Best Sustainable Laundry Detergent Formulations
Sustainability majorly defines the development of different products, goods, and services to meet human needs without affecting the requirements of future generations. To address complications, sustainable development has now become an utmost requirement for most of the paramount sectors of industry, including consumer goods. Laundry & household care is one of the prime consumer goods sectors contributing to greenhouse gas emissions, energy consumption, and freshwater utilization. Most key players aim to develop laundry detergent products efficiently to troubleshoot all the issues regarding sustainability. In this article, we will provide summarized information related to detergents & their sustainability, industrial goals & regulatory concerns, laundry detergent innovations concerning sustainable development, and market trends & analysis.
What Are Detergents?
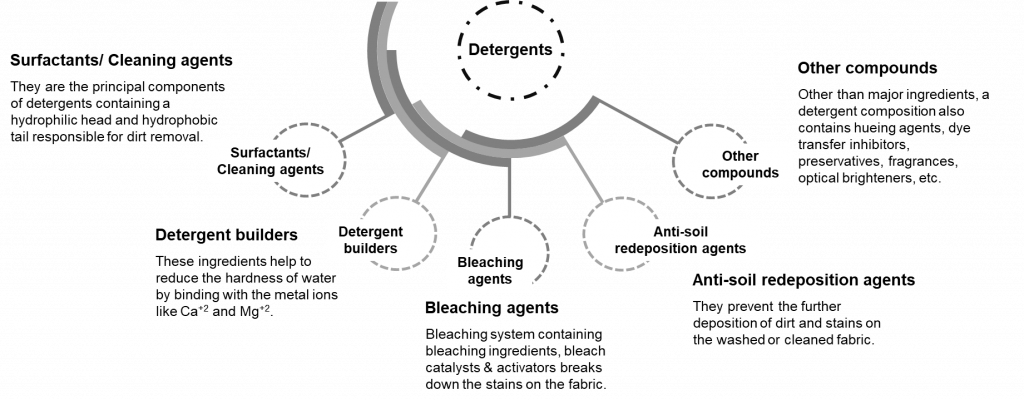
Detergents are chemical mixtures containing surfactants as chief ingredients and other additional ingredients. The top ingredients, i.e., surfactants, consist of hydrophilic head groups helping them to solubilize in water and hydrophobic tails responsible for fabric dirt and stain removal.
Besides surfactants, builders, bleaches, anti-soil redeposition agents, optical brighteners, hueing agents, dye transfer inhibitors, preservatives, fragrances, etc., are also present in a detergent composition.
Influence of Sustainability on Detergents
Concerning day-to-day demands, various ingredients are introduced to upgrade cleaning efficiency and time. However, their hazardous nature has a prominent effect on the environment and animal health. Toxic, precarious, non-biodegradable, synthetic chemicals, such as petroleum/ fossil fuel-derived surfactants, strong chlorine bleaches, artificial fragrances, phosphate-based builders, isothiazolinone-containing preservatives, etc., not only affect human health and lifestyle but also damage the overall ecosystem.
In the context of environmental and animal safety, the sustainable production of detergent components is gaining attention among inventors and consumers. Incorporating alternative, eco-friendly packaging and natural, green, decomposable ingredients with revised carbon, water, and energy footprints is becoming more popular and in demand in all types of detergent formulations.
Laundry Detergent: Innovations in Terms of Sustainability
Recent reforms & sustainable goals from various industries and regulations target less GHG emission, low water consumption & more wastewater use, and renewable energy utilization for detergent manufacturing. Different novel forms and technologies are coming out or are in the research phase to improve the current sustainable development scenario.
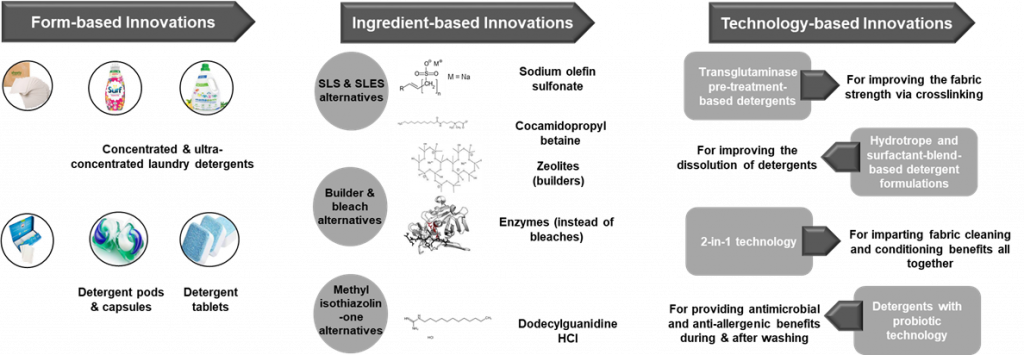
In developed countries like the USA and Europe, concentrated detergents and laundry sheets are already occupying the market. Detergent formulations produced with sustainably sound ingredients and technologies are already in demand worldwide, and leading companies in this segment are already changing their products.

