Next-Gen Connectivity: 5G Core as a Service (5GCaaS)
The emergence of 5G is driving a disruptive shift to connect, communicate, and consume information. While improving the speed and latency performance, 5G offers a new concept of 5G Core as a Service (5GCaaS), emerging as a revolutionary development in the telecommunication industry. The idea of 5GCaaS is built upon the principles of virtualization, software-defined networks (SDN), and cloud-native technologies. The 5GCaaS is a flexible subscription-based architecture providing prospects for enabling efficient network management, scalability, and cost-effective solutions to network operators and private enterprises.
This article discusses the 5GCaaS concepts and their various aspects while highlighting key implementation challenges, market players that offer solutions to address these challenges, various research initiatives to enhance 5GCaaS capabilities, and market activities undertaken by different market players.
What is 5G Core as a Service?
5GCaas refers to the division of the 5G core network infrastructure into multiple parts and then offering the services on a cloud-based infrastructure depending upon a private enterprise’s QoS requirement. 5GCaas reduces the need for large-scale infrastructure, saving the enterprise capital expenditure.
5GCaas helps private companies deploy secure and reliable 5G services at their site where the 5G network or Wi-Fi is not up to the mark. Further, companies can avoid upfront investments required to purchase and maintain their physical infrastructure, including hardware and software components of the 5G core network. The service provides flexibility, scalability, and faster deployment of 5G networks, enabling operators to focus on delivering innovative 5G services to customers.
5G Core as a Service Framework
5GCaaS can be implemented with a simple three-tier architecture wherein the 5G network core and access points will be deployed at the enterprise premises, and the orchestration and management are performed through the orchestrator platform by the mobile operators. The figure below showcases the implementation framework of 5GCaaS
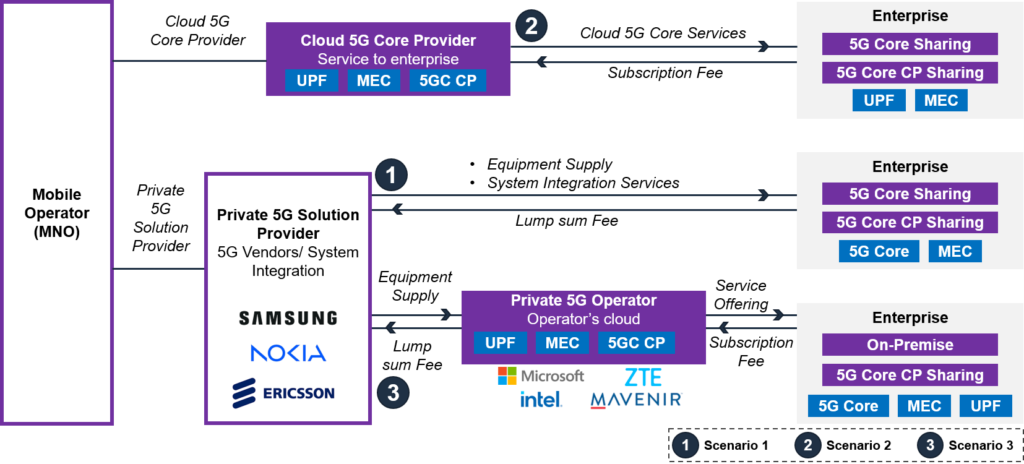
Figure: 5G core as a service (5GCaaS) Framework
Based on the enterprise requirements, the 5GCaaS framework disaggregates the various 5G core network functions such as User Plane Function (UPF), Network Exposure Function (NEF), Session Management Function (SMF), etc. It deploys them as separate micro-services on a multi-access edge computing (MEC) platform. The 5GCaaS framework provides a modular approach that enables the mobile operators or service providers (MNOs) to scale the individual components based on the demand and reduces the need for capital expenditure for large-scale network infrastructure deployments.
