Blockchain in Food Industry: Supply Chains
To make the Agriculture industry more open and accountable, new methods and innovations are needed as part of current agricultural development and reform. When panic buying occurs, the supply network lacks accurate information to reflect the purchase behaviors, which makes quick responses impossible. Efficient coordination among parties at a global scale is necessary to generate quick and appropriate responses in real-time and reduce time spent in red-taped bureaucratic procedures. These lessons emphasize the necessity of using blockchain technology to enhance the food industry’s supply chain systems.
Some top companies offering blockchain technology solutions to the food industry include IBM Corporation, Ripe Technology Inc., AgriChain Pty Ltd., Ambrosus, arc-net, Etherisc, Seedsbit, Unova, Agriledger, Demeter, FoodCoin Ecosystem, TE-Food International GmbH, Provenance, OwlTing.
What is Blockchain, and How Does it Help the Food Industry?
Blockchain is a decentralized platform that allows one to gain control of one’s own data and establish secure and sometimes anonymous access to applications over the internet. In the food industry, Blockchain is transforming ICT (Information and communication technology), which can revolutionize how data is utilized in agriculture. It is becoming a decentralized and secure infrastructure that enables data storage, visibility, and resistance to substitution. It helps the food industry in the following ways-
- Improve transparency in agriculture-food supply chains
- Providing farmers and businesses with access to agricultural financial services
- Generating smarter market data for better decision-making with data science in agriculture
- Legally proving certifications to relevant authorities.
- Tracking a product along its entire path from farmland to consumer end.
- Simplifying all stages of the agricultural supply chain
- Improving food safety and eliminating counterfeit items
- Reducing financial risks and promoting inclusive trade
Basic Building Block
1.) How Blockchain Works?
- In blockchain technology, the integration of advanced computational and cryptographic techniques in a distributed data structure enables the creation of a digital trust system in an untrusted environment
- The hash function serves as the fundamental component for data authentication, creating distinct IDs through its algorithmic method
- To protect data integrity, the stored chain format includes inserted hash values to check for any alterations in the data
- Data senders and receivers in stored transactions use a digital signature to confirm their true identities
- The consensus mechanism involves all computer nodes and minimizes the potential risks of data being manipulated by minority attackers.
The image below provides information about the process of Blockchain technology. It focuses on how it helps in different phases of the food chain process.
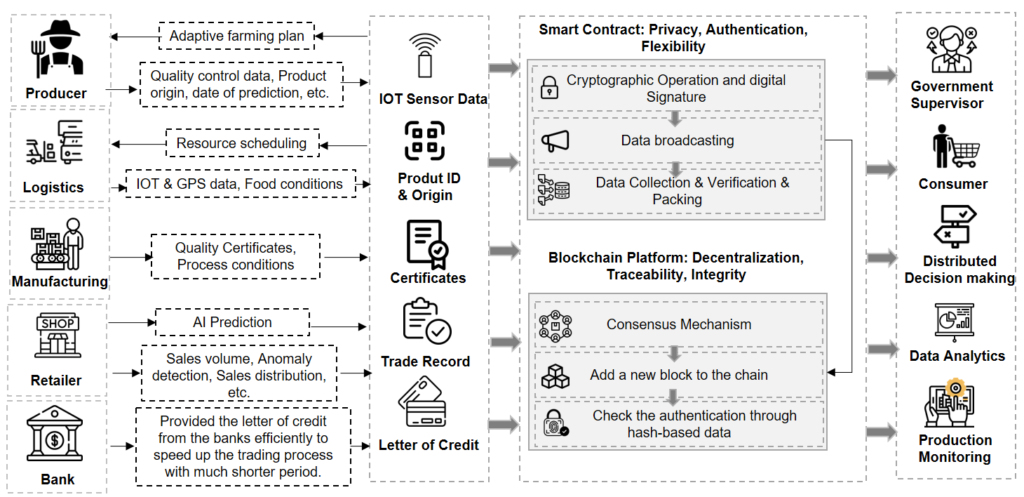
2.) Blockchain in Different Phases of the Food Chain Process:
- Production: Monitors and validates every stage of agricultural production, including planting, fertilizing, and applying natural pesticides
- Weather & Forecasting: Obtain real-time weather data from weather stations throughout the area. Users examine the data by selecting the location.
