Blockchain in Healthcare: Resolving Challenges
The healthcare industry faces numerous data storage, exchange, and verification issues. Patient data is stored in segregated silos with no access to doctors at the time of need while easily approachable by hackers. Some challenges the healthcare industry faces are drug counterfeiting, health data accuracy and interoperability, drug traceability, and poor management. With the proliferation of ineffective healthcare database systems, the implementation of a block as a service (BaaS) became necessary with the rising demand for a transparent and irreversible distributed ledger in the healthcare market. The execution of Blockchain in healthcare facilitated effective data sharing among healthcare professionals, improved official diagnosis and appropriate treatment, and delivered cost-effective treatment to health providers. Thus, it redefines data modeling and governance for the healthcare sector due to its adaptability and unparalleled capacity to segment, secure, and distribute medical data and services.
Blockchain in Healthcare: Technology Overview
What is a Blockchain, and How Does It Affect Healthcare?
Blockchain is a distributed database that stores transactional records electronically while assuring security, transparency, and decentralization. It collects information in groups, called blocks, to create a data chain. Because each block has a distinct identity, known as a hash, the system’s recorded data cannot be altered, hacked, or faked. According to Statista, the blockchain technology market is forecast to grow by nearly 1,000 trillion dollars by 2032.
This technology utilizes advanced cryptography mechanisms to increase data security. As a result of the Blockchain’s permission technique, individuals have ownership of the data. Thus, its transparency facilitates clinical trials by documenting and time-stamping all the details. It authenticates health data and ensures high security so that patient data is not compromised. Thus, it offers the healthcare industry distinctive contract management and payment features.
Workflow of Blockchain in Healthcare Applications
The workflow of blockchain-based healthcare technologies is described below. It is composed of four verticals, including raw healthcare data, blockchain technology, healthcare applications, and stakeholders.
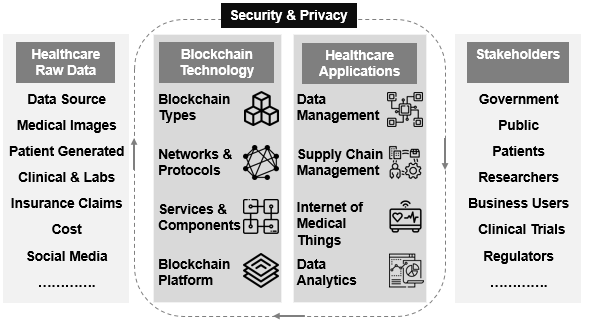
- Initially, all the data from medical devices, labs, social media, and other sources are integrated to generate raw data and the first vertical of the stack as it is the foundational component of the entire blockchain-based healthcare system.
- The second vertical comprises blockchain technology, regarded as the core framework for developing a secured healthcare framework that is composed of four parts.
- Public, private, or hybrid Blockchain types make up the first element.
- The second component includes networks, such as P2P, centralized, decentralized, and distributed networks, whereas protocols like Ethereum, Ripple, Hyper ledger Fabric, etc., facilitate users’ creation and management of transactions.
- The third parts include services & components that comprise smart contracts, signatures, wallets, digital assets, etc.
- The fourth element is the blockchain platform, which includes various features such as consensus algorithms and protocols. The next step is ensuring that the applications are integrated within the entire system.
- The third vertical comprises blockchain-based healthcare applications broadly classified into four classes, which are explained in the next section.
- The final vertical is stakeholders, which includes those who profit from Blockchain-based healthcare applications, including business users, researchers, and patients. Users at this tier are primarily concerned with efficiently sharing, processing, and managing data without endangering its security and privacy.
