Transforming Healthcare with POC Diagnostic Devices
The healthcare sector expanded rapidly following the introduction of point-of-care diagnostic (POC diagnostic) technologies. These tools will make it possible to make diagnostic decisions quickly and frequently, which will help improve patient outcomes. Particularly in rural locations, they will significantly refine the patient’s quality of life. They have an edge over traditional diagnostic tools because of their portability, rapidity, simplicity of use, and versatility.
Several illnesses, including cancer, heart problems, chronic illnesses, and infectious diseases, can be diagnosed with the POC diagnostic device. The devices will incorporate many cutting-edge technologies, including molecular diagnostics, immunoassays, biosensors, microfluidics, and lateral flow assays. The article will discuss and highlight different types of POC diagnostic devices, some recent trends, and their benefits. Further, we will address the inherent challenges associated with POC diagnostic devices, along with the future scope.
What Are Point-of-Care Diagnostic Devices?
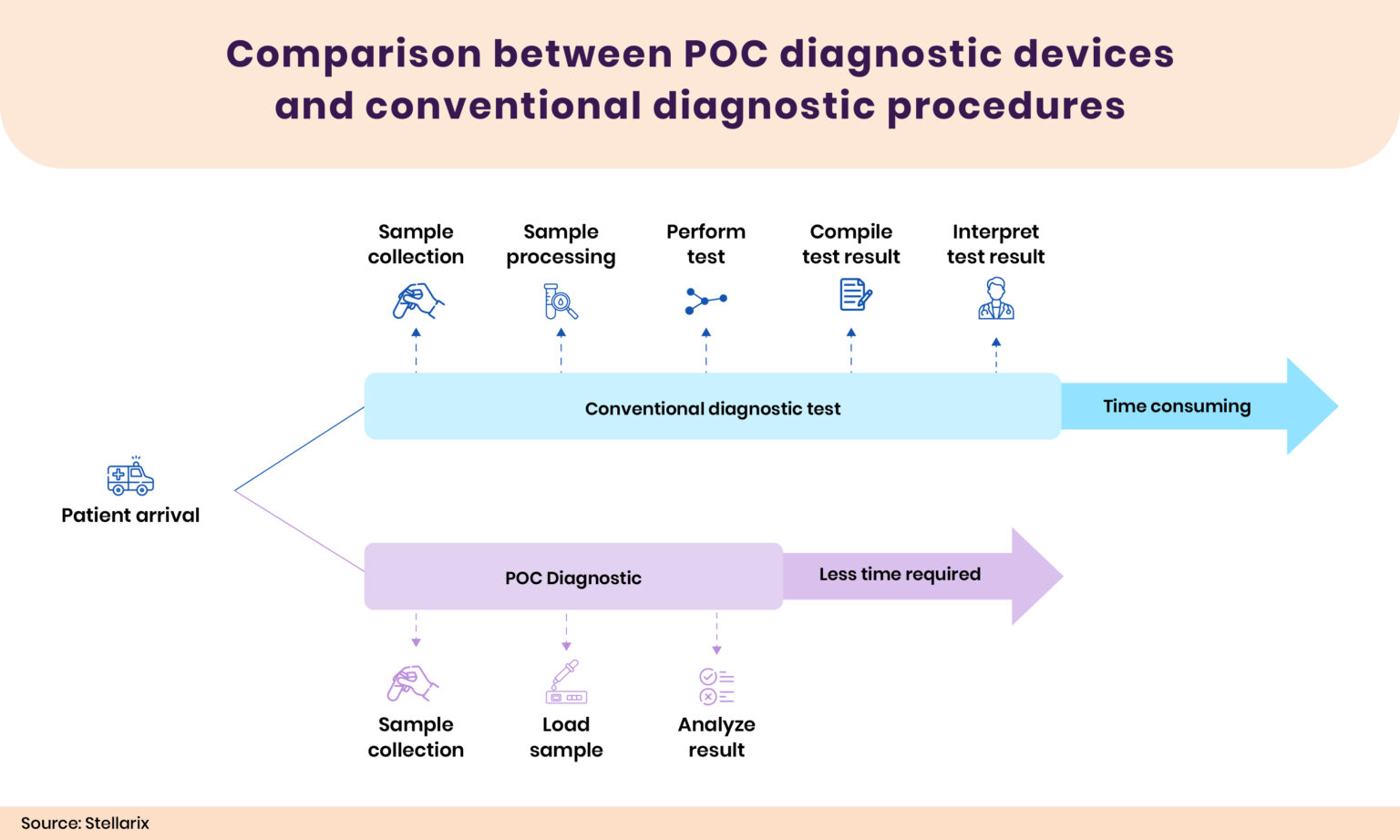
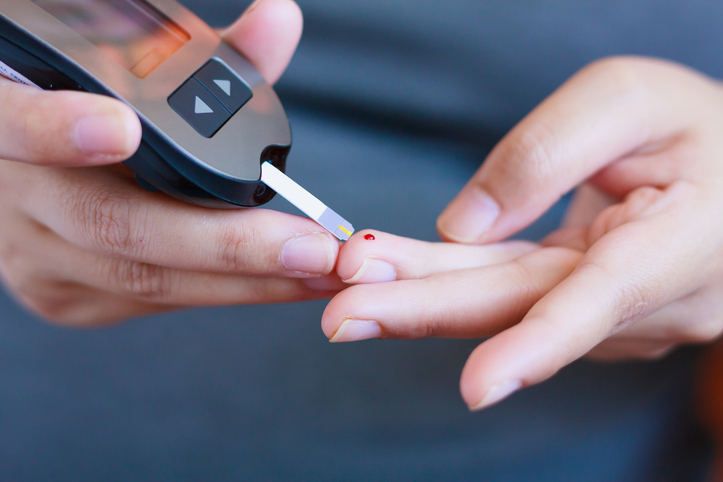
A point-of-care (POC) diagnostic device is used to obtain specific patient clinical data in clinical and resource-constrained situations. Testing at the point of care has several benefits, such as expedited results and, if essential, quicker therapy implementation. The diagnostic parameters are obtained by utilizing biological samples, including blood, saliva, urine, feces, or other bodily fluids, and subject body parameters or images. They are often easier to use, simpler, and more portable