- Supply chain: Manage the entire supply chain from production to distribution, alert regulatory agencies in the event of fraud, and solve food safety concerns.
- Finance: It offers cheap, effective crop insurance solutions, ensuring that many farmers are covered and receive timely crop insurance benefits.
3.) Food Authentication and Provenance Traceability:
- Users employ blockchain traceability systems to collect data and transactions according to the requirements of the applications
- Storing all relevant information on the food product’s origin and movement with little chance of tampering is the most effective technique to improve food safety and decrease fraud and food scandals
- The tracking of every manufactured product item in real-time is achieved through corresponding digital tokens
- To ensure better information traceability, upload various event types specified in the Electronic Product Code Information Services (EPCIS) specification, including Object Event, Aggregation Event, Quantity Event, and Transaction Event, into the blockchain. This is done to provide unique codes for items and their primary transaction events.
- The integration of product certification documents into the transactions ensures conformance with health and safety standards
- Traceability systems, such as IoT sensors or RFID tags, automate the data collection, reduce manual mistakes for data integrity, and improve the efficiency of the data on-chain process
4.) Smart Contracts:
- A smart contract executes a blockchain system by incorporating states, values, addresses, and logical operations as essential components
- It helps simplify the entire process and improve supply chain transparency. It is necessary at the business model layer of a system to execute contracts automatically and increase model efficiency.
- It uses predefined rules to obtain peer endorsement from the blockchain network and receives transaction requests as input to begin the business logic.
- Once the system receives all the endorsements, it contacts the ordering services to validate them and add the verified transactions to blockchain blocks
- DApps can query the states of the on-chain data since the records saved in the blockchain are immutable, making it impossible for anyone to alter them
5.) AI-based Decision Support Systems
- The integration of blockchain techniques with Artificial Intelligence and machine learning enables the system to achieve higher efficiency.
- Up-chain parties, including producers, manufacturers, and logistic companies, explore the uploaded shopping data in the system for better coordination and resource allocations. So, a closed loop is formed when the retailer’s/customers’ data are stored in the blockchain.
- Using AI-based retail sales prediction helps to reduce on-chain data. Retail forecasting has offered an opportunity to optimize retailers’ planning to maximize their profit margins. That’s done by setting reasonable inventory levels based on the popularity of food products.
Market Activities
The following section includes some of the prominent commercialized blockchain solutions providers, collaborative ventures, IP market analysis, and future outlook in the food industry.
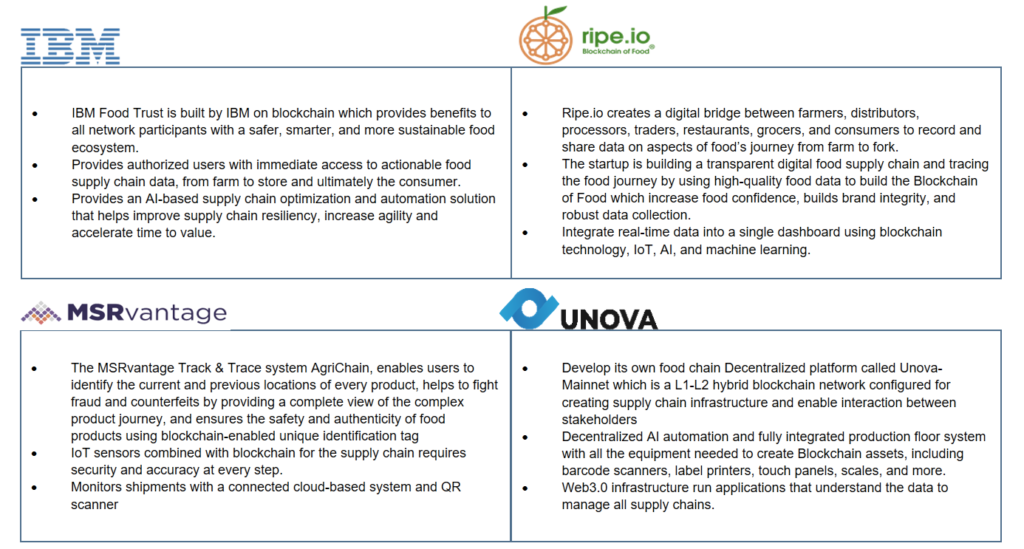
Joint Ventures
Ant Group (Ant Financial) and Bayer jointly develop a blockchain-based blockchain system for agricultural product monitoring, including AI and IoT.