Below are some of the prominent deployment scenarios for 5GCaaS:
Scenario 1: For Large Enterprises
- The private 5G solution provider offers 5GCaaS to large enterprises who want to develop on-premise type, which means the 5G base station, 5G core, and MEC (enterprise application) are all installed at the enterprise site
- Enterprises apply for private 5G frequencies that will be used at their location and then use the frequencies to build their own private networks
- The 5G network service providers purchase 5G network equipment, such as core RAN, MEC, etc., from the private 5G solution providers and support the large enterprises in building and operating private 5G services.
Scenario 2: For Small and Medium Enterprises
- The 5G service provider offers cloud 5G core subscription services to small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) that wish to establish their own private 5G networks
- The 5G Core is hosted in the public cloud (e.g., AWS), while the 5G Radio Access Network (RAN) is deployed at the enterprise site
- The 5G service provider provides the cloud 5G core as a service, eliminating the need for SMEs to purchase expensive 5G core equipment
- Enterprises obtain private 5G frequencies and build their own base stations by paying a subscription fee to access the 5G service provider’s cloud 5G core
- The 5G service provider acts as a service provider and receives revenue through service fees from these enterprises
Scenario 3: For Operator’s Cloud Provider to Enterprise
- As a private 5G solution provider, the service provider sells private 5G solutions (such as equipment, terminals, OSS systems, etc.) to new private 5G operators.
- The 5G private operators obtain equipment from private 5G solution providers or vendors and help the enterprise set up their private 5G network.
- Recognizing the diverse landscape, the private 5G solution provider caters to specialized network operators aspiring to establish their own private 5G networks.
- This inclusivity broadens the reach and impact of private 5G solutions. The core business model revolves around revenue generation by selling these bespoke solutions to private 5G operators.
Navigating Challenges in 5G Core as a Service Implementation
Although the 5GCaaS framework offers a large number of benefits, this rewarding framework presents a set of challenges during its implementation. The below list includes some prominent challenges that various players face and the potential solutions for efficiently implementing and deploying the 5GCaaS framework:
Challenge – Security and Privacy:
Robust security and privacy are crucial in a 5G core as a service ecosystem. Ongoing challenges include protecting user data, preventing unauthorized access, and addressing security threats.
- Cisco has developed solutions to secure the 5G Core (5GC) and Evolved Packet Core (EPC)with Cisco’s zero trust security to the 5G core network infrastructure.
- Microsoft Azure has developed Azure Private 5G Core to provide simple, scalable, and secure deployment of private 5G core networks on an Azure Arc–managed edge platform within the Azure private multi-access edge compute (MEC) solution.
The private 5G core can be easily deployed and connected for indoor and outdoor applications. Azure private 5G core is equipped with Microsoft Zero Trust solutions to provide security to the 5G network, workloads, etc., of enterprises and customers.
Challenge – Service Orchestration and Management:
Managing services in a 5G core as a service environment involves complex service chains, dynamic network configurations, and diverse requirements.
- Mavenir provides a next-gen Operations Support System (ngOSS) as part of its MAVscale platform. This system combines AI, analytics, automation, and orchestration to enhance network performance and enable intelligent network operations to enhance the performance of 5G networks.
Challenge—Interoperability and Integration:
Achieving seamless interoperability and integration in the implementation of 5GCaaS is a multifaceted issue involving integrating various components and technologies from different vendors.
- Samsung provides a 5G Open Lab, known as the 5G Innovation Hub, which facilitates interoperability testing and integration of various network functions (NFs) with Samsung’s 5G Core.
- Alepo has designed a 5GC Solution that consists of cloud-native 3GPP standards-compliant 5G Core network functions (NFs) to implement subscription services, enable secured connectivity to subscribers, and handle charging and policy management.
Challenge – Scalability and Performance:
Meeting the growing demand for 5G services requires scalable, high-performance infrastructure. Key requirements include supporting massive traffic volumes, low-latency applications, and providing quality user experiences.