than traditional diagnostic tools. As a result, they can be used in a range of locations outside of hospitals, including clinics, physician offices, patient homes, ambulances, pharmacies, and even isolated or resource-poor areas. Because of its user-friendly features, patients, healthcare professionals, and their families can use it. Different POC diagnostic devices are available based on the test and the technology. The devices can detect various diseases, including infections, heart-related issues, chronic diseases, etc. Numerous technologies, such as lab on a chip, microfluidics, biosensors, immunoassays, and PCR, are available to quickly estimate results. The maximum share of POC diagnosis is associated with blood glucose detection devices and cardiac disease detection devices.
Need for POC Diagnostic Devices
Adopting point-of-care diagnosis devices to diagnose infectious diseases will reduce the chance of further spreading infections as the test will be completed in a single visit or as it will be done from home. Also, time is of the essence for detecting infectious disorders such as COVID-19. The automatic multiplex analytical tool of the gadget interprets the results, which avoids the need for a skilled technician. Point-of-care blood testing simplifies the diagnostic procedure by utilizing portable instruments. This guarantees that patients can be observed and isolated correctly.
Exploring the Range: Diverse Point-of-Care Diagnostic Devices
OC diagnostic devices are utilized to diagnose various diseases and differ based on the test type. Most POC diagnostic devices are available as rapid test kits, portable devices, lab-on-a-chips, or smartphone-based systems.
