Floating Solar Farms: Energy Production With Global Reservoirs
Integration and scalability of renewable energy are reaching new heights. With shrinking land resources, innovation is shifting to water and air. Floating solar panels are emerging as one such extensive solution that is revolutionizing clean energy production. These farms leverage underutilized water surfaces for power generation while neutralizing water and land preservation challenges. This blog analyzes recent developments in the floating solar sector and outlines the opportunities and challenges shaping the future of this segment.
Floating Solar Farms Market Growth and Projections
The global floating solar farms market was valued $5.3 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach $40.35 billion by 2034 at an implied CAGR of 22.5%. The key market drivers behind this growth include:
- Strong Regulatory Support: Governments in Europe and the Asia-Pacific are highly inclined towards the incorporation of floating solar panels into their national energy grids. They plan to include these in their renewable energy targets and follow a streamlined path to their development.
- Technological Standardization: With technological maturity, the relative costs of floating solar panels will come under affordable limits. It will help manufacturers ensure ROI and gain better capital investments.
- Integration with Preexisting Infrastructure: The trend of relocation of solar panels over water surfaces like industrial water bodies and treatment plants is opening up high-value, low-conflict opportunities.
What Are Floating Solar Farms?
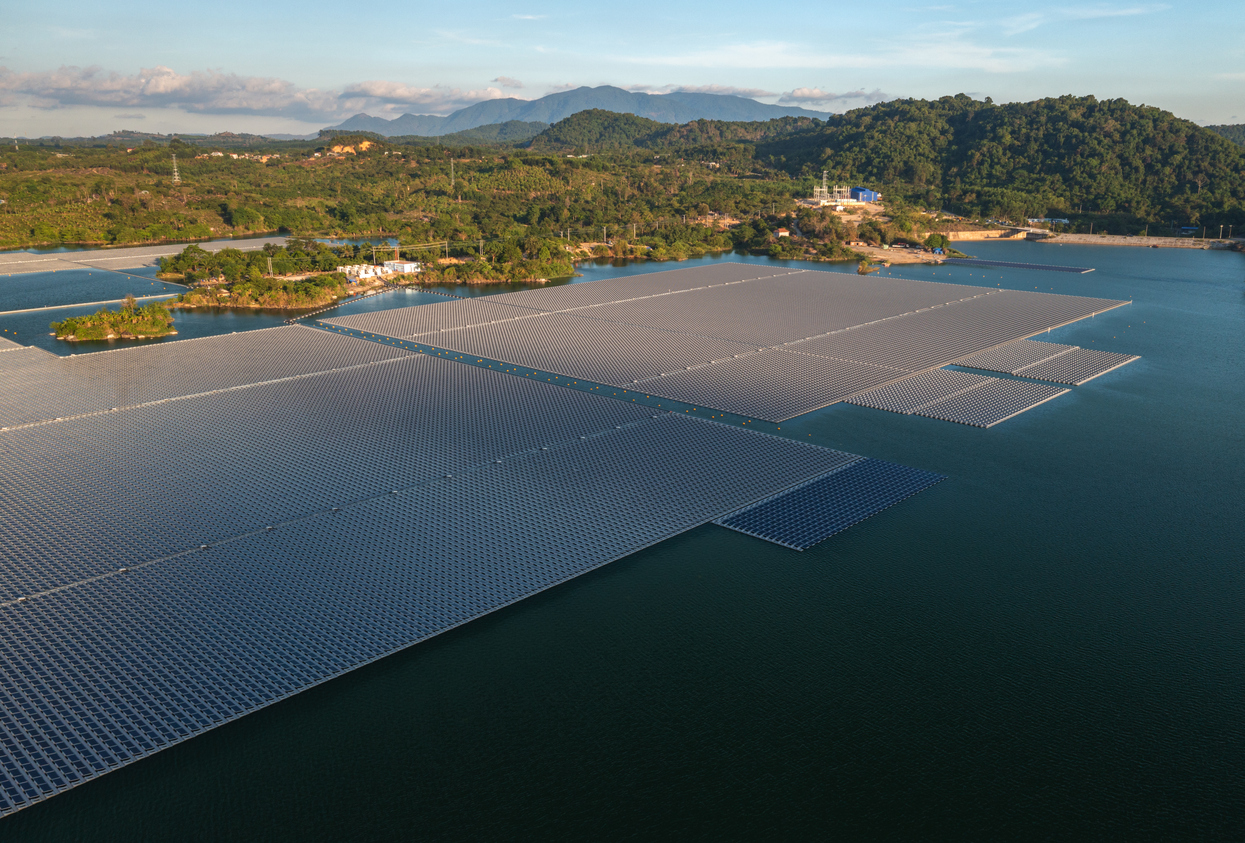
Floating solar farms, also known as “floatovoltaics” or floating photovoltaics, represent an innovative approach to harnessing solar energy. These floating solar farms consist of solar panels mounted on buoyant structures that float on bodies of water, such as reservoirs, lakes, irrigation canals, and remediation ponds. Water surfaces offer sustainable and environmentally friendly electricity generation, blending marine and renewable energy technologies.
