We are at a crossroads with 5G networks, cloud/edge services, the Internet of Things, artificial intelligence/machine learning, and others. The advent of 5G networks marks a transformative shift in the telecommunication network domain. Infrastructure is actively being created to facilitate a broad spectrum of services and applications in this new era. To manage these services and applications, you need a competent and highly efficient management or service control system. With the promise of unprecedented speed, low latency, and connectivity, the development of 6G technology is already in progress. An essential component that underpins both these generations of wireless technology is end-to-end orchestration (E2E). E2E orchestration plays a pivotal role in ensuring the smooth operation of these telecommunication networks, providing seamless integration of various network components.
This article explores E2E orchestration, highlighting its differences and technical advantages over conventional orchestration, its components, market activities, and others.
What is E2E Orchestration?
End-to-end orchestration is a comprehensive approach to network management that goes beyond conventional orchestration. A traditional orchestration model separately manages individual network components like radio access, core networks, and edge computing. E2E orchestration, however, integrates, manages, and controls these components as a unified whole to optimize the entire network efficiently. It provides an abstraction layer known as the Service Orchestration and Management layer between the Business support systems (BSS) layer and the Multi-domain 5G Network layer, including Open RAN, Business Edge, Transport, and Core. Moreover, this E2E orchestration allows for effective network & cloud service lifecycle orchestration, service management across various vendor technologies, hybrid networks, and a single view of critical data and processes.
End-to-End Orchestration Challenges in 5G and Beyond
The high heterogeneous nature of 5G network devices, combined with various link-layer technologies, poses significant challenges. These challenges include latency, resilience, and security constraints, further complicating the orchestration of 5G networks. These challenges are heightened when incorporating 5G networks and even more so for 6G networks. Listed below are the main challenges for orchestration in 5G networks.
Latency, Reliability, and Availability:
5G and 6G networks have strict latency, resilience, and availability requirements, with particular specifications for Ultra-Reliable and Low Latency Communications (URLLC) services. Some of the URLLC services include wireless control and automation in industrial environments, inter-vehicular communication, tactile internet, and others. These services require minimum latency and almost 99.99% reliability in a dense, complex ecosystem where millions of physical and virtual components interact with each other.
Device Management:
Managing the collection of devices with computing, storage, and networking capabilities poses a challenge. The diversity in devices, including variations in traffic and mobility patterns, energy requirements, and computing power, adds complexity to the task.
Security:
The 5G and 6G networks have a denser deployment of cells, mesh networks, and Device-to-Device connectivity. With more vulnerable devices, attackers can perform malicious activities better. Integrating technologies, such as blockchain and quantum computing, also brings challenges.
Slicing Support:
The virtualization of network functions over physical resources is a requirement for 5G and 6G networks. Network slices must provide service isolation and automated deployment, considering general-purpose use cases, where Virtual Network Function (VNF) and Physical Network Function (PNF) can be shared among users.
So, to overcome all these challenges and build successful 5G services, it is essential to consider the variety of technological domains. That includes multiple generations of RANs, core networks, the Cloud-to-Edge continuum, continuous network optimization for Service Level Agreements (SLAs), and others.
Integrating E2E service orchestration overcomes challenges, ensuring high-quality service delivery regardless of user location or device. This streamlines network management in complex environments, enhancing overall service quality.
Components of E2E Service Orchestration
End-to-end service Orchestration is the process of connecting many service domains and coordinating with various components to ensure seamless service delivery to synthesize consumer E2E services. A few technologies and solutions that aid in its realization are described below:
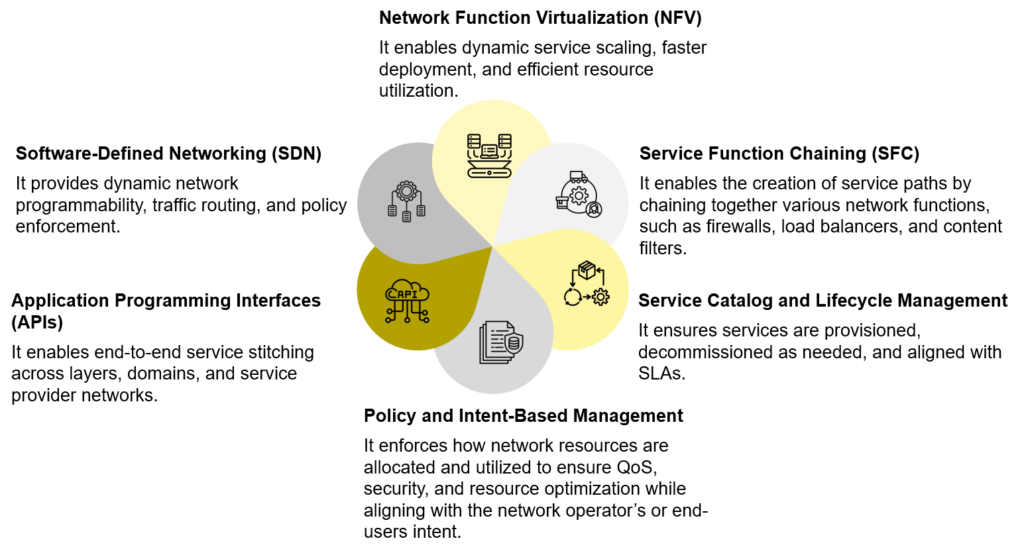
Figure 1: Key Components of E2E Service Orchestration
One thing to note here is that the NFV and SDN technologies allow CSPs to integrate cloud innovations, automation, and software-driven solutions into networks to pave the way for delivering advanced digital services on demand.