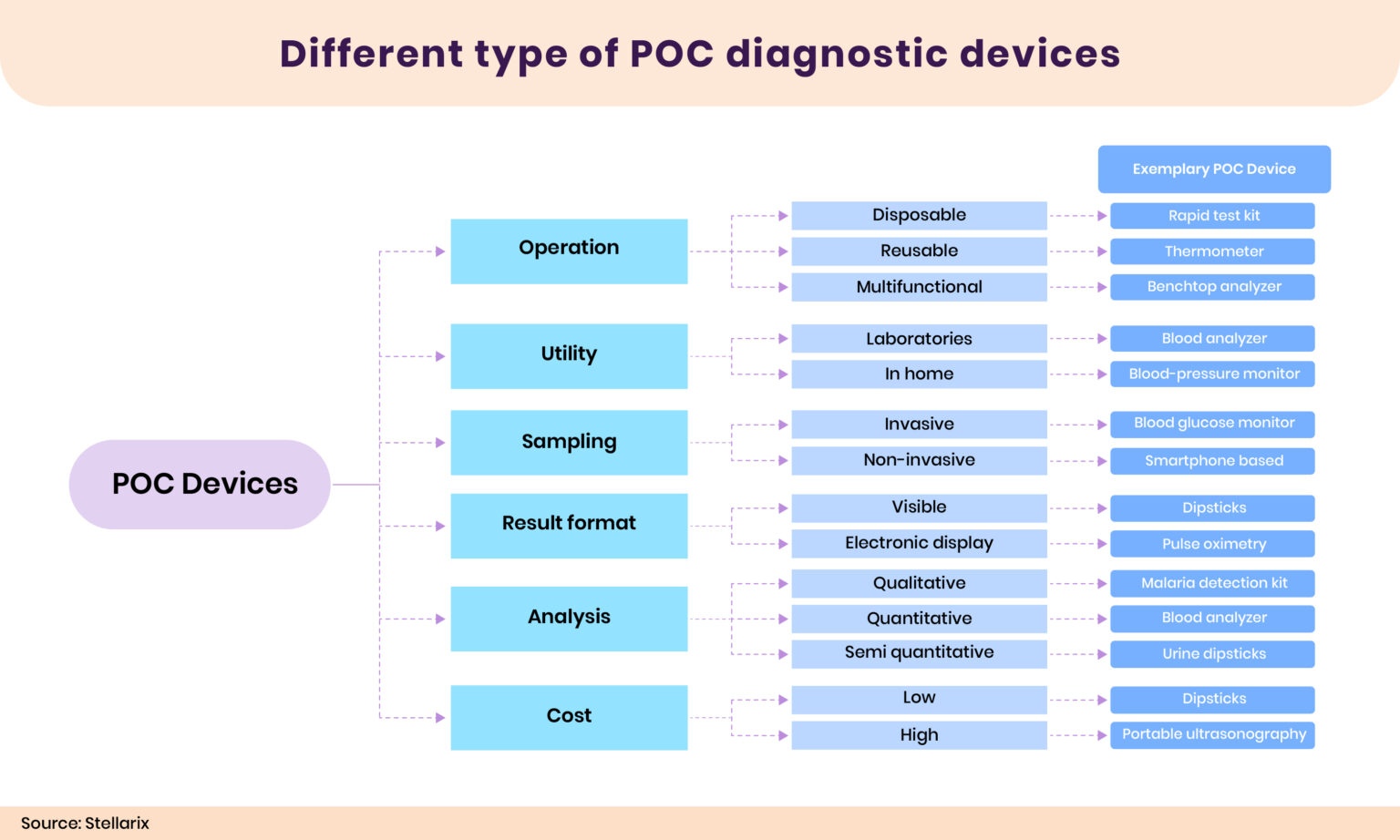
- Rapid Test Kits: Rapid test kits can provide results within 20 minutes or less instead of hours or days. Various diseases, like malaria, COVID-19, and infectious diseases, are diagnosed by utilizing rapid test kits. The kit will utilize biological samples such as blood, urine, saliva, or nasal secretion, mix them with a special substance, and lead to a chemical reaction to indicate the diagnostic status.
- Portable Devices: Portable diagnostic instruments are compact and easy to use. They offer great potential and shorten the time needed for diagnosis when traditional diagnostic tests are inaccessible. Portable diagnostic devices, like handheld ECGs, blood pressure monitors, and portable ultrasounds, are available in various forms. They integrate variable technologies like sensors, AI/ML, etc.
- Lab-on-a-chip Devices: Lab-on-a-chips are miniaturized microfluidic devices usually used in a laboratory setting. They are utilized to diagnose various diseases, such as cardiovascular disease, cancer, infectious diseases, and chronic diseases. The system allows for the biological and biochemical investigation of various samples on one platform.
- Smartphone-based Devices: Integrating AI into a smartphone allows the smart camera to diagnose diseases like anemia and cancer.