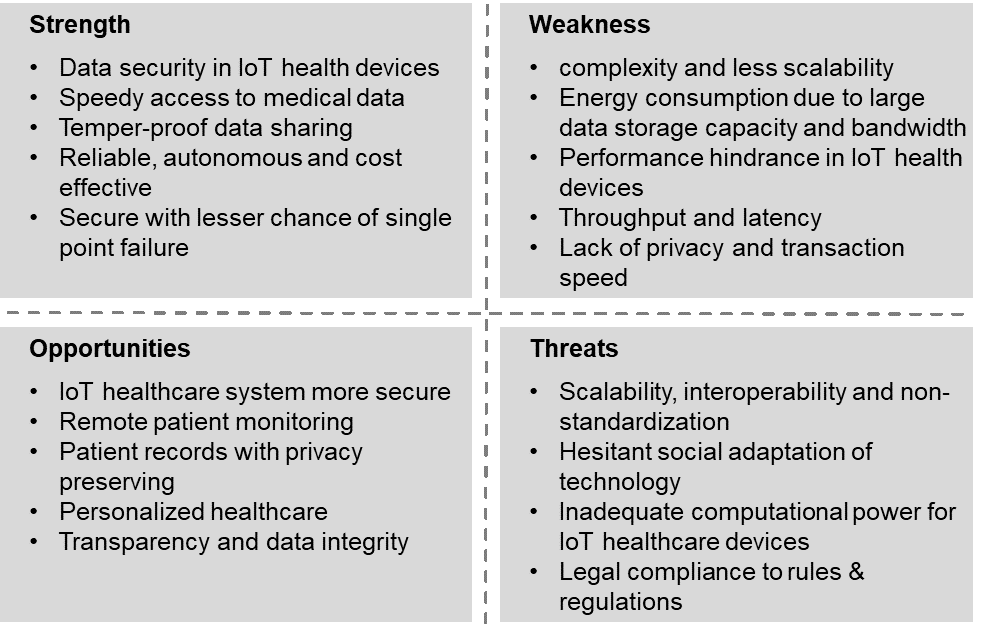
SWOT Analysis of Blockchain-Based Applications in the Healthcare Industry
Healthcare Application Benefit
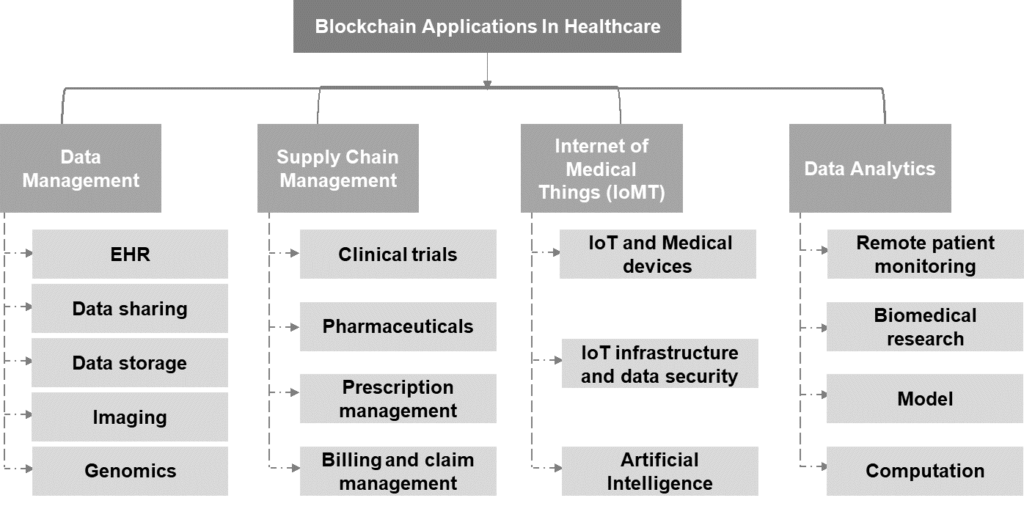
Data Management and Data Analytics
The progress in electronic health-related data, cloud healthcare data storage, and patient data privacy protection regulations have made health data management flexible and convenient for patients to access and share their health data.
Use Cases
- Health Education: Utilizing Blockchain in healthcare ensures that knowledge is secured and non-altered. It allows easy tracking of the most utilized and effective learning modules.
- Security: Blockchain technology has overcome the security challenges of the EHR in Healthcare. EHRs are created when a patient is admitted to a hospital, when a physician diagnoses a patient, or when a diagnostic result such as an MRI scan is stored in the EHR system. Therefore, the security of such digital information is essential, and by using blockchain, this information becomes secure.
Blockchain in Healthcare: Supply Chain Management
Blockchain monitoring technology improves the process of tracking the movement of pharmaceutical and medical supplies. It is simple to instantaneously check the origin of the medicine, the vendor, and the distributor because all transactions are recorded onto the ledger, and every node in the blockchain keeps a transaction record. Thus, demand forecasting, data provenance, fraud protection, and transactional efficiency are significantly enhanced.
