Heat Pumps: Future of HVAC
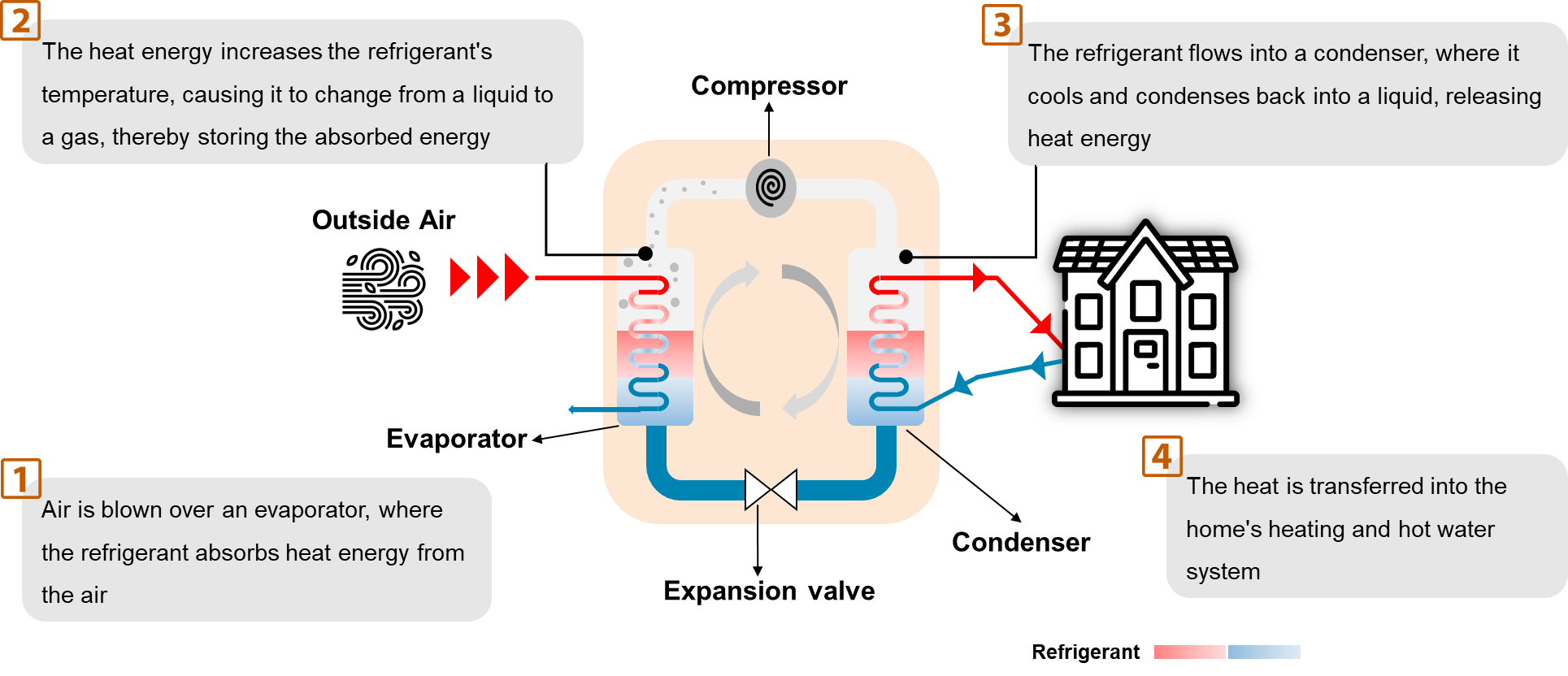
A heat pump is a system that heats our home or building, similar to a furnace or boiler, but without burning fuel. It operates using the same heat transfer process and equipment found in air conditioners. While air conditioners use a closed-loop refrigerant system to extract heat from indoors and release it outside, heat pumps reverse this process, drawing heat from the outdoor air and transferring it inside.
Working Principle
The working of a heat pump is shown below:
Different Types of Heat Pumps
The different types of heat pumps are as follows:

Why Heat Pump Is The Future of HVAC?
Heat pumps are emerging as the future of HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) due to their energy efficiency, environmental benefits, and adaptability to heating and cooling needs. Here’s why heat pumps are positioned to revolutionize the HVAC industry:
1. Energy Efficiency
Heat pumps are far more efficient than traditional heating systems, such as furnaces or boilers, because they move heat rather than generating it using combustion. For every unit of electricity used, heat pumps can deliver 3-4 times more energy, making them highly efficient compared to conventional systems.