Advantages of Point-of-care Diagnosis Over Conventional Diagnosis
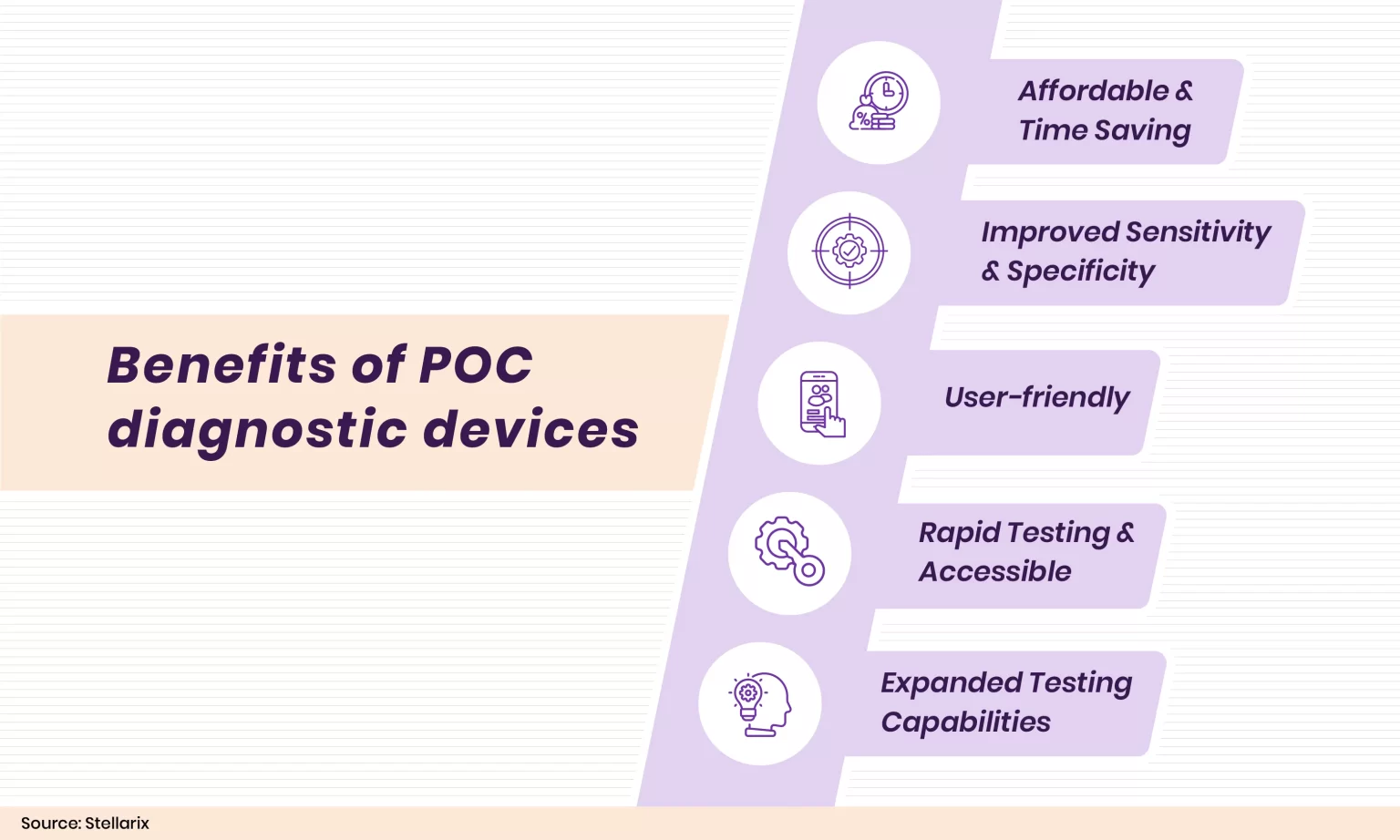
Point-of-care (POC) diagnostics have several advantages over conventional diagnostic devices. The POC devices are essential for providing accurate and timely diagnostic information. Comparing most POC devices with traditional diagnostic devices, they are more affordable and yield results faster. The portability enables medical personnel to conduct and get results at the patient’s site or close by, which will help to enhance patient care. This will eliminate the requirement to schedule an appointment to take tests.
An experienced technician handling several samples during a conventional diagnostic test may result in incorrect labeling and an erroneous diagnosis. Handling errors and contamination will be reduced as the POC devices require less human effort. The conventional test requires a professional technician to interpret the results, while the user-friendly POC devices offer results that users can interpret themselves. The POC devices permit patients to be examined more regularly because of their portability and reduced financial effect, particularly at locations where laboratory services are not consistently available.
What Cutting-edge Technologies are Enabled in POC Diagnostics Devices?