- Ericsson offers solutions to address scalability and performance aspects of 5G core networks, such as cloud-native architecture, network function virtualization (NFV), and advanced management and orchestration capabilities.
Research Advancements in 5G Core as a Service
5GCaaS has a growing research landscape, with continuous research focused on enhancing and optimizing various aspects of 5GCaaS. Key areas of research include:
- Improving Charging Capabilities Regarding Delivering Core Capabilities of 5G Network Using Cloud Infrastructure
- Deutsche Telekom’s researchers have started working on a method to enable network-slice-aware, procedure-based charging for multi-tenant cloud-based core-as-a-service deployments.
- A mobile network core that is being deployed as a managed service, i.e., as a core network instance within a cloud infrastructure, is realized, and based on each subscriber’s subscription, connectivity is provided for a specific data network.
- The cloud provider that is providing cloud infrastructure will charge each subscriber for the functional resources of the cloud infrastructure that the subscribers use.
- Protection of 5G Core Elements using a Message Bus Controller
- The researchers from AT&T have introduced a method to protect the network functions or core elements, such as AMF, SMF, AUSF, etc., from intrusion detection using a message bus controller.
- The network functions can communicate with each other using a unified centric message bus.
- The message can access the message received from the message bus. After receiving the message, the message bus controller accesses the contextual message and identifies whether any abnormality or malicious content is present in the message.
- If an abnormality is detected, the message bus controller drops the message and protects the 5 G’s network functions; if no abnormality is detected, the message is transferred to the network functions.
Key Market Insights
As various industry enterprises are adopting the deployment of 5GCaaS, the market activities are picking up steam and reflecting the competitive and dynamic environment. Below are some of the key market activities conducted by the prominent market players:
| Rakuten | Rakuten Mobile and NEC have collaborated to develop a Containerized Standalone (SA) 5G Core Network. Rakuten and NEC have collaborated to develop the containerized SA 5G mobile core that is compatible with the Rakuten Communications Platform (RCP), The containerized 5GC on RCP has allowed customers and enterprises to purchase and deploy fully virtualized SA 5G core network solutions to their networks quickly and easily. |
| Mobileum | Mobileum, provides solutions for analytics related to testing and monitoring, roaming and network services, security, risk management, and testing and monitoring had acquired Convene Networks, a technology provider of integrated core network solutions for 3G/4G/5G networks. The acquisition expands Mobileum’s core network technology footprint to extend its portfolio of 5G Core (“5GC”) solutions and provide commercial off-the-shelf (“COTS”) 5G-in-a-box for small enterprises and private networks. |
| Nokia | Nokia launched Core Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) for 5G, providing a complete core solution through a SaaS delivery model. It includes a 5G Packet Core and other cloud-native network functions. Nokia Core SaaS offers a flexible, automated, and scalable software model, enabling faster time to value and greater business agility for communication service providers (CSPs) and enterprises. The solution eliminates the need to deploy customized software on private infrastructure, offering a cost-effective subscription service with on-demand access and avoiding upfront capital expenditure. |
| Elisa | Elisa and Nokia have partnered to deploy 5G core-as-a-service at Nokia Arena, which will improve operational efficiencies in network service production. This partnership explores the potential of Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) to transform telecom services, unlocking benefits such as greater agility, efficiency, faster time to value, and better customer experiences |
Conclusion
5GCaaS offers companies a cost-effective, flexible solution for deploying and managing 5G networks. 5GCaaS allows small and medium-scale enterprises to deploy 5G core functionalities on their existing networks. The implementation of 5GCaaS is still in a nascent stage but various companies like Ericsson, Nokia, Huawei, etc. provide solutions related to various challenges such as security, service orchestration, interoperability, etc. and a lot of research is also going on to enhance the capabilities of 5GCaaS. Moreover, the 5GCaaS can benefit small and medium-scale enterprises. It will open new opportunities for them to compete in the telecom market and end the monopoly of the prevailing telecom provider.