2. Dual Functionality: Heating and Cooling
Unlike conventional HVAC systems, heat pumps can provide heating and cooling in a single system. This eliminates the need for separate air conditioning and heating systems, simplifies installations, and reduces maintenance needs.
3. Reduced Carbon Footprint
Heat pumps operate on electricity and don’t rely on burning fossil fuels, making them a cleaner and more sustainable option. With the growing use of renewable energy sources like solar and wind, heat pumps are becoming even more eco-friendly, helping to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
4. No Use of Harmful Refrigerants
Traditional HVAC systems often use refrigerants like hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), contributing to global warming. Recent advancements in heat pump technology, such as CO2-based refrigerants and solid-state electrocaloric or shape memory alloy systems, eliminate or reduce the need for these harmful substances, making them more environmentally responsible.
5. Adaptability to Various Climates
Technological improvements have made heat pumps effective in a broader range of climates, including very cold regions. New cold climate heat pumps are designed to work efficiently even in freezing temperatures, overcoming a traditional limitation of earlier heat pump models.
6. Cost Savings
Although heat pumps may have higher upfront costs, their operational efficiency leads to significant energy savings over time. With growing energy costs and incentives for renewable energy, heat pumps provide long-term financial benefits for homeowners and businesses alike.
7. Government Support and Incentives
Governments worldwide are increasingly incentivizing the adoption of heat pumps through rebates, tax credits, and other support programs as part of efforts to meet climate targets. These policies make heat pump installations more affordable and encourage widespread adoption.
8. Integration with Renewable Energy
Heat pumps can easily integrate with renewable energy sources like solar panels, further reducing their energy costs and carbon footprint. When paired with energy storage systems, heat pumps can operate independently from the grid during peak times, maximizing efficiency and sustainability.
9. Future-Proofing Against Energy Regulation
As regulations on energy efficiency and emissions become stricter, heat pumps provide a future-proof solution. Their reliance on electricity and compatibility with renewables make them a resilient option in a market that is shifting away from fossil fuel-based systems.
10. Technological Advancements
Innovations in solid-state heat pumps, such as those using electrocaloric effects or shape memory alloys, promise even greater efficiency and environmental friendliness. These emerging technologies could soon replace traditional compressor-based systems, making heat pumps more versatile and efficient.
Recent Innovation in Heat Pumps
Recent heat pump technology innovations drive improved efficiency, sustainability, and performance. Some of these technologies are listed below:
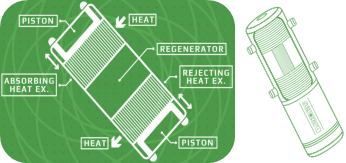
Refrigerant–free Heat Pump
Sencera, an American company, has developed a refrigerant-free heat pump using the Stirling thermodynamic cycle. It uses a Stirling thermodynamic cycle rather than the current vapour-cycle systems. This system transports the working gas between a heat-absorbing exchanger and a heat-rejecting exchanger. The pressure and volume of the working space vary sinusoidally, with a time difference between their phases, which forms a Stirling thermodynamic cycle. As a result, the gas changes temperature, becoming colder than the absorber at one stage of the cycle and warmer than the rejector at another stage. The system uses Nitrogen or Helium between a heat-absorbing exchanger and a heat-rejecting exchanger. This zero-carbon heat pump is 30% more efficient than traditional units and is used for heating and cooling.
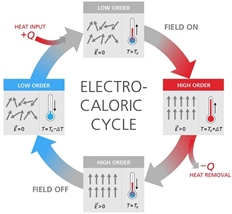
Solid-state Technology
Scientists in Germany have achieved a significant breakthrough in developing solid-state electrocaloric heat pumps, a promising alternative to traditional compressor-based systems. Unlike conventional heat pumps, electrocaloric models require no refrigerants and offer the potential for greater efficiency. Researchers at the Fraunhofer Institute for Applied Solid State Physics IAF have created an ultra-efficient circuit topology for voltage converters, achieving over 99.74% electrical efficiency, which is crucial for improving the overall performance of electrocaloric heat pumps. While conventional heat pumps operate at around 50% of the physical Carnot limit, electrocaloric heat pumps could theoretically reach up to 85%. However, this depends largely on advancements in power electronics, such as the Fraunhofer team’s innovation.

Acoustic Heat Pump
Equium, a French company, has developed a heat pump that uses sound energy to exchange heat with solid substances. It works with 3 disciplines: thermal, acoustics, and fluid mechanics. Acoustic waves are autonomously generated and amplified either through temperature gradients or by electricity. These waves perform compression and expansion tasks like a piston in a heat engine or compression machine, which makes it possible to achieve highly efficient heat pumping without moving parts or the use of greenhouse refrigerant gases.

