Adaptive & Intelligent Manufacturing: The Future of Flexible & Autonomous Production
Flexible and autonomous production refers to the level of flexibility in manufacturing different types of products or performing various operations. It combines flexible production systems and automation to improve productivity, efficiency, and other aspects of the manufacturing process. This approach allows manufacturers to easily adapt to changes in the quantity and variety of products they produce. As customer demands shift, companies should maintain a diverse product lineup, which necessitates flexible production lines and machinery. Autonomous production enhances this flexibility by using artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to develop self-optimizing or self-regulating processes, reducing the need for human input. With flexible and autonomous production, businesses can enhance operational quality, ensure greater sustainability, and improve safety in manufacturing.
Types of Flexibility & Autonomy in Manufacturing
Flexibility in production can be classified into various clusters, including production, volume, process, scheduling, and resource allocation, which can be further categorized into machine flexibility and routing flexibility.

The types of flexibilities are as follows-
- Machine Flexibility: The ability of a machine to produce different types of products or to perform a wide range of operations
- Production Flexibility: It refers to the ability of the manufacturing system to quickly adapt to variations in production requirements
- Volume Flexibility: The ability to adjust the volume of production based on fluctuations in demand
- Routing Flexibility: The ability to utilize alternate machines to ensure the continuity of the production process despite any disruptions or breakdowns
- Resource Allocation Flexibility: The ability to adjust the usage of resources such as machines, labor, and materials to meet the changing demands in production
Production automation is classified into various types based on the level of human intervention required, application, and complexity, etc., wherein the key autonomy levels are demonstrated below:
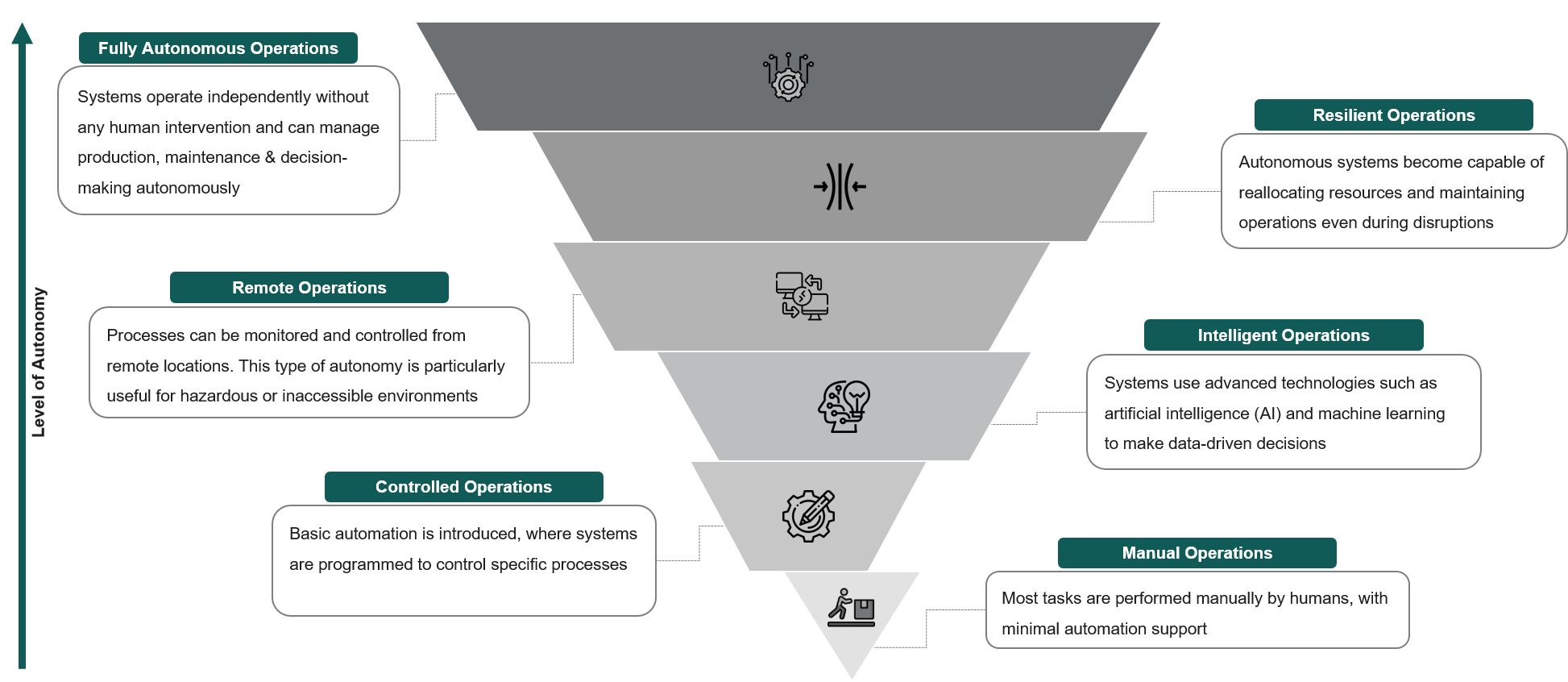
Enablers of Flexible & Autonomous Production
The key enablers of facilitating the adoption of flexible and autonomous production are listed below.
Robotics in Production
Through quick adaptability and improved quality, robots play a crucial role in rendering flexible and autonomous production. Robots can be reprogrammed to handle various tasks effectively, thereby reducing downtime and enabling manufacturers to adapt to changing customer demands. Also, robots enhance safety in production lines by performing hazardous tasks, thereby allowing the workers to assume more strategic roles.
Digital Twins in Manufacturing
Digital twins enable flexible and autonomous production by generating a virtual replica of physical assets, production lines, or entire manufacturing facilities using real-time data. Digital twins allow predictive maintenance, reduce downtime, and improve productivity by utilizing simulations to optimize production processes. With the help of virtual testing of processes, users can eliminate the cost of physical prototyping and implement quick changes without incurring significant costs. With digital twins, manufacturers can test the production process without physical implementation.
3D Printing in Manufacturing
Conventional manufacturing methods require the use of dedicated machinery and tools for a specific product, making it difficult to adapt to the frequent changes in production requirements. 3D printing eliminates the need for tooling in manufacturing and can produce a variety of products using various materials, thus increasing overall flexibility in the production line.
Research Innovations in Flexible Manufacturing
A few of the key research innovations are discussed below:
- Innovation 1: Flexible manufacturing powered by a large language model agent
- Brief: The framework is built around three key components: matching manufacturing tasks with process parameters, designing autonomous tool paths, and integrating embodied intelligence into robotic simulations. The system demonstrates the capabilities of LLM agents in understanding and responding to human-defined constraints, efficiently generating planar tool paths, and adapting within simulated 3D industrial tasks. (Source)
- Assignee/University: National University of Singapore, California State University
- Application Area: Smart manufacturing and robotic automation
- Value Proposition: It improves task planning, reduces reliance on explicit programming, and the ability to learn and adaptation through few-shot learning and reasoning techniques like chain-of-thought (CoT). Experimental outcomes highlight GPT-4’s superior performance in task planning, outperforming traditional models.
- Innovation 2: Enhancing flexible manufacturing systems (FMS) through integration of AI, digital twin, and Wi-Fi-based indoor localization
- Brief: The innovative approach leverages Wi-Fi fingerprinting combined with advanced machine-learning models and deep reinforcement learning to enable precise, real-time asset tracking and autonomous navigation within manufacturing environments. The system utilizes the extensive UJIIndoorLoc dataset, which contains Wi-Fi signal data from multiple floors and over 520 access points. Machine-learning algorithms, including Support Vector Machines (SVM), Random Forests, Decision Trees, K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN), and Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN), were evaluated for their localization accuracy. KNN achieved the best localization accuracy, with a mean coordinate error ranging from 1.2 to 2.8 meters, while CNN optimized with the ADAM algorithm yielded a mean squared error of 0.83, demonstrating superior performance. The framework also incorporates deep reinforcement learning to guide Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs), enabling them to navigate and avoid obstacles autonomously in a controlled laboratory setting. This integration enables real-time tracking and operational optimization via Digital Twin technology, facilitating remote monitoring and management. (Source)
- Assignee/University: Ghulam Ishaq Khan Institute of Engineering Sciences and Technology, Aberdeen’s Robert Gordon University (RGU) Home
- Application Area: Using Wi-Fi signals and deep learning to build Digital Twins of Flexible Manufacturing Systems for smarter manufacturing.