The solar panels are securely fixed on these floating structures, ensuring they remain afloat on the water’s surface. This technology can be applied in various water bodies, including drinking water reservoirs, hydropower plants, and wastewater treatment plants. One of the significant advantages of floating solar farms is their ability to optimize space usage. They offer a promising alternative in locations with limited land availability, as they do not require valuable land resources for installation.
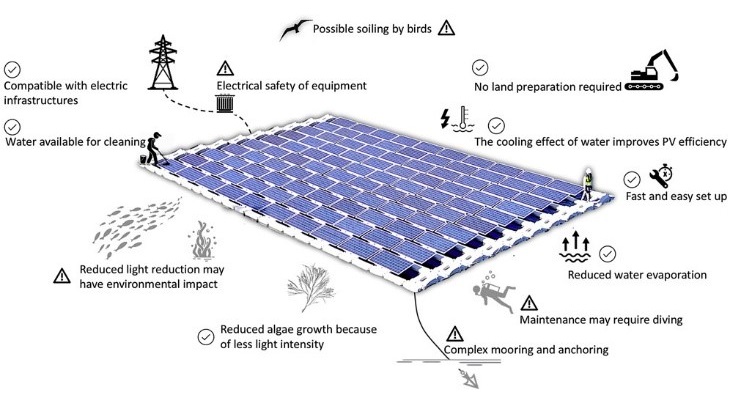
Figure 1: Graphical Abstract of Floating Solar Farms
Advantages Compared To Land-Based Solar Farms
Floating solar farms offer numerous advantages compared to their traditional land-based counterparts. Let’s explore some of the key benefits of these innovative installations:
- Improved Water Quality: Floating solar panels can help prevent the evaporation of water and minimize unwanted algae blooms by shading the water. This can lead to improved water quality.
- No Erosion: Traditional solar farms can cause erosion because solar panels block the sunlight from reaching the ground below. Floating solar farms do not have this issue, as they are not located on land.
- Don’t Require Land Space: Floating solar farms can be installed on any calm body of water, so they do not require valuable land space. This makes them a good option for locations with limited square footage.
- Generates More Power: Floating solar panels can generate more power than their land-based counterparts due to the cooling effects of water. Being in proximity to water helps the solar panels stay cool and absorb more sunlight, which can lead to increased productivity.
- Flexible Location: Floating solar farms can be installed in various locations, including reservoirs from wastewater treatment plants, drinking water reservoirs, or hydropower plants. This makes them a good option for areas near cities, where feeding power into the urban grid is easier than supplying it from remote solar farms in deserts.
Additionally Efficient
Floating solar panels can supposedly be more efficient than land-based ones due to the cooling effect of the water. Solar panels operate more efficiently when kept cool, and the presence of water helps to keep the panels cool, which improves their efficiency and electricity generation compared to land-based solar farms. A study conducted by scientists from the Copernicus Institute at Utrecht University in the Netherlands found that a floating system was 12.96% more productive than a ground-mounted array, generating 1,346 kWh annually per kilowatt installed, compared to 1,192 kWh for the land-based system.
Challenges And Solutions
Floating solar farms have several advantages, but they also face some challenges. Here are some of the challenges and solutions for floating solar farms:
Challenges:
- Durability: Harsh weather conditions, such as strong winds and waves, expose floating solar panels to potential damage, affecting both the panels and the floating structure. The panels also need to be able to withstand corrosion from the water.
- Maintenance: Floating solar panels require regular cleaning to remove biofilms caused by microbial activity, which can reduce their efficiency. Regular inspections are necessary to ensure the panels are functioning correctly.
- Cost: Floating solar farms can be more expensive to develop than land-based solar farms due to the additional costs of the floating structure and anchoring system. They also require specialized equipment and expertise for installation and maintenance.
Solutions:
- Durability: Floating solar panels demonstrate exceptional resilience by incorporating robust materials, enabling them to endure challenging weather conditions and resist corrosion. Moreover, their flexible design allows them to adapt seamlessