Blockchain Technology Empowering Genetics
The field of genomics has a lot of potential to improve healthcare in the health industry. This article will cover topics like genomics, its challenges, and how blockchain technology helps solve them. Moreover, we will discuss the benefits of blockchain in this sector, the fundamental process flow architecture of data sharing, and who the major players are.
What Is Genomics?
There are some challenges in maintaining genomic data, like
- The growth in genetic data has brought some issues with data access, security, and privacy
- The individual genetic information is sold to other research companies without his knowledge
- By selling this genetic data, companies are earning huge profits without the permission of individuals
- Properly combining omics data with other available data makes diagnosing, tracking, and treating diseases more difficult
- The ability to retain genomic data safely. Moreover, high integrity represents a significant obstacle to extending human genome sequencing.
So, researchers use blockchain technology to tackle this issue and simplify data operations. It provides unique health-related information about each individual in a non-invasive way and offers excellent data confidentiality and integrity for genomic data, which is particularly sensitive and important.
Impact of Blockchain Technology on Genomics
Blockchain plays a significant role in healthcare, particularly in genomics. If the technology is applied more widely in genomics, scientists or researchers will be able to better understand disease causes and develop better therapies and treatments for various diseases while maintaining privacy and security. The below figure shows some of the advantages of Blockchain in Genomics.
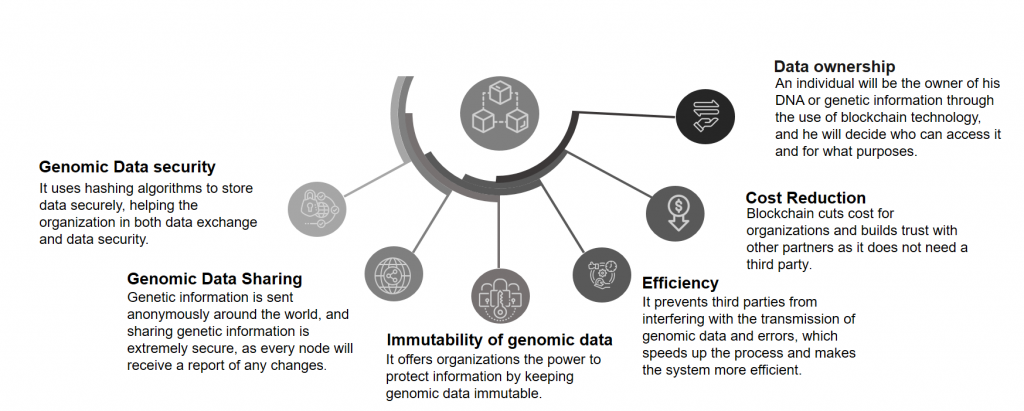
Architecture for Blockchain-based Genomic Data
The steps of the blockchain’s application in genomics are described below with a flow diagram.
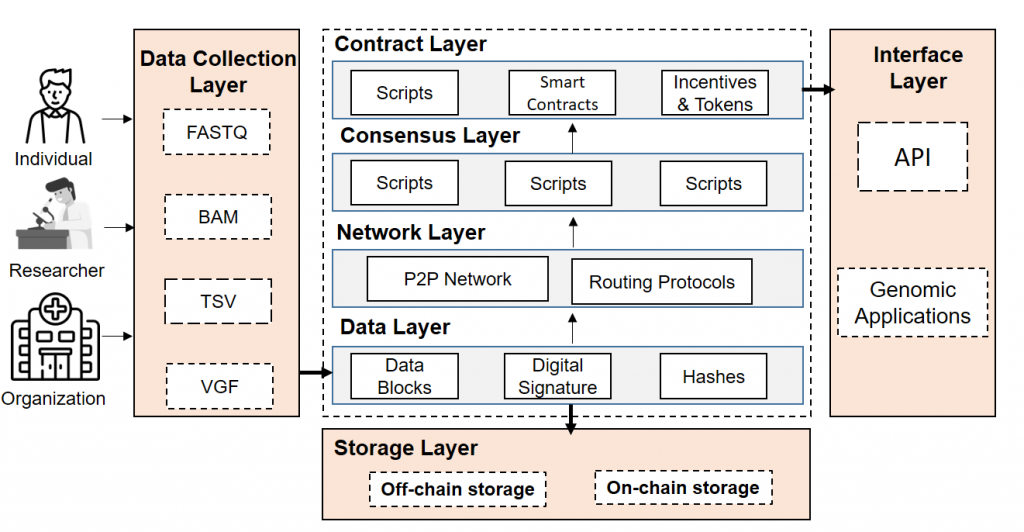
- Each node in the first layer of the architecture is in charge of gathering and sorting genomic data, which arrive in various formats, including BAM or FASTQ.
- These system nodes represent an individual, a group of researchers, or an organization that wants to share genetic data.
- After the collection, the data is sent to the data layer for applying blockchain operations like cryptographic hashing and digital signature to maintain the security and privacy of genomic data. Then, it is sent to the next layer for storage.
Storage Data
- In the storage layer, the data can be stored in different ways depending on the requirements of either on-chain or off-chain storage
- By adding the data (in binary format) to the transaction, we can achieve the storage of data on-chain, effectively integrating it into the chain itself. This will eventually make the data immutable and highly available as the transaction will be distributed to all nodes in the network.
- Since all nodes in the network have public access to on-chain data, the privacy of the stored data must be considered.
- On-chain storage is most suitable for
- Small data types require immutable and tamper-proof storage. Additionally, it includes meta-data and small genomic data
- Small data types such as audit trails and observations of gene-drug interactions are effectively stored on-chain
- The genome data stored in files such as BAM or VCF are large and difficult to store on-chain
- Off-chain storage is used for large data files or for data that requires strict access control. In these cases, either cloud storage or other decentralized file systems, such as IPFS, are used.
- Off-chain storage techniques involve hashing data, which results in a small string. This string can be efficiently stored in blockchain transactions or in a smart contract. The actual data is then stored in a centralized or decentralized storage system.
- The data is then broadcasted to the network using a specified network protocol such as P2P and Routing Protocol
- Using a consensus technique like Proof-of-Work, the network’s nodes reach an understanding of the blockchain’s current state on the consensus layer
- The contract layer is where smart contracts are written. Moreover, deployed to facilitate various application functions
- The presentation layer is responsible for interacting with smart contracts and blockchain
Blockchain Technology in Market Activities
Some of the top companies offering blockchain technology solutions in Genomics include GenoBank.io, Nebula Genomics, SimplyVital Health, Zenome.io Ltd. LunaDNA, LLC, Encrypgen, Digital DNAtix Ltd. Longenesis Ltd, WuXi Nextcode Genomics, Shivom Ventures Limited, Genecoin, Embleema, Zenome, Genesy and many more.
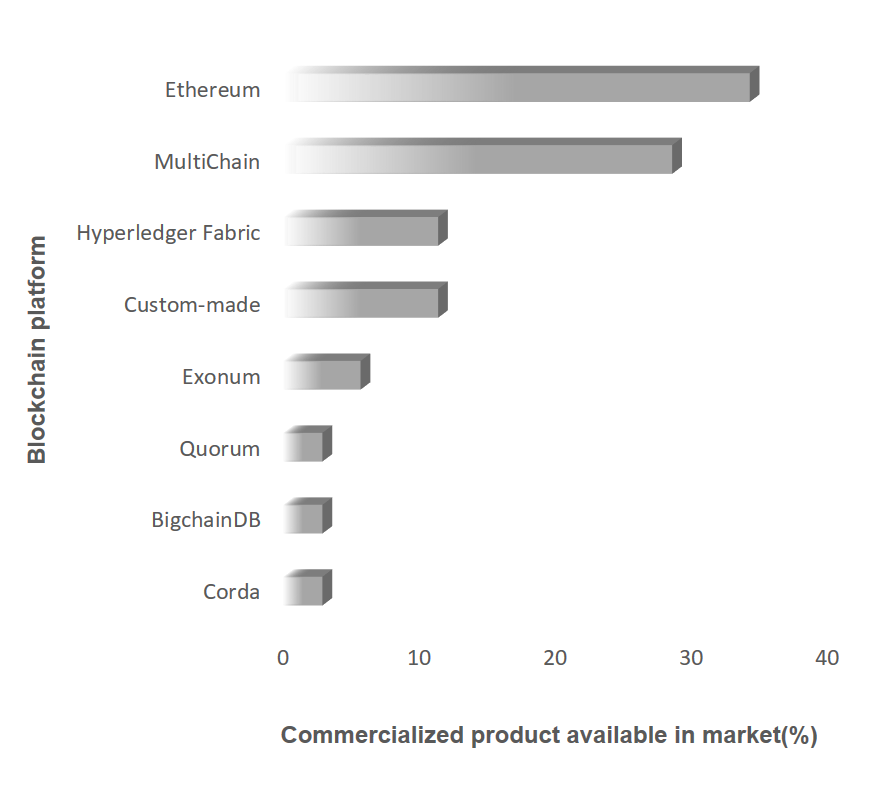
The following section includes some of the prominent commercialized blockchain solutions providers, IP market analysis, and future outlook in the life science industry.
1.) Company’s Products
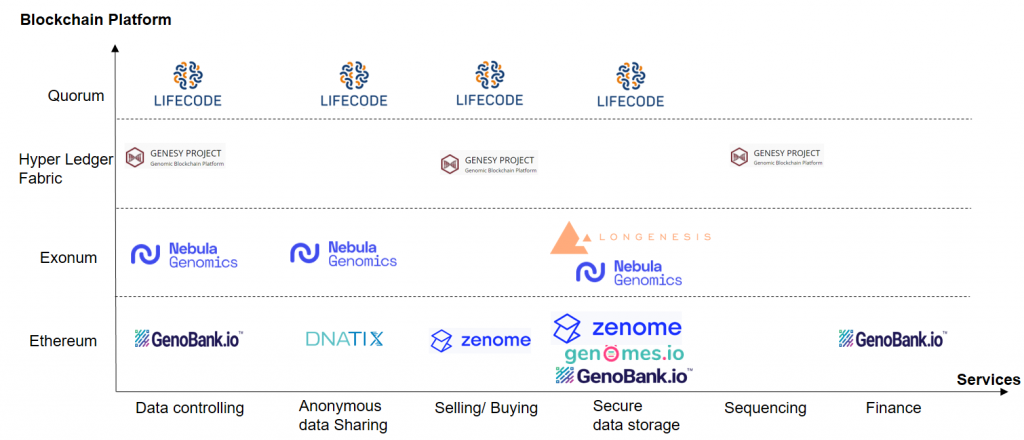
- Nebula Genomics created a multiparty access control system that is Exonum blockchain-enabled. Using a blockchain record, encrypted storage, and in-depth analysis in a black box environment provides user-controlled access to genetic data.
- Longenesis uses the Exonum blockchain platform for patient consent at healthcare organizations. It also offers HIPAA- and GDPR-compliant data storage options.
- GenoBank provides a safe platform for processing data using the Ethereum blockchain and controlling genomic data using a DNA crypto wallet.
- Zenome uses the Ethereum blockchain to provide secure storage, sell access to genetic data, and buy genetic services
- Genomes.io is an Ethereum-based blockchain platform that offers a secure DNA vault for individuals and financial benefits for (anonymous) donations to medical research.
- DNAtix uses the Ethereum blockchain to offer services like anonymous genetic testing and anonymous genomic data reports. Moreover, it allows individuals to communicate anonymously with those who share their genetic traits.
- Genesy offers sequencing services, genetic data access for sale, and a blockchain-based ecosystem for exchanging genomic data using the Hyperledger blockchain.
- LifeCode.Ai uses the Quorum blockchain, offering personal health data ownership, a data sharing mechanism, and safe, decentralized health data administration.
