Soil Release Polymers: The Future of Textile
Over time, there has been a gradual update in the purpose of fabric cleaning. Based on the current situation, effective cleaning is not only related to removing soil and dirt from the fabric. Prevention of the redeposition of soil onto the fabric surface has also become one of the significant credentials for cleaned fabrics. Soil-release polymers are essential additives of laundry detergents whose function enables soil release from fabric and prevents soil redeposition during the washing cycle.
Treatment of dirty fabrics with detergents containing surfactants or a mixture of surfactants pulls out the soils from the fabrics. Still, some of the residues remain within the capillary structures of the fabrics. Due to this phenomenon, physical adhesion or electrostatic attraction causes dirt to get to the surface. Therefore, a constant need for a material capable of protecting clothes from soil redeposition has become one of the driving thrusts for industries. Moreover, leading manufacturers and inventors are developing various soil-release polymers that effectively prevent dirt from adhering to the cloth surface. This article summarizes soil-release polymers, their functioning and benefits, their classes with innovations, and their market trends.
What are Soil-release Polymers?
Soil-release polymers (SRPs) are essential additives of laundry detergents. They enable soil release from fabric and prevent soil redeposition during the washing cycle. SRPs are polymeric surfactants/ reagents applied to the fabric to make it more soil-resistant. Numerous polymers are used in detergents and cleaning products, such as polycarboxylates, polyvinyl pyrrolidone, etc. These polymers can be applied during the manufacturing of textile fabrics or in washing/ wet cleaning.
Mechanism of Action & Benefits
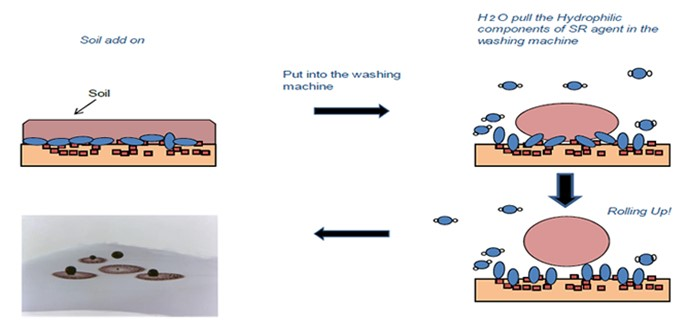
- Soil-release polymers form a coat or barrier on the surface of the fibers and protect them from deeper penetration of soil/ dirt into the fibers.
- These polymers can be applied during the manufacturing of textile fabrics, making the soil release process easier during laundering.
- These polymers help in lowering the frequency of the washing cycle.
- These polymers bring cleaning results by effectively removing stains from the fabric surface.
- They prevent the re-deposition of stains during a wash cycle.
- Along with soil resistance, wear & tear resistance is also enhanced by these polymers.
Classification of Soil-release Polymers
Classifications of soil-release polymers can be done based on various factors and are as follows
A. Acrylic Acid Products: Polyacrylate/ Polymethacrylate-based soil-release polymer finishes come under this category. Diepoxy compounds are used to crosslink these compounds on the fabric surface to form a film.
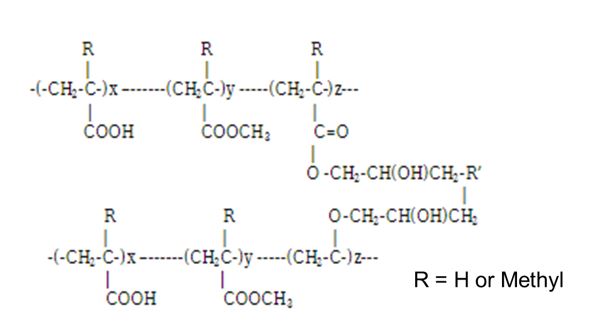
B. Fluoro Chemicals
Fluorine-containing polymers are blocked with polyoxyethylene and adsorbed onto the fibers. The polyoxyethylene part orients itself above the fibers and provides a hydrophilic finish. A durable press resin is used to crosslink this type of system.
C. Terephthalate-based Products
Polyoxyethylene terephthalate polyester compounds come under this category.
As shown in Fig. 3, it consists of polyester and polyoxyethylene parts, which orient themselves on the fabric’s surface, forming the hydrophilic layer on the surface.
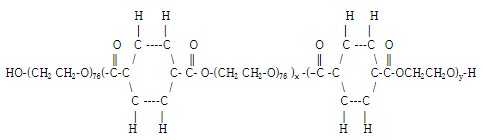
D. Polysaccharide-based Products
Cellulose-based soil releases agents like carboxymethyl cellulose, hydroxyethyl cellulose, methylcellulose, and hydroxypropyl cellulose, which fall under this category. These agents get adsorbed on the fiber surface, forming hydrogen bonds. This increases the hydrophilicity of the surface and reduces soil penetration.