Shape Memory–based Heat Pump
Exergyn, a United Kingdom company offers an innovative shape memory alloy (SMA) technology without relying on planet-polluting F-gas refrigerants, which are commonly used in most HVAC systems today. Shape memory alloy is made from nitinol and nickel-titanium alloys. There are two stages in this technology: compression and expansion; upon compression, heat is generated, and on expansion, cooling is generated. This technology is zero GWP, non-toxic, non-flammable, and cost-effective, opening up new possibilities for energy efficiency. This technology can be used in the Automobile, marine, and Aerospace Industries.
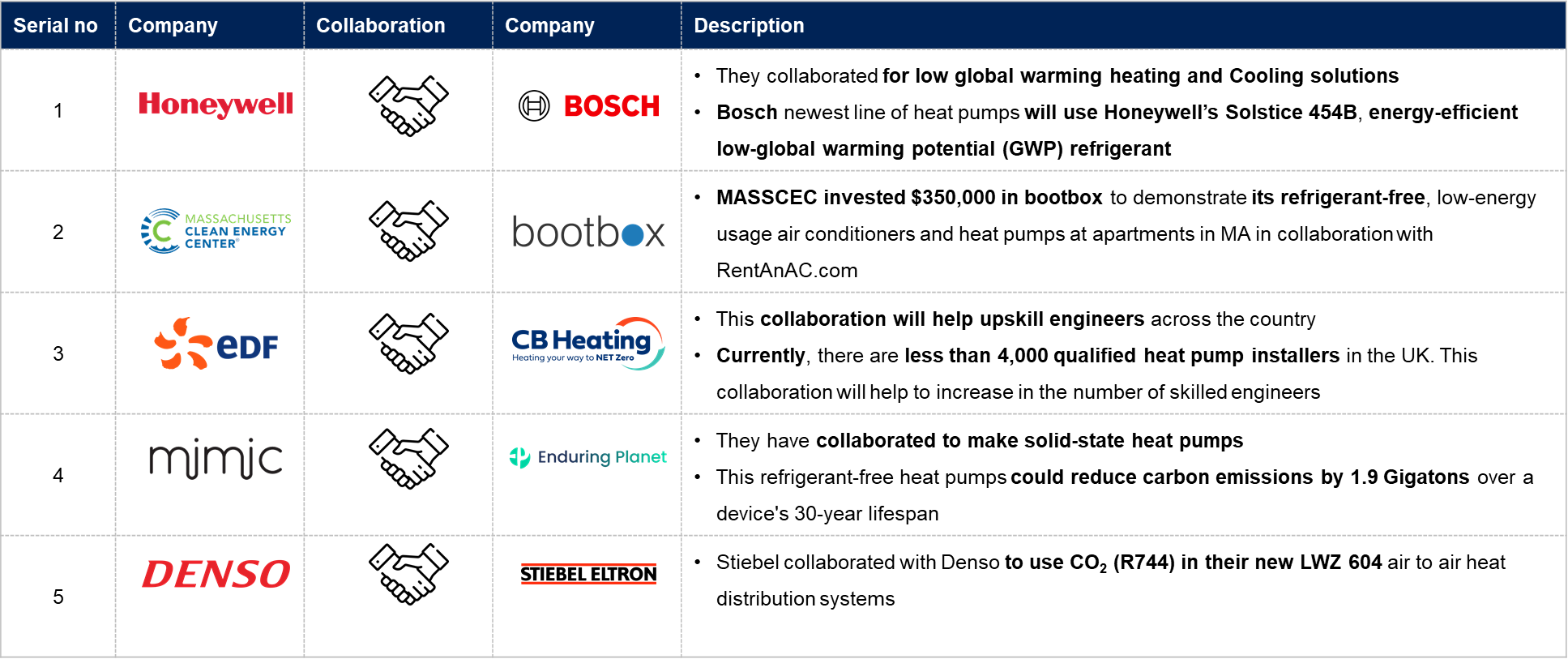
Prominent Key Players and Collaborations

ConnectM’s AI-driven heat pump system optimizes home heating and cooling, reducing energy costs and carbon footprint. Integrated with the Energy Intelligence Network, this innovative system leverages IoT technology and an AI engine to ensure peak performance and efficiency. It features predictive maintenance and real-time monitoring for optimal performance and is designed to reduce noise levels, ensuring a comfortable indoor atmosphere.