Various cutting-edge technologies are interpreted into POC diagnostic devices to ensure a precise and rapid diagnosis. Below are a few of the notable cutting-edge technologies currently evolving in the field of POC diagnostics.
- Integration of Advanced Technologies: Advanced technologies like artificial intelligence, machine learning, and IoT are incorporated into the POC diagnostic devices. Artificial intelligence or machine learning techniques interpret the data and provide precise diagnostic information. The IoT integration helps transfer real-time data and guarantees lag-free connectivity.
- Portable Gene Sequencing Devices: Portable gene sequencing devices enable the analysis of an individual’s RNA or DNA from anywhere. It has a great potential to diagnose patients more quickly, particularly in remote locations.
- Screen-printed Electrodes: Screen-printed electrodes are electrochemical measurement devices constructed by printing various inks on a plastic or ceramic substrate. They are cost-effective and enable rapid testing without the need for a technical expert.
- Expanded Test Menus and Multiplexing Capabilities: The extended test menu enables testing of multiple tests by using a single device rather than multiple devices, and the multiplexing capabilities allow for simultaneously testing multiple analytics, which lowers costs and increases productivity.
- Enhanced Connectivity and Data Management: POC diagnostic devices facilitate coherent amalgamation with EHR systems, and the data management feature helps to provide evidence-based decision-making.
- Adoption of Disposable and Single-use Devices: Conventional diagnostic devices require sterilization frequently, while adopting single-use or disposable POC diagnostic devices avoids the need for time-consuming and expensive sterilization procedures, lessening the chance of cross-contamination and infection.
- Paper-based Analytics Devices: Paper-based analytic devices work based on the conducting properties of paper. It will allow conducting multiple bioassays at a time by using a single sample drop.
POC Diagnostics Prominent Players
