insufficient Nursing Staff: The world is under immense pressure because of the deficit in nursing staff, which is particularly heightened in many countries. This situation is further exacerbated by an aging population, retirements, and a general rise in demand for healthcare services. While humanoid nursing robots have advanced sensors and AI algorithms, they often focus on patient-related activities. This would decrease the burden on human nurses since more hours could be devoted to high-touch care.
- Integration of AI and IOT Advances Robot Features: The integration of IoT and AI technologies significantly advances the features of humanoid carebots. AI in robots allows learning and adaptation of the needs expressed by patients, accuracy in care, and performance efficiency. Meanwhile, IoT connectivity allows for real-time monitoring and data exchange so that flawless communication and coordination with providers are possible.
- Enhanced Patient Care: These humanoid carebots can provide continuous and reliable support. They are programmed to remind patients about their medication and appointment schedules, helping ensure that patients get the care they need exactly when they need it.
- Reducing Staff Workload: Nurses’ workloads are too high because more and more people attend health services. Therefore, when nurse humanoid robots take over the repetitive jobs, nurses can focus on compassionate care. This helps them have a less overburdened workflow and more positive patient outcomes.
- Emotional Connection: One of the most exciting features of humanoid nurse robots is the emotional bonding between a patient and these nurse robots. They can pick up on the feelings of a person feeling down and give them comforting gestures in return. These robots are personal digital companions that are always available to lend you an ear. This would then support care, especially for aging or long-term care patients.
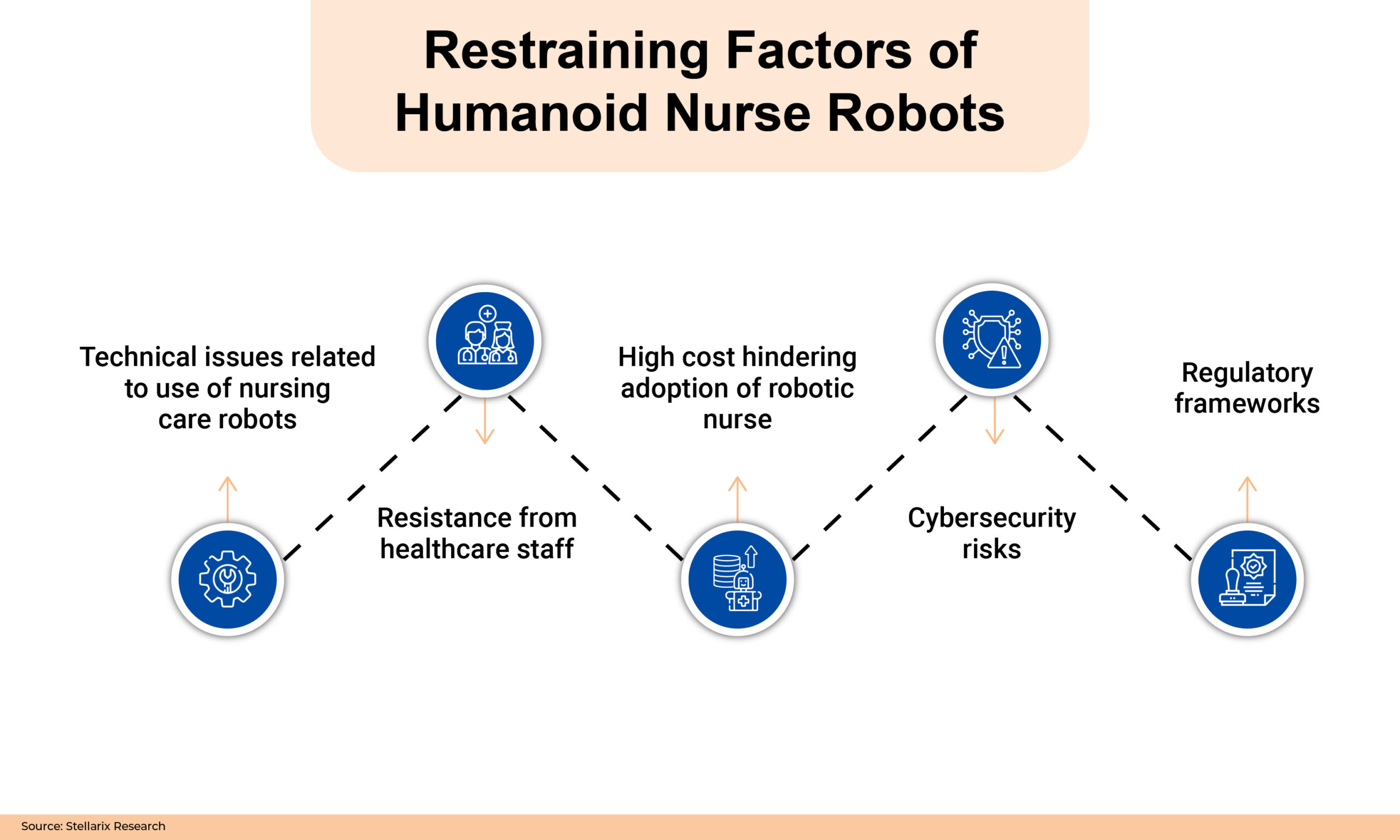
Restraining Factors of Humanoid Nurse Robots
Even humanoid carebots come with problems of their own. Some people may feel uneasy about dealing with machines in a health setting. The cost implication of implementing these technologies could be high, limiting their availability in some facilities. Following are a few challenges that prevent the humanoid carebots market from growing:
- Technical Issues Related to the Use of Nursing Care Robots: Enabling an understanding of the capabilities and limitations of robots to avoid performing tasks that the programming or training has not supported.
- Resistance from Healthcare Staff: Addressing concerns and biases around using humanoid robots in healthcare settings so that patients and healthcare professionals feel comfortable interacting with them.
- High Cost Hindering Adoption of Robotic Nurses: For most health organizations, robots are too costly to develop, acquire, and maintain. The initial investment, maintenance, and training costs are high and cannot be justified by the benefits derived.