Use Cases
- Claims and Billing Management: Excessive billing is one of the main challenges with medical billing. There is a lack of transparency and no confidence between doctors, patients, and insurance companies. Blockchain can provide such a transparent system, ensuring everyone is involved in the entire process and eradicating any mistrust if it exists.
- Quality management: One of the primary problems that must be handled for quality management is detecting counterfeit drugs. The issue is remedied when pharmaceutical manufacturers store data. It includes product serial numbers and package numbers on the Blockchain so that pharmaceutical firms, medicine producers, and consumers connect to the Blockchain and verify the data’s authenticity. Thus ensuring low-cost quality control, product registration, drug tracking, and drug counterfeiting throughout the SCM process.
Blockchain in Healthcare: Internet of Medical Things
IoMT technology enables real-time data collection, processing, and sharing over the Internet for medical devices. It includes body scanners, heart monitors, and wearables. With the development of AI, for instance, healthcare providers can capture an image using the IoMT paradigm. Moreover, spot dubious cells or even cancerous portions and communicate this information with righteous people to access it. Thus, the IoMT Blockchain technology offers a solution for the safe transfer of patient health reports to protect medical data. It does that by cryptographically storing it on connected blocks.
Use Cases
Lack of Standardization: IoMT is the building block for telehealth monitoring applications, as wireless devices are associated with recording biosignals. Therefore, medical data must be sent in a tamper-proof manner. The significant heterogeneity in communication protocols, medical devices, and platforms causes this lack of standardization. Therefore, to protect such a variable standardized transmission medium, Blockchain is utilized to resist unauthorized access. This happens during data transmission over an unknown network, as a diverse communication standard of a system does not affect the blockchain’s performance.
Market Activity
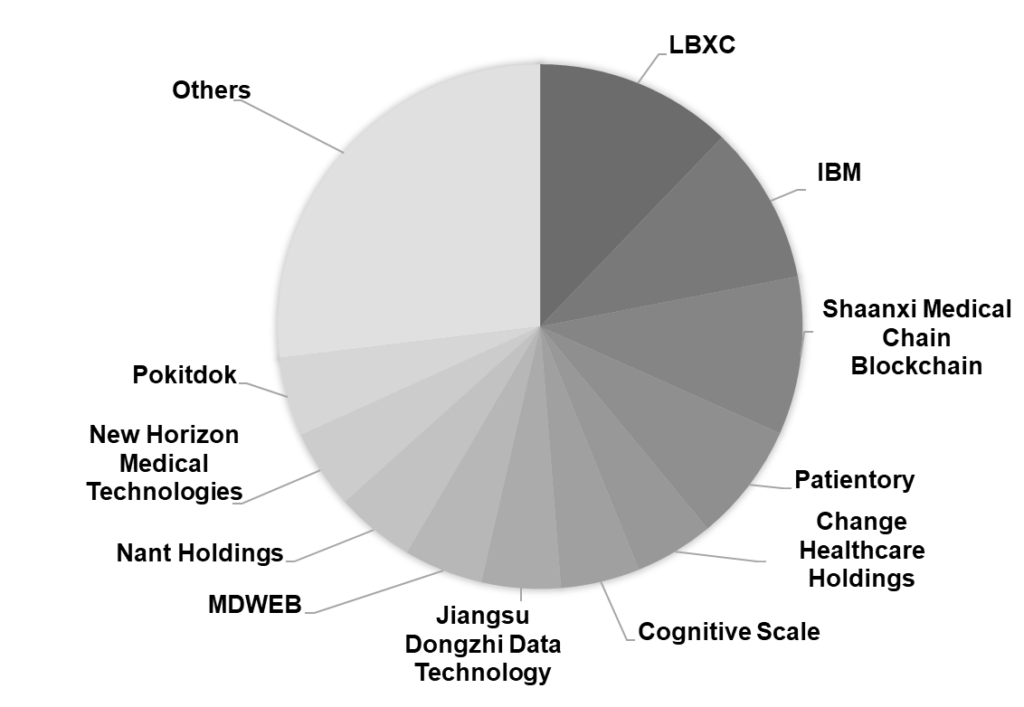
IP Insights
The top assignees actively working in the blockchain-based Healthcare domain are shown in the chart below:
Commercialized Solutions
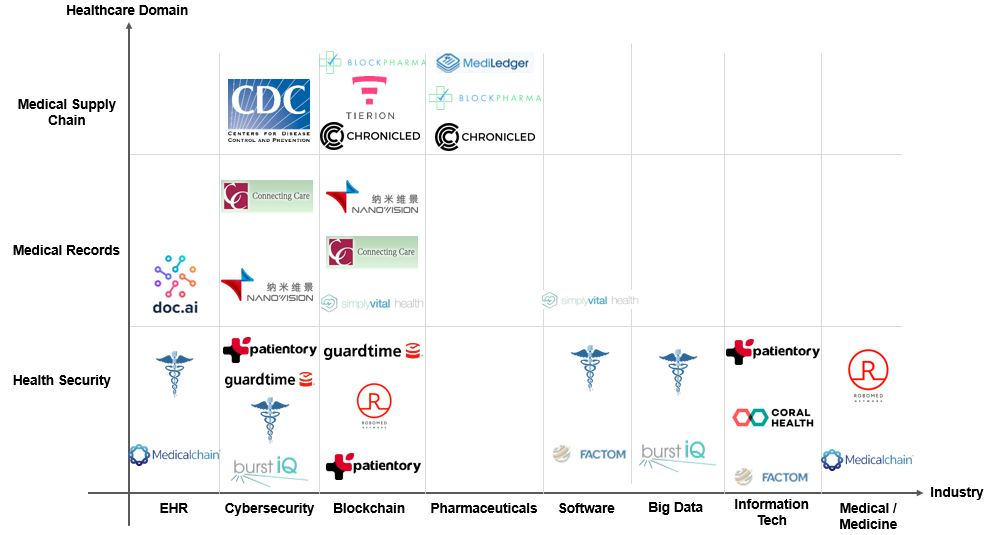
The chart below summarizes health-related Blockchain products and prominent players offering proprietary Blockchain solutions across different domains of application.
Future Scope for Using Blockchain in the Healthcare Domain