- To increase efficiency, improve farmers’ income, ensure the production of high-quality food, and aid in the digitization of agriculture.
Demeter and Seedsbit combined and built the Persephone system, a Blockchain solution for agriculture applications.
- It incorporates smart contracts and other blockchain features from the SeedsBit traceability platform into the main Demeter project.
- Its traceability extends from the field to HoReCa, which utilizes numerous blockchain platforms and operates with many supply chains
BASF and arc-net collaborate to use blockchain technology for livestock sustainability and provide transparency in the agri-food industry.
- BASF’s calculation tool AgBalance Livestock considers the life cycle impact of all inputs and outputs of animal protein production, i.e., feedstuff seed production to animal farming and manure management to slaughter.
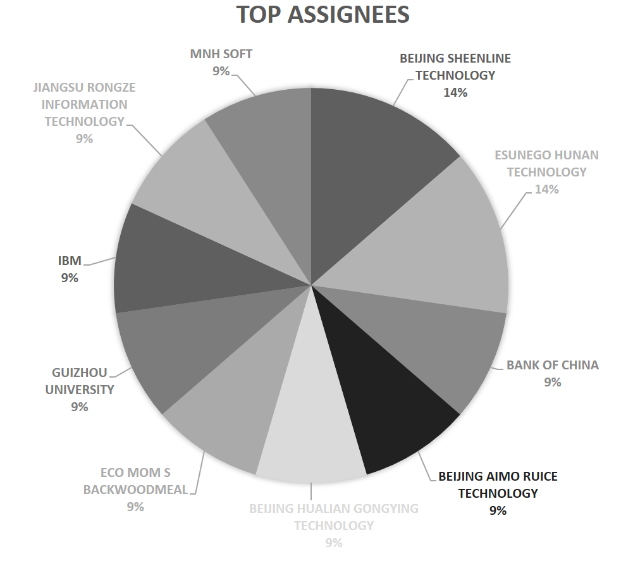
IP Insights
The chart below shows the top assignees working in the food industry’s blockchain-
Future Perspectives
The value of blockchain in the food and agriculture industry on the global market, which was around 32.2 million US dollars in 2017, is expected to reach over 1.4 billion US dollars by 2028.
Conclusion
The food and agriculture industries now have a secure and open platform due to the deployment of blockchain technology. Interestingly, blockchain in the healthcare and pharma sector is offering revolutionizing solutions. It is reshaping the whole sector to solve the food crisis in this century. It plays key roles in many aspects, from the farm to the folk. That includes ensuring data privacy and integrity by combining smart farming and precision agriculture techniques to improve farm productivity. It creates a more efficient food supply chain by establishing trust among involved parties, thus simplifying the process, and it enables farmers to maximize their profit via a trusted platform. Overall, it adds great value to all stakeholders in the entire agricultural sector. Since customer satisfaction depends heavily on transparency, more stakeholders will begin to realize the blockchain’s great potential in the future as its use in the food supply chain expands.
Let's Take the Conversation Forward
Reach out to Stellarix experts for tailored solutions to streamline your operations and achieve
measurable business excellence.