Based on the circumstances, high cleaning efficiency, enzymatic compositions, surfactant blends, non-ionic surfactants, waterless formulations, carbon-neutral products, etc., are becoming crucial requirements for consumers, and the rising demand for such products is growing very fast.
Leading brands and manufacturing organizations like Henkel, P&G, Unilever, Kao Corporation, etc., provide laundry detergent formulations with a lower water footprint and less water consumption. Thus, that helps purchasers and users.
Role of Industries & Regulatory Authorities
The global consciousness of sustainability has greatly impacted the key players and inventors of the laundry detergent industry. Innovative technologies and formulae are phasing in through convenient partnerships and contrivances. With 40% of the market volume, companies like Unilever, P&G, and Henkel have taken the lead in the sustainable development of their laundry detergent products.
Unilever has allied with Evonik to develop biodegradable laundry formulations containing rhamnolipid-based biosurfactants that are safe for aquatic ecosystems. It has also collaborated with India Glycols and Lanzatech to produce surfactants from industrial carbon emissions.
P&G and Henkel have also targeted to work on their sustainability goals. In detergent formulations, water is about 1/5th of the total composition, and in the case of liquid detergents, it takes a more significant portion than in other forms. Detergent processing pipelines must make significant improvements in water consumption and wastewater reutilization. On this account, P&G aims to reduce its water footprint by 50% in the upcoming 5 years, and Henkel has reduced its water consumption in manufacturing detergent products by 28% per ton of product.
Latest Developments
Potential players face challenges developing cost-effective, environment-friendly detergent compositions with better carbon, energy, and water footprints without considering regulatory authorities. They play an essential role by justifying the limits, rules, and regulations related to restricted ingredients or useful information about detergents.
The United States Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA) and the European Commission (EC) are the USA’s and Europe’s principal governing authorities, respectively. These two organizations regulate all kinds of prohibitions and permissions regarding conventional or novel ingredients/ products.
When it comes to sustainability, biodegradability implies a critical contribution. The main constituent of detergents, i.e., surfactants, should be nature-friendly so that they undergo a certain degree of biodegradability in environmental conditions. They should be readily and inherently biodegradable by “The Detergent Regulation (EC) No. 648/2004 – Annex IIIA, IIIB, and IV,” and consumers should be notified about the biodegradability through proper labeling.
The USA and Europe have recently updated the rules on phosphates and their usage in detergents. Besides surfactants, most detergent compositions contain 35-75% phosphate salts as detergent builders. After laundering, these ingredients wash off towards the nearest water bodies and cause eutrophication. Therefore, alternatives/ substitutes of them have also become one of the primary objectives of inventors.
Laundry Detergent: Market Trends & Analysis
Some top companies developing sustainable detergents include Unilever, Henkel, P&G, Kao Corporation, EUD Group AS, Church & Dwight Co. Inc., The Clorox Company, BASF SE, Reckitt Benckiser Group Plc Clariant AG, Croda International, etc. Concerning the present situation, the laundry detergent market is expected to grow in the Asia-Pacific region. Innovative detergent forms like laundry capsules, concentrated laundry detergents, or laundry detergent sheets have already captured established markets. They include the USA and Europe. Companies are now targeting the expansion of their business and innovations in one of the fastest-growing CPG markets, i.e., Asia-Pacific.

The top key players working in the field of laundry detergents are shown in Figure 4.
Along with the essential inventors, a few startups are gaining attention regarding the sustainable production of different detergent compositions and forms. One of the primary aims of their products is innovative and virgin plastic-free packaging.
Truearth is one such startup that was launched in Canada in 2019. It produces laundry detergent sheets that are environment-friendly and use less water.

Frey is another laundry sheet-based company that makes sheets 100% plastic-free. It is working towards producing laundry sheets that use less water in manufacturing and consumer use.
Dropps is working on making pods made with biodegradable polymers for single-time use with a proportional amount of detergent. These pods help reduce water usage for every load of washing.
Ocean Forest, a Chinese startup founded in 2014, aims to tackle eutrophication-related issues. The detergent comprises oxygen, washing soda, lemon & palm fruit extract, and biological enzymes.
Consumers’ main requirements are being vegan and animal-cruelty-free. Because of this, startups and big companies focus on manufacturing detergents with vegan/ animal cruelty-free certifications. Some potential candidates are AspenClean, Ecos, Method, etc.
Conclusion
Today’s society is extensively observing sustainability and working on increasing awareness about the adversely affected environment by orthodox household products. These sustainable detergent products are one of a kind, helping the planet to recuperate. Inventions are now more focused on achieving different sustainability goals set by the major players. It may lead to an impact on significant footprints, i.e., carbon footprint reduction, water footprint reduction, and renewable energy. Moreover, it is also concerned with consumption, cost-effectiveness, and social equity. Growing consumer acceptance of natural ingredients will be the key driving force of innovation in the market in the future.
Let's Take the Conversation Forward
Reach out to Stellarix experts for tailored solutions to streamline your operations and achieve
measurable business excellence.