Blockchain systems have fundamentally redefined healthcare sectors by increasing operational efficacy, data privacy, and expenses. In contrast, integrating medical services with Blockchain technology introduces several technological hurdles. These include Blockchain size, sustainability, integration, latency, trouble interfacing with traditional medical systems, intricacy, and a shortage of Blockchain professionals. Below are a few recommendations for the successful future integration of Blockchain technology with healthcare.
- Quantum Computing: The use of quantum-resistant digital signatures can be a potential solution for the security challenge of public-key cryptography-based Blockchain systems
- Data Tokenization: The adoption of tokenization enables the digital representation of healthcare data, allowing patients to read and restore their medical records without the need to decrypt or re-encrypt them. It removes control from centralized counterparties. Patients can keep and exchange healthcare data with anyone, which reduces their medical care expenses. Also, patients may receive tokens that can be used to pay for medical bills as payment for sharing this information with institutions.
- IoT-based consensus mechanism: The consensus protocol is fast evolving to meet blockchain-oriented healthcare applications’ demands. In contrast to transaction syntax alone, it collects consensus data through data transaction validation, such as sensor measurements of IoT devices used in the healthcare industry. Therefore, the collaborative nature, body area network, reading similarity, and IoT connectivity are prerequisites for developing data-centric consensus methods.
Conclusion
The introduction of blockchain technology in different sectors is resolving various challenges. Blockchain is revolutionizing food supply chains, and this technology has left an indelible impact on the healthcare industry through data integrity, access control, logging, data versioning, nonrepudiation of patient health records, etc. The use of blockchain for healthcare applications like patients’ EMRs, biomedical research & education, remote patient monitoring, supply chains, health insurance claims, and health data analytics promotes the monetization of health information, enhances interoperability between healthcare organizations, and helps combat counterfeit medicines.
Despite the shortcomings of utilizing Blockchain in the healthcare industry, various types of solutions, platforms, or devices are developed by companies and institutes to advance the healthcare domain. The future of the healthcare industry significantly depends on the potential in conjunction with advanced technologies. It includes smart contracts, consensus protocol, tokenization, quantum computing, or AI integration for the future. Overall, this technology will significantly improve and eventually revolutionize how patients and physicians treat and use clinical records and improve healthcare services.
Let's Take the Conversation Forward
Reach out to Stellarix experts for tailored solutions to streamline your operations and achieve
measurable business excellence.