Innovations in Soil Release Polymers
- Solvay has launched an environmentally friendly technique called Repel-O-Tex®. It is made of sugarcane-based polymeric products that enhance soil repellence.
- A polymer compatible with most detergents has a non-ionic soil release mechanism. It is also designed to reduce the need for hot water, heavy tumbling, and aggressive washing agents. Clariant Industries, known as TexCare®, recently developed the product.
- Companies like Ariel have started using special polymers to prevent stains from re-depositing after detergent removal.
Market Trends
The rise in household usage of detergents and laundry additives is expected to boost the demand for oil-release polymers in the near future. The compatibility of soil-release polymers with polyester and polyester cotton fabric increases consumer demand. Also, it tends to offer a better solution to customers that hinges on sustainability.
- It is available in solid and liquid forms, increasing its application in various industries and attracting consumers with different buying habits. Know more:
- The rapid growth of the tourism industry has pumped up the demand for laundry detergents. This is likely to propel the demand for soil-release polymers in various domains.
- The virus outbreak has led to substantial growth in categories such as cleaning and hygiene products. Prominent growth in the cleaning products business is also one of the outbreak’s positive influences.
- The recent COVID-19 outbreak has made consumers more conscious about health measures. Moreover, it has triggered awareness about cleanliness and hygiene, increasing demand for detergents. This trend is projected to considerably impact the demand for soil-release polymer.
- Asia Pacific is a significant consumer of soil-release polymer across the globe. The region is likely to witness a substantial rise in demand for soil-release polymer owing to the expansion of the production of various detergents and cleaning agents in the region.
- Emerging economies such as India, China, and Thailand have been exhibiting an upward trend in consuming soil-release polymers. Low manufacturing and labor costs in emerging economies, including China and India, have encouraged detergent industry players with bases in mature economies to shift to emerging economies to achieve economies of scale.
The following section overviews the leading companies working in soil-release polymers.
Headquartered in Ludwigshafen, Germany, BASF has a wide range of products for soil-release polymers. It has launched a range of Sokalan CP, a modified maleic acid-acrylic acid copolymer sodium salt used in laundry detergent as a soil anti-redeposition agent. Furthermore, Sokalan HP 30, an alkoxylated polyethyleneimine, is formulated to address stain removal at low temperatures.
With various operating domains, such as detergents, polymers, petrochemicals, etc. Repel-O-Tex®, a range of sugarcane-based polymeric products launched by Solvay, provides better soil repellence.
Clariant has developed the TexCare® range, a non-ionic soil-release polymer, and is also compatible with most cleaning detergents used for textile finishes. Moreover, using this polymer helps reduce the need for hot water, heavy tumbling, and aggressive use of washing agents. Also, it forms a protective layer, removing stains easily, and offers the optimal solution for the user.
Dow, founded in 1897, formed Dow Inc. in 2019 after demerging from DuPont. The company’s headquarters are located in Michigan, U.S. The ACUSOL 445N range of polymers provides soil release features and inhibits dirt precipitation back on clothes.
Startec Science and Technology
Established in 1997, Startec Science And Technology Co., Ltd. is a high-tech enterprise specializing in surfactants, synthetic esters, emulsifiers, and functional polymers. Additionally, its product Ucebuilder NPA-70K is an active ingredient soluble in alcohol to replace traditional polymer synergists and part of surfactants. It has excellent synergistic detergency and anti-redepositing ability. It is suitable for common and concentrated liquid laundry detergents.
Ashland is a chemical company with its headquarters in Kentucky, United States. Additionally, the company launched SOREZ 100 POLYMER, a modified polyester copolymer forming a thin film on fabric, imparting soil release and anti-soil redeposition. It provides soil release properties on cotton blends, and synthetic fabric adds anti-soil redeposition properties for synthetic and cotton blends. It prevents the deposition of oil-based soils on a range of fabrics.
Conclusion
Soil-release polymers are the future of textile finishing products as they boost the performance of cleaning products. Biodegradable soil-release polymers are very few in the market. This has created a scope for the rest of the companies to conduct more research on the biodegradability aspect of their existing products. Also, numerous studies are being conducted on synthesizing and developing soil-release polymers. Unilever has patented hydrophobically modified polysaccharides as a soil release agent for laundry applications. Moreover, the high cost of these products produces hindrances in targeting customers. Further studies and trials can be conducted to produce low-cost and sustainable alternatives to the currently used materials to develop SRPs. Improvising and researching the white spaces in soil-release polymers can enhance their applicability and availability to every segment of the industry and society.
Let's Take the Conversation Forward
Reach out to Stellarix experts for tailored solutions to streamline your operations and achieve
measurable business excellence.