Importance of E2E Service Orchestration
The 5G network is intended to provide services such as Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB), URLCC, and massive Machine Type Communication (mMTC). They provide benefits such as high-speed data, widespread deployment of connected devices, and highly reliable connections with short latencies. Enabling E2E service orchestration for 5G networks involves integrating dynamic digital services across all technology and cloud domains in real-time. The E2E service orchestration layer comprises a full suite of microservice and containerized components. This layer includes essential elements such as Service/Slice Catalog, Service Inventory, Service Orchestration, Service Quality Management, and Service Assurance. Collectively, these components contribute to the seamless and efficient management of services in the dynamic landscape of 5G networks.
The intended targets of the service are achieved by performing network slicing and automating the E2E QoS (Quality of Service) management in 5G networks. Service orchestration can enhance network slicing, providing an end-to-end dedicated resource for each slice, as each slice remains isolated. The E2E network slice orchestration is summarized below:
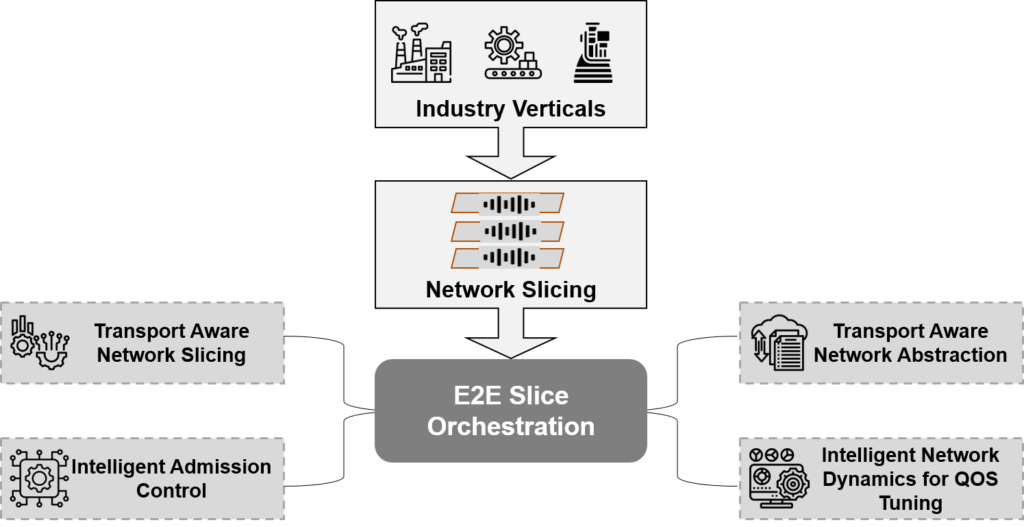
Figure 2: Key E2E Orchestration Advantages
E2E Network Slice Orchestration
In a 5G communication, network slices are created based on tracking areas to ensure eMBB, URLCC, and mMTC to the end-users. Each slice needs to operate as an isolated E2E network to provide the QoS to the end users. The orchestrator decides the type of isolation for a slice based on the transport technology the slice uses. The working of the E2E network slice orchestrator is based on interworking the four separate components, as shown in Figure 1. The significance of these components is briefed below.
Transport-aware Network Slicing
It is tasked with mapping traffic from a slice/group of slices to the transport resource that meets the QoS requirements of the slice/group of slices. Further, mapping the QoS parameters with the network resources associated with the slice uses a Radio Access Network (RAN), Core Network (CN), and transport abstraction. This enables the orchestrator to the complete scenario regarding network resources.
Transport-aware Network Abstraction
Transport-aware abstraction is a component that provides the QoS parameters to the E2E orchestrator. Network abstraction helps simplify the resource details for the E2E orchestrator so that the orchestrator can simultaneously consider various network features.
