AI-Driven Diagnostic Tests in Mental Health Disorders
Mental disorders are a significant global health issue impacting millions of people across the world. Mental health disorders, in the sense of varying conditions like depression, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, and anxiety, have made diagnosis and treatment complex tasks. Recently invented artificial intelligence-based technologies have become real alternatives to traditional means, including but not limited to mental disorder diagnosis and management.
Enhancing and complementing traditional modalities for addressing such issues, the AI diagnostic test has proven to be a robust alternative method that facilitates new approaches to detecting mental health problems at an earlier stage, prescribing appropriate treatments, and closely monitoring their progress. In mental health, AI-powered diagnostic tests are advancing at a fast rate and have the potential to change the domain of mental health care radically.
The Rise of AI in Mental Health Diagnostics
Mental health disorders like bipolar disorder and schizophrenia often show complex overlapping symptoms that make diagnosis difficult. The majority of traditional diagnoses rely heavily on clinical interviews, questionnaires where patients write their responses, and visual checks that may be influenced by the patient’s perspective and the clinician’s experience. Artificial intelligence is being used to complement traditional approaches by adding objective, data-driven insights that can help improve how we diagnose and plan treatment. AI-based diagnostic tools use advanced algorithms and large datasets to make mental health diagnoses more accurate and efficient. This offers real promise in a field that has long struggled with subjective and inconsistent assessments.
Types of AI-driven Diagnostic Tests
Artificial intelligence-based diagnostic technologies for human mental care are becoming increasingly sophisticated, leveraging improvements in machine learning, NLP, and data analytics.
Here are some prominent types:
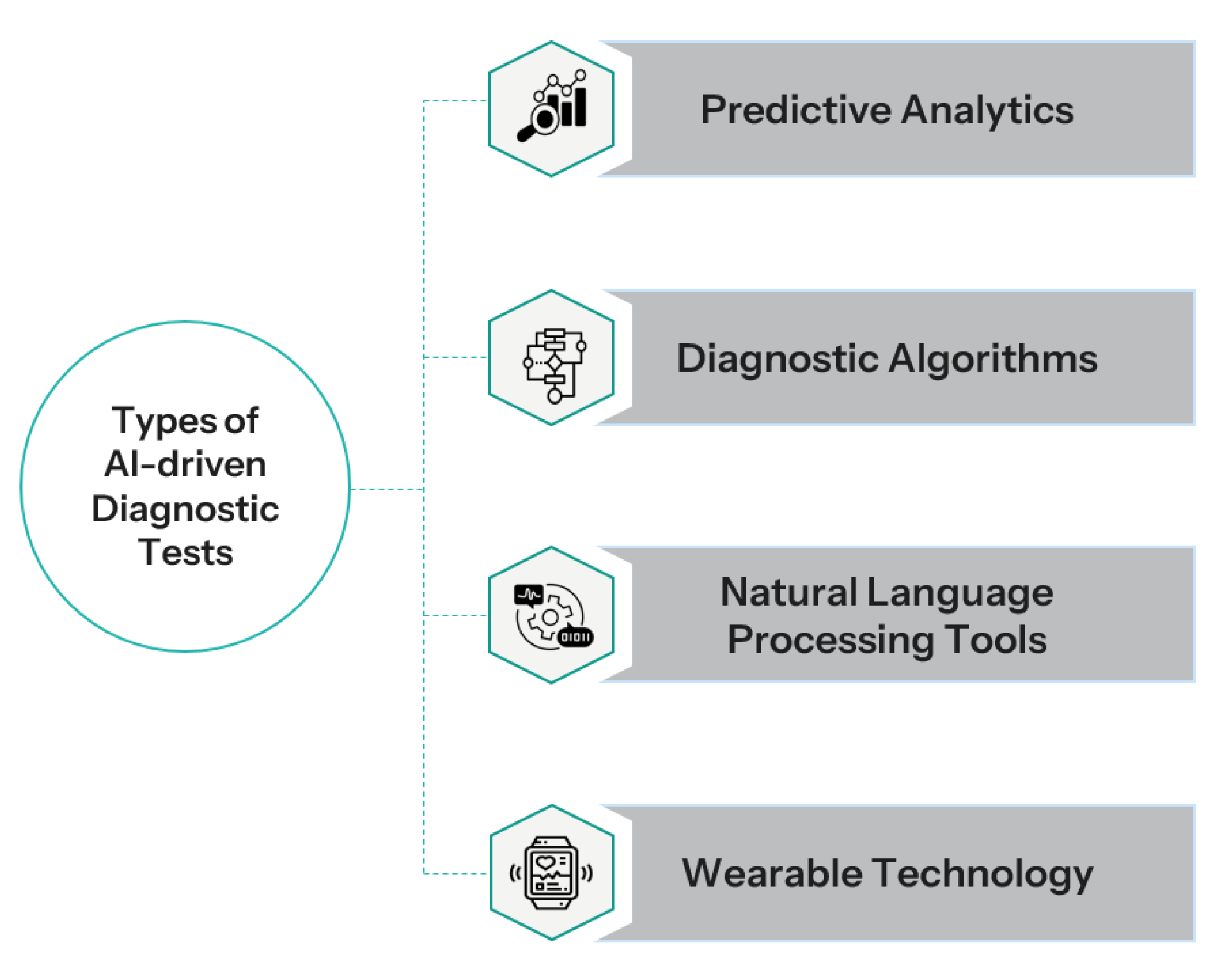
- Predictive Analytics: Predictive analytics utilizes past and present data to estimate the chances of developing mental health disorders. Using AI algorithms, one can uncover individual risks even before clinical indications set in, just by analyzing patterns within client data such as genetic information, lifestyle factors, and past medical history, among other things. For instance, early symptoms and lifestyle changes could aid in making predictions on the chance of getting depression or bipolar disorder, according to AI models that have been successful.