Government Initiatives to Promote Heat Pumps
Governments around the world are increasingly recognizing the importance of heat pumps in reducing carbon emissions and improving energy efficiency and are implementing various initiatives to promote their adoption. Some of the key government initiatives for installing heat pumps include:
1. Financial Incentives and Rebates
- United States: The U.S. federal government, through programs like the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA), offers tax credits of up to 30% for heat pump installations, capped at $2,000 annually
- Europe: Under the Renovation Wave initiative in the European Union (EU), governments are providing subsidies to replace fossil fuel-based heating systems with heat pumps as part of efforts to meet climate goals. Countries like Germany, France, and the UK offer grants and rebates
- Germany has a specific subsidy program under the Federal Funding for Efficient Buildings (BEG), offering grants covering up to 35% of the installation costs for heat pumps
- In the UK, the Boiler Upgrade Scheme (BUS) offers grants of £5,000 to homeowners who are replacing traditional gas boilers with heat pumps
- Canada: The Canadian government offers rebates through the Greener Homes Initiative, providing up to $5,000 in grants for the installation of heat pumps in homes to reduce reliance on fossil fuels
2. Zero-Interest Loans and Financing
- France offers zero-interest loans under the Eco-PTZ program for homeowners to finance energy-efficient home renovations, including heat pump installations
- Sweden provides long-term, low-interest loans to help homeowners switch to heat pump systems, encouraging the transition away from oil and gas heating
- In the UK, some banks have introduced green mortgages with better interest rates for homes using energy-efficient systems like heat pumps
3. Building Regulations and Standards
- European Union (EU): Under the Energy Performance of Buildings Directive (EPBD), the EU mandates that all new buildings must be nearly zero-energy by 2025, and heat pumps are being promoted as a key technology to meet these stringent energy performance standards
- United Kingdom: The UK has established the Future Homes Standard, which will require all new homes built from 2025 onwards to be zero carbon-ready, with a strong push toward installing heat pumps in new buildings
- United States: Many states, including California and New York, have updated their building codes to encourage or require the installation of heat pumps in new construction as part of decarbonization efforts
4. Decarbonization and Climate Action Plans
- European Green Deal: The European Commission’s Green Deal aims to decarbonize buildings by reducing reliance on fossil fuels, with a target of 35 million heat pumps installed across Europe by 2030
- Clean Heat Standard (Vermont, USA): The state of Vermont introduced the Clean Heat Standard, encouraging the use of cleaner heating systems like heat pumps to help meet greenhouse gas reduction targets
- Japan has set targets under its national decarbonization plan to increase the installation of heat pumps in residential and commercial buildings as part of its strategy to achieve carbon neutrality by 2050
5. Research and Development Funding
Governments are investing in R&D to drive innovation in heat pump technology:
- Horizon Europe: The EU’s research funding program is supporting projects that focus on improving the efficiency and affordability of heat pumps
- The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) is investing in advanced heat pump research as part of its Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy (EERE) program, focusing on developing heat pumps that perform efficiently in cold climates and use low-GWP refrigerants
6. Public Awareness Campaigns
Governments are launching public awareness initiatives to educate homeowners and businesses about the benefits of heat pumps:
- In the UK, the government’s Heat Pump Ready program provides resources and guidance to help consumers understand heat pump technologies and how they can reduce energy bills and emissions
- In the EU, the Renovate Europe campaign promotes heat pumps as a central component in building renovations to improve energy efficiency and combat climate change
7. Utility-Run Programs
Many government-backed utility companies offer programs to incentivize heat pump installations:
- In the U.S., programs like Mass Save in Massachusetts provide rebates for heat pump installations, while utility companies in states like California and New York offer financial support and free assessments for heat pump conversions
- In Canada, utilities such as BC Hydro offer rebates and incentives for heat pump installations as part of their energy efficiency programs
Conclusion
Heat pumps are transforming the future of heating and cooling with their superior efficiency, reduced emissions, and seamless integration with renewable energy. As technology advances and costs decline, they are set to become the cornerstone of modern HVAC systems, offering a clean, versatile, and energy-efficient alternative to traditional methods. Whether it’s the high efficiency of ground source systems, the flexibility of air source models, or the eco-friendly potential of solar-assisted solutions, heat pumps provide adaptable options for a variety of climates and applications.
With rising energy costs and a growing demand for sustainable solutions, heat pumps are well-positioned to become the standard for residential and commercial heating and cooling. Government initiatives, through financial incentives and supportive policies, are further accelerating their adoption, paving the way for a greener, more energy-efficient future. These advancements make heat pumps central to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and driving the global transition toward a cleaner, more sustainable HVAC landscape.
Let's Take the Conversation Forward
Reach out to Stellarix experts for tailored solutions to streamline your operations and achieve
measurable business excellence.