Intelligent Network Dynamics for QoS Tuning
Tuning QoS in a network is challenging as the service parameters change during the service lifecycle. Thus, an intelligent (AI or ML-based) tuning can be executed, which dynamically adjusts the QoS parameters for a transport layer within a network slice.
Intelligent Admission Control
Intelligent admission control determines whether enough resources are available to support QoS and traffic parameters for a new connection.
Technical Advantages of E2E Orchestration
The traditional orchestration services for the 5G networks face challenges such as security & privacy concerns, interoperability issues, legacy network integration, strict SLAs, and others. To mitigate all these challenges, the E2E orchestrations come into the picture and provide the following technical advantages, as shown in the figure below.
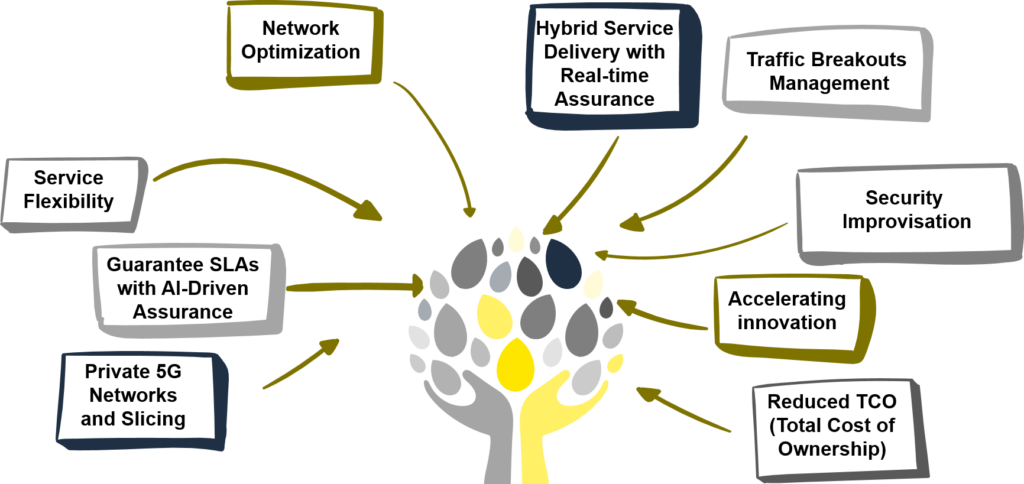
Figure 3: Key E2E Orchestration Advantages
Prominent Market Synopsis for E2E Orchestration
The growing demand for advanced network scaling solutions propels the need for End-to-End orchestration. Simultaneously, there is an increasing requirement to manage complex communication infrastructures, further emphasizing the importance of End-to-End orchestration. Numerous companies are working with the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) to boost their E2E orchestration technology portfolio.
European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) ZSM members for E2E Orchestration
ETSI ZSM (Zero Touch Network and Service Management) aims to define a future-proof, end-to-end, operable framework, solutions, and core technologies. It enables zero-touch automation for emerging and future networks and services.
One of the ZSM group member companies, NTT DOCOMO, has successfully tested E2E orchestration (E2EO) technology based on the ZSM specification of ETSI for 5G network slicing.
Key Players Activity
Building successful 5G and digital service offerings necessitates business communication service providers (CSPs) to offer and scale services. This scaling should occur on demand to meet users’ dynamic requirements and ensure the services’ efficiency. CSPs must also continuously optimize the network for SLA and resolve problems without impacting the services to meet evolving demands. To enable the CSPs to provide End-to-end orchestration, the market players are making efforts to provide the desired technology solutions.
- Intel, Capgemini, Cloudify, and AWS Services have collaborated to automate an end-to-end 5G network slicing, which includes Open5GS core components and numerous outpost edges running DU and CU components
- ASOCS and VMware have teamed up with Sterlite technologies to allow users to quickly build and manage end-to-end 5G enterprise solutions with high performance, security, and flexibility
- Cisco and IBM have collaborated to build end-to-end SLAs for network slices and to coordinate traffic across the network
Conclusion
End-to-end orchestration has been a cornerstone of 5G’s success, and it will continue to evolve and play an even more vital role as we transition into the era of 6G. The seamless integration of diverse network components positions E2E orchestration as a critical tool. Its technical advantages make it essential for delivering the promise of high-speed, low-latency, and highly connected 6G networks. Additionally, network orchestration stays at the forefront as technology progresses to ensure effective and efficient network operations. It plays a key role in connecting the world by expanding through various means, including increased automation and transport awareness.
Network orchestration aims to minimize over-provisioning and maximize the efficient traffic supply as technology advances. For the future of 5G and beyond, the E2E orchestration digital services will necessitate new capabilities. This includes advanced E2E QoS at scale in specified deployment zones (local, limited-wide, general-wide), where services fluctuate dynamically in time and space.