2.) IP insights
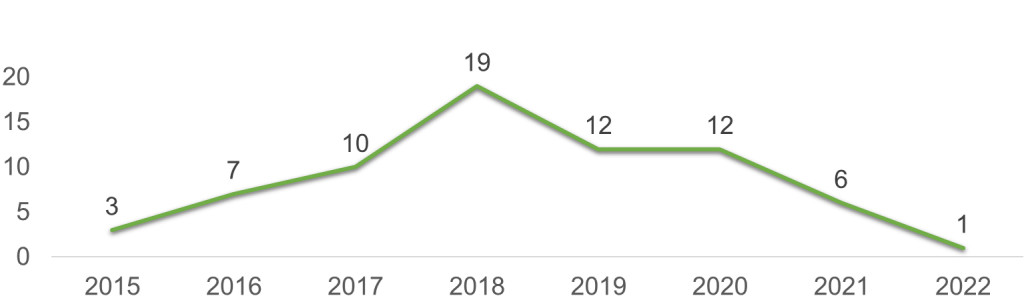
The charts below represent the priority year distribution of the patents filed in Blockchain in Genomics.
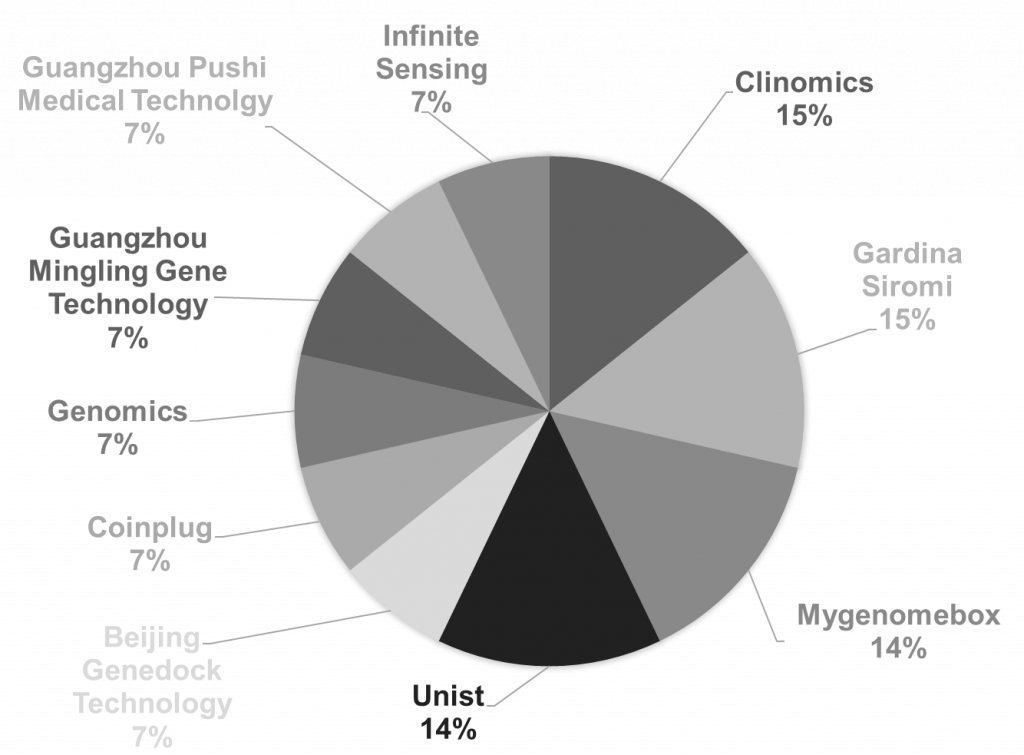
The top assignees working in the Genome blockchain are shown in the chart below-
3.) Future Perspectives
The market for blockchain in genomics was USD 40.62 million in 2020. It is expected to reach USD 2,086.26 million in 2028, with a CAGR of 65.8%. Also, in terms of regional markets, North America dominates the global blockchain in the genomics market.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology has enormous potential to build future systems that will shape the medical world in new ways. Researchers and industry experts are still in the early stages of utilizing blockchain technology in genomics. They have yet to explore many areas that could potentially change the current genomic ecosystem. Moreover, blockchain will increase trust, process automation, and data sharing. Additionally, blockchain offers design incentives that will facilitate the sharing, storing, and processing of human genomic data in a fair way.
Let's Take the Conversation Forward
Reach out to Stellarix experts for tailored solutions to streamline your operations and achieve
measurable business excellence.