- Cybersecurity Risks: Employing robust cybersecurity measures to block unauthorized access, hacking, or breaches that may compromise patient confidentiality or weaken the robot’s performance.
- Regulatory Frameworks: Regulatory guidelines must be defined to govern how the humanoid nurse robot is designed, deployed, and used so as not to compromise patient safety and medical ethics.
Under Developed Technologies
Researchers and developers are exploring several solutions to address the issues associated with humanoid nurse robots. For example, developing emotional intelligence in these robots will help them understand patients’ emotional needs more and react accordingly. A strict set of regulatory laws and guidelines established for humanoid nurse robot use should lead to their ethical and responsible deployment in healthcare settings.
An artificial brain for the humanoid nurse robot represents a complex system that is advanced in technologies such as machine learning, natural language processing, and computer vision. This brain is purposed to provide an ability for thinking, learning, and adapting to new situations for robots, as human brains do. There are multi-layers employed by robots, including sensors that capture data from the environment, processing units that analyze and interpret this data, and actuators responsible for controlling the robot’s movements. The state-of-the-art algorithms implemented in the brain enable it to learn from experience and, based on that experience, recognize patterns to make independent decisions. This allows the robots to execute patient assessment, diagnosis, and treatment planning, among others, besides responding to the changing needs of the patients and the environmental demands.
Future of Humanoid Carebots
Humanoid robot nurses are expected to form the main and critical backbone in delivering healthcare services as they change practices with potential benefits for patients and the service. When appropriately regulated and supervised, these robots are applied in various settings, from hospitals to homes. It is essential to address the benefits of this despite some challenges and ethical considerations about improvements in patient care and efficiency in health care.
There is more development and diffusion of these robots into innovations where they will revolutionize health care services and the experiences in hospitals. By embracing these new technologies and surmounting the challenges, we can do much more toward creating a much more efficient, accessible, and patient-centered health system. Humanoid nurse robots have significantly advanced patient care through workload reduction and the quality enhancement of patient experiences. The possibilities are endless when technology meets compassion, leading to a much healthier future.
Let's Take the Conversation Forward
Reach out to Stellarix experts for tailored solutions to streamline your operations and achieve
measurable business excellence.