Some of the major companies working in the arena with strong portfolios are Abbott, Johnson & Johnson, ThermoFisher, Siemens, Roche, Becton Dickinson, etc., which are providing disruptive technologies revolutionizing the healthcare industry.

Recent Market Activities
Medical device manufacturers are leveraging various technologies and techniques to improve the efficacy of existing products and develop new, often disruptive devices. The figure below illustrates some recent happenings and insights related to POC diagnostic devices.
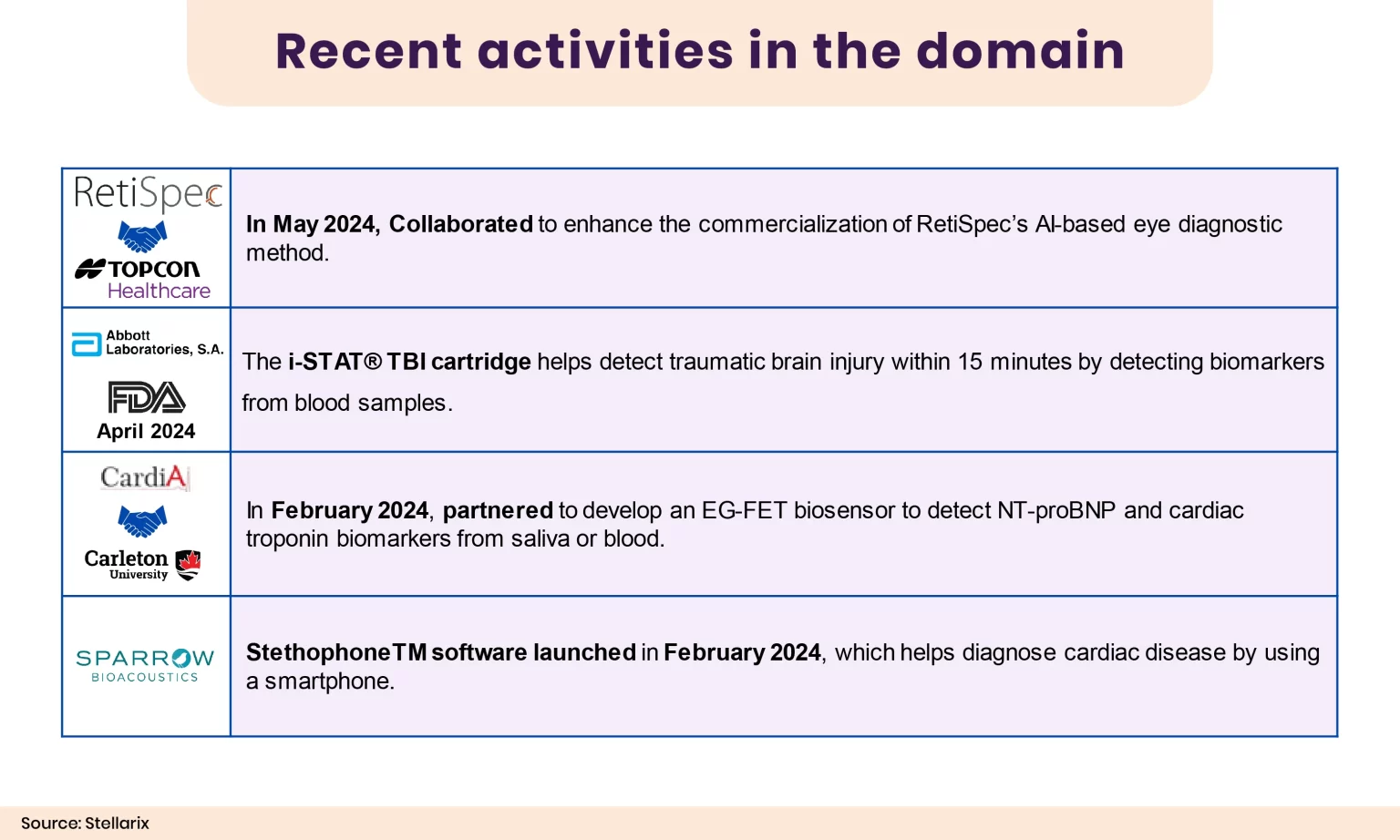
Figure 5: Recent Activities in the Domain
How Will the Field of POC Diagnostics Evolve in the Future?
POC diagnostic technologies are widely accepted and are expanding quickly. Below are a few futuristic technologies that can potentially improve the capabilities of POC diagnostic devices.
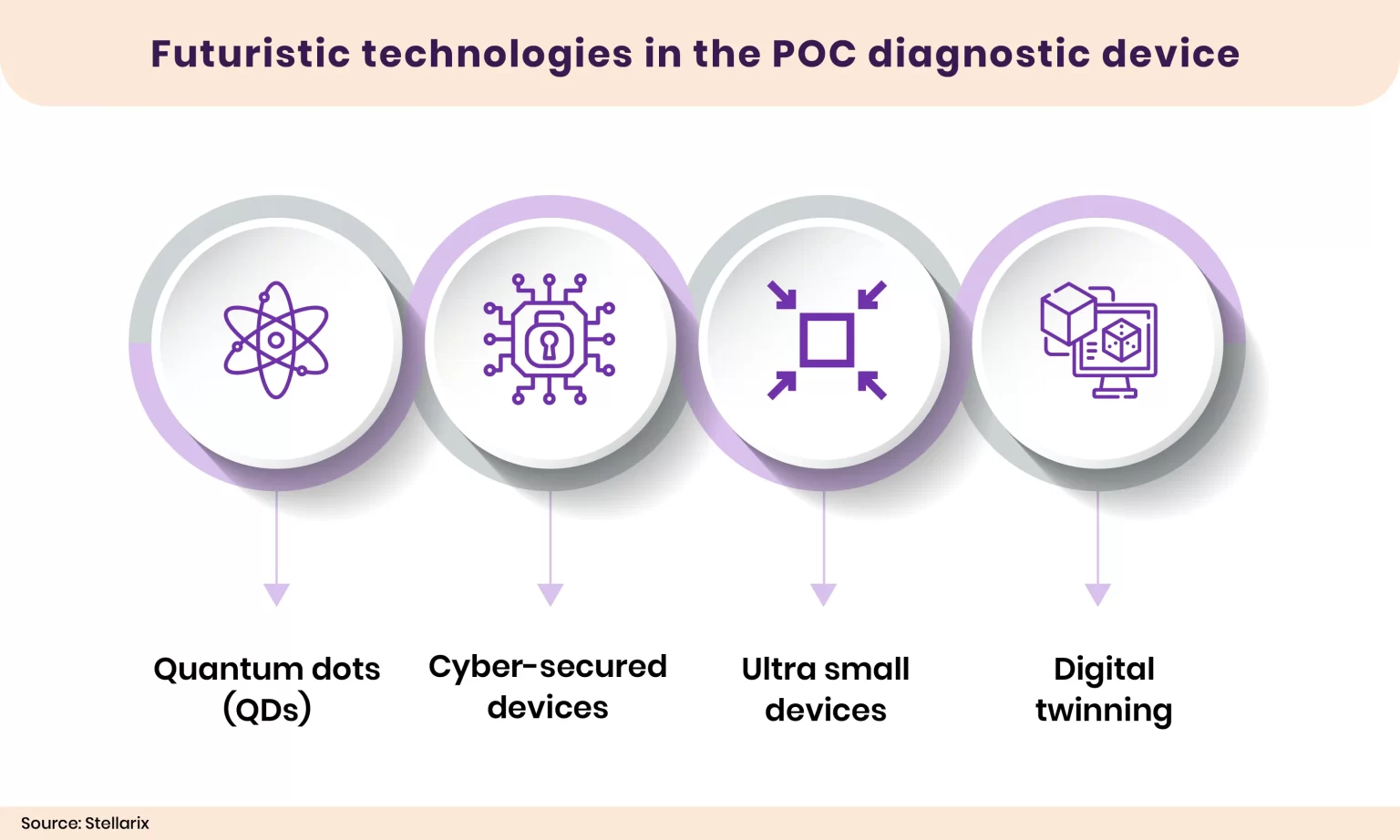
- Quantum Dots (QDs): Quantum dots will detect biomolecules based on fluorescent processes, but compared to conventional fluorescent dyes quantum dots provide a brighter fluorescence intensity and are long-lasting. The method has various benefits including high brightness and photostability, tunable emission spectra, capacity for surface functionalization, biocompatibility, and low toxicity.
- Cyber-Secured Devices: Data security is a major concern when transferring confidential medical data. A biomedical microelectromechanical system (BioMEMS)- based sensor can enable signal encryption at the physical sensor level.
- Ultra Small Devices: A miniaturized cylindrical phosphorescent reader head with a diameter of only 25.4 mm can be designed to detect the concentration of different bio-analytes, including oxygen and glucose. The device will enhance portable devices’ user-friendliness.
- Digital Twinning: Digital technology can simulate various patient attributes and replicate their actions and reactions in particular circumstances. Such replicated data can be used to assess health and diagnose disease.
Challenges Associated with POC Devices
Although POC diagnostic devices offer numerous advantages, specific challenges still need to be overcome. Some of the notable challenges are listed below:
- Quality Control and Quality Assurance: No structured procedure guarantees the daily or weekly quality or accuracy of the POC diagnostic equipment. Furthermore, no formal procedures exist for organizing the reagents or upgrading the software.
- Regulatory Consideration and Standardization: Robust regulatory frameworks and established standards are necessary to develop various POC diagnostic devices. The established standards will ensure consistent performance, safety, and reliability. Sometimes, the devices or kits might not have FDA approval for every application.
- Privacy and Security Concerns with Data Transmission and Storage: Data security and privacy become increasingly important as POCT devices become more connected and integrated with electronic systems. Patient data must be sufficiently protected both when it is sent and stored. Data encryption, authentication, and regulations are essential to protecting highly sensitive medical data.
- Accuracy and Reliability: Various factors, like user error, environmental conditions, and technological constraints, may compromise the accuracy of POC diagnostic devices.
- Human Error: The way POC diagnostic device results are interpreted will be greatly influenced by the eyesight and cognitive abilities of the person evaluating the results.
Conclusion
The healthcare sector is advancing by adopting POC diagnostic devices, which provide rapid results and enable great accessibility to diagnostic testing. The devices hold enormous potential to enhance the healthcare industry, especially in rural areas. POC diagnostic technologies offer several advantages, including mobility, simplicity, ease of use, and speed, ensuring rapid diagnostic information, enhanced patient outcomes, and reduced healthcare costs. The POC devices can vary depending on the technology and kind of test. As technology advances daily, POC diagnostics will become more accurate, reasonable, and reliable. As these devices continue to evolve, their widespread adoption promises to revolutionize medical practice, bringing diagnostics closer to the point of need and ultimately enhancing global health outcomes.
Let's Take the Conversation Forward
Reach out to Stellarix experts for tailored solutions to streamline your operations and achieve
measurable business excellence.