- Value Proposition: It provides a cost-effective, scalable, and accurate solution for real-time indoor asset tracking and navigation in manufacturing. It enables Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) to navigate safely with 100% obstacle avoidance and supports remote monitoring through Digital Twins, facilitating better decision-making. Tested models, such as KNN and CNN, showed high accuracy, making this Wi-Fi-based approach more flexible and scalable than traditional sensor-based methods. This framework advances smart manufacturing by improving productivity and cutting costs.
Key Challenges & Strategic Solutions
- Challenge: The advanced systems require employees to possess technical skills in automation, robotics, and data analytics, as well as a willingness to adapt to continuous technological changes. Without proper training and a proactive attitude toward innovation, workers may resist new processes, struggle to operate or maintain complex machinery, and be unable to respond effectively to real-time data and system exceptions.
- Solution: Small and mid-tier manufacturers are addressing the workforce challenge by leveraging robotics certification programs offered by organizations such as Yaskawa Motoman and FANUC America. These certifications enable employees to become proficient and officially qualified in operating industrial robots, boosting their technical competence and confidence.
- Use Case: Yaskawa Academy offers over 75 specialized robotics training courses, covering areas such as basic and advanced programming, maintenance, concurrent I/O, and customized training tailored to specific needs. (Link)
- Challenge: As these systems rely heavily on interconnected devices, sensors, and cloud-based platforms to collect, process, and share vast amounts of sensitive operational data, they become attractive targets for cyberattacks. Unauthorized access, data theft, or manipulation can often result in increased production downtime, compromised product quality, loss of intellectual property, and even safety hazards.
- Solution: To mitigate data security risks in flexible and autonomous manufacturing systems, manufacturers can implement device and software authentication alongside robust data encryption techniques to safeguard the confidentiality and integrity of critical data.
- Use Case: Thales Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) offer comprehensive protection by securing code signing processes, ensuring that only authentic and approved software is used throughout manufacturing operations. It helps manufacturers maintain compliance with regional data security regulations, providing a strong defence against cyber threats targeting various aspects of the manufacturing process. (Link)
Key Players Driving Intelligent Manufacturing

Siemens Opcenter, Manufacturing Operations Management (MOM), is a comprehensive solution designed to optimize the efficiency and effectiveness of end-to-end manufacturing processes. Siemens Opcenter is used by Boeing to manufacture execution systems, demonstrating the high demand in the American aerospace and defense industries. Similar to Opcenter, other solutions offered by Siemens for flexible and autonomous production are the TIA Portal and Simove.
ABB AMR Studio Suite is a powerful software that provides all the necessary tools to install, manage, and monitor the AMR fleet, featuring a user-friendly interface and advanced algorithm capabilities. ABB Ability™ Manufacturing Execution System and AppStudio are some of ABB’s solutions for flexible and autonomous production.
Techman Robot is a leading manufacturer of collaborative robots located in Taiwan. Techman Robots offers solutions, including collaborative robots, software for simplified interaction with collaborative robots, and a user-friendly design, along with AI vision for enhanced visual inspection, enabling flexible and autonomous production.
Future Perspective on Flexible and Autonomous Production
The upcoming trends in flexible and autonomous production will increase the use of cutting-edge technologies, such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, to facilitate on-demand production, self-diagnosis, real-time optimization, and other advanced capabilities. The implementation of robotics in production will enhance processes with minimal human involvement. These developments in flexible and autonomous production will help minimize setup duration and improve overall flexibility.
Alongside these developments, dark factories, also called lights-out factories, are growing in number, using fully autonomous production without human involvement to boost efficiency and precision.
Conclusion
Flexible and autonomous production represents a shift in manufacturing that enables companies to quickly adapt to changes in market demand for various products without requiring significant modifications to the production line. Leading solution providers, such as ABB and Siemens, focus on technologies like industrial robots and autonomous mobile robots. Companies are also investing in integrating AI into their production systems to boost efficiency and quality with minimal human involvement.
Let's Take the Conversation Forward
Reach out to Stellarix experts for tailored solutions to streamline your operations and achieve
measurable business excellence.