- Diagnostic Algorithms: In recent times, machine learning algorithms have been deployed in diagnostics. They have shown promising results while handling data from various information sources such as patients’ interviews, psychological tests, and even EHRs. Such algorithms can help mental health practitioners in the diagnosis of disorders by providing data-driven approaches to the problem and suggesting more likely disorders based on symptoms and the patient’s background. For example, AI tools are able to analyze voice and speech patterns, the use of hands or other body parts, and even writing to assess the presence of affective or psychiatric disorders.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) Tools: Language processing tools function on and analyze human language; therefore, one can extract significant concepts from patient interactions, medical records, or therapy notes. Using both spoken language and text for analysis, AI programs can recognize the distinction in language associated with psychological conditions, like some alterations of speech linked with schizophrenia or bipolar disorder. NLP tools are very useful in assessing how patients respond during therapy sessions and making modifications in their treatment plans in accordance with such assessments.
- Wearable Technology: Wearable apparatus with sensors gathers information regarding physiological and behavioral indicators; for example, it can track sleeping habits, body movements, and how often heartbeats change. AI algorithms can analyze the data and detect disorders in their early stages, and the mental health status. For instance, wearable devices can monitor variations in sleep patterns or activity levels that may indicate depression or anxiety symptoms.
Applications of AI-driven Diagnostics in Mental Care/ Health
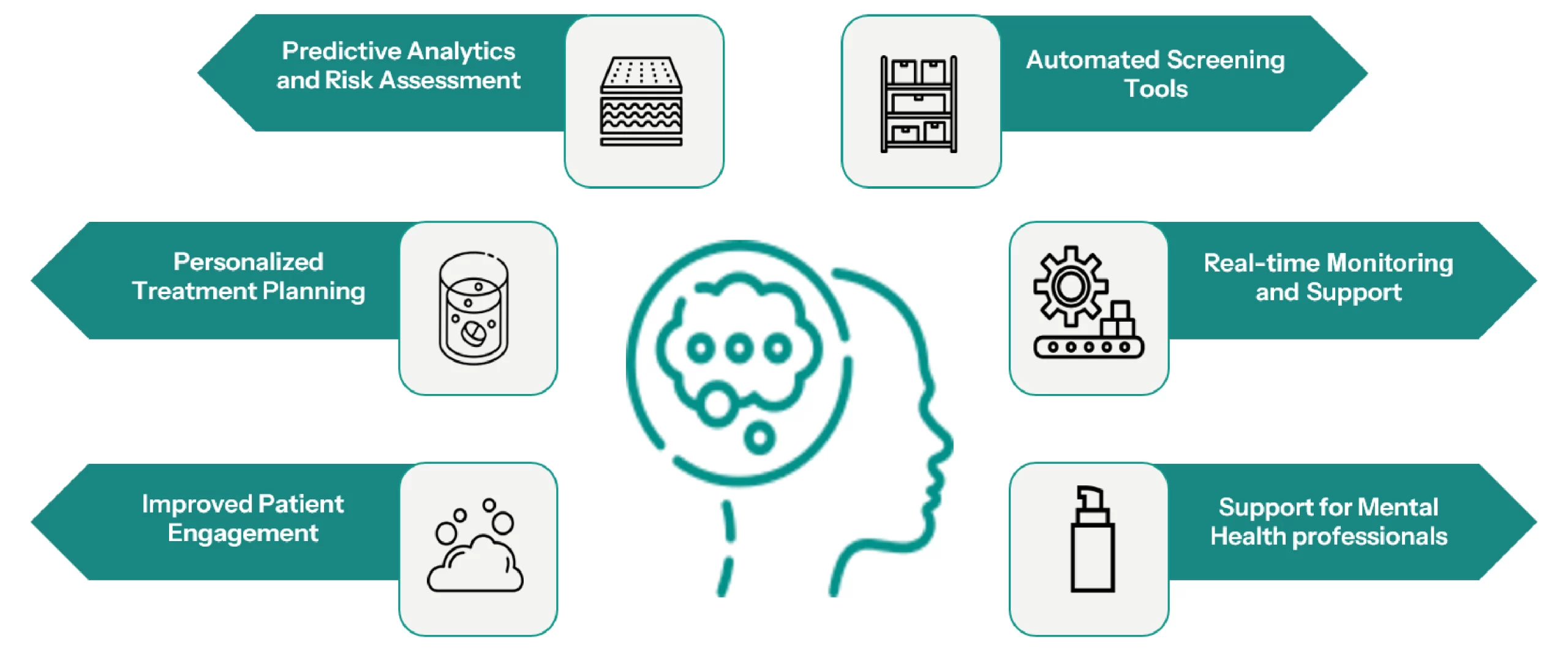
Artificial intelligence is vital for the early detection and treatment of human mental health. AI-powered diagnosticians can be applied in healthcare, including mental health problems. Here is an exploration of the topics:
- Predictive Analytics and Risk Assessment: AI can help make sense of complex data by spotting patterns that might not be obvious to humans. It can even estimate someone’s risk of developing a mental health condition by looking at things like their family history, daily habits, and environment. By identifying these risks early on, AI can play a big role in helping people get the support they need before problems become more serious.
- Automated Screening Tools: AI-based guides made for screening that can be used to estimate mental health problems like depression, anxiety, or bipolar disorder in their early stages. These tools frequently rely on algorithms to evaluate responses from surveys or behavioral observations. AI-powered chatbots serve as perfect examples of how they communicate with the patient to obtain data and give early diagnostic indications.
- Personalized Treatment Planning: Algorithms of artificial intelligence can be capable of creating individualized treatment approaches when relevant patient-related parameters such as past treatment history, genomic information, and behavioral aspects are present. One could say that the AI can evaluate the individual differences between patients and determine the most successful therapeutic regimen for the patient based on that intrinsic variability.
- Real-time Monitoring and Support: With the help of AI-powered wearables, it’s now possible to keep track of things like heart rate, sleep patterns, and activity levels around the clock. This real-time data can offer valuable insights into a person’s overall mental well-being. On top of that, AI-driven apps are being used to support mental health by tracking mood and behavior, and even recommending personalized self-care tips or coping strategies.
- Improved Patient Engagement: AI chatbots and virtual assistants are there to support patients, guiding them through their mental health journeys and motivating them to adhere to their treatment plans. With interactive sessions designed to meet individual needs, AI-powered platforms can deliver therapeutic content, including exercises from cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT).
- Support for Mental Health Professionals: In particular, navigational AI tools offer insights and recommendations to physicians, enabling them to make better choices in relation to the diagnosis and treatment. To accommodate the time spent attending to patients, mental health practitioners have been assisted by AI technologies in taking over tasks such as setting appointments and documentation.
Benefits of AI-Driven Diagnostics in Mental Health Disorders
Use of AI in diagnosing mental conditions can change how mental healthcare is done by improving its precision, accessibility, and personalization, and increasing the productivity and effectiveness of mental health services. The following are some of the main benefits that AI-driven diagnostics for mental health/ disorders can offer to mental health care:
- Increased Accuracy: Vast amounts of data are handled by AI algorithms accurately, reducing diagnostic mistakes and making mental health evaluations more accurate and dependable. Artificial Intelligence-based diagnostic examinations may enhance the accuracy of diagnosis because they can analyze intricate data sets, which manual processing is sometimes impossible for human doctors. Through intricate pattern recognition, these AI tools will eliminate the chances of misdiagnosis and guarantee that patients receive the appropriate treatment.
- Early Detection: AI can detect complex patterns and the level of risk in the engagement of individuals regarding their mental health, thus enabling timely treatment. To assist patients better and achieve positive treatment results, there is a need to ensure that mental health disorders are diagnosed at an early stage. This can be accomplished by the use of AI algorithms that allow for the assessment of specific measures and early signs associated with the occurrence of mental health problems, thus enabling prevention before such problems become problematic.
- Consistency: Tools powered by artificial intelligence ensure uniform valuations, thus mitigating variability and enhancing the accuracy of diagnosis across different practitioners and environments.
- Personalization: Artificial Intelligence has the potential to create specialized medical tests and treatment calendars for each patient by collecting personal information that may lead to more successful medical interventions. Using information about the patients and their responses to various treatments, AI can assist in formulating individualized treatment options for the patients. This personalization addresses several challenges, which improve the efficacy of the treatment and contribute to better outcome measures.
- Scalability: AI methodologies have the potential to efficiently analyze large volumes of data for diagnostic purposes in different populations around the world, rendering them an efficient solution in mental health.
- Increased Accessibility: Advanced AI-based diagnostic systems can render psychological treatment easily available to more people, as they allow for remote diagnosis and support physicians in areas that are less populated or economically disadvantaged.
Challenges and Considerations
AI-driven diagnostics for mental disorders show a lot of hope but carry several challenges and considerations. Tackling these concerns is vital to ensure the effective and moral adoption of AI in the provision of mental healthcare services. Several major issues have to be put into cognizance, as highlighted in the following section:
- Data Privacy and Security: Aid in diagnosing mental health concerns using AI has raised concerns about data privacy and security. To ensure that data is safe from anyone who is not authorized, patient data has to be protected from unauthorized access and misuse, in addition to regulations that protect data.
- Ethical and Bias Issues: Artificial intelligence algorithms depend solely on the information they have been taught. If the data used for training is partial or incomplete, AI devices will also have inaccuracies and prejudices. Addressing these ethical and bias issues is essential to ensure that AI-driven diagnostic tests are fair and equitable.
- Integration with Clinical Practice: The integration of AI-based diagnostic devices into practice settings requires attention towards their incorporation with existing state-of-the-art practices and workflows as well. If these technologies are to be encouraged in the daily clinical practices, the clinicians must be trained and supported on how to use them effectively.
- Validation and Regulation: For the safety, efficacy, and dependability of the diagnostic tests that integrate AI technology, these tests must undergo a thorough examination and validation process before they are issued to the general public. There have to be appropriate and specific protocols and procedures developed for the use of any AI tools to enhance service provision while preserving the safety of our patients.
- Cost and Accessibility: The costs associated with the development and deployment of AI-powered diagnostics are limiting for a number of patients and healthcare professionals. To prevent inequalities in the treatment of mental health, equity in the distribution of artificial intelligence systems is very important.
- Patient Engagement and Understanding: AI tools should be user-friendly and accessible to all patients with different levels of technological capability. Patients need to know how to use AI tools effectively and how these tools fit into their mental health care regimen.
Future Directions
The realm of diagnostics for mental health with the use of AI is increasing at a fast pace due to continuous investigations and enhancements, trying to deal with present-day obstacles as well as enhance the functions of such technologies. Further trajectories comprise:
- Advanced Algorithms and Models: Owing to the continuous evolution of machine learning and artificial intelligence-based algorithms, the acquisition and predictive performance of diagnostic tools will be improved. Scholars are developing novel methods to define intricate mental health disorders through the integration of multiple data sources.
- Personalized and Adaptive Systems: Personalized and adaptive systems that learn and change based on each individual’s information will be the focus of upcoming AI-based diagnostic instruments. This will help these devices to recommend treatments that are specifically catered to each patient dynamically and in real-time, thus yielding better results for them than before.
- Collaboration and Interdisciplinary Research: The collaboration of the practitioners in artificial intelligence, the healthcare providers, and the data scientists will be central in addressing ethical, legal, and practical concerns. The inter-disciplinary approach will help in identifying gaps and ensuring that there is AI development and utilization that is responsible.
- Global and Cultural Considerations: With the increasing use of AI-powered diagnostic tools, it is necessary to take into account the global and cultural variations in mental health. The success and influence of these technologies depend on their ability to adapt to various demographic groups and situational contexts.
Conclusion
AI-oriented diagnostic examinations can transform mental health treatment by enhancing diagnosis precision rates, early recognition, and individualizing therapy. There are difficulties and challenges within this domain that need to be addressed, including ethical concerns; however, the potential benefits from such inventions are numerous. Going forward, an ongoing inquiry into these developments shall necessitate interdisciplinary cooperation and careful execution to unleash the maximum utility of AI in mental health diagnosis and care for people suffering from psychological conditions.
Let's Take the Conversation Forward
Reach out to Stellarix experts for tailored solutions to streamline your operations and achieve
measurable business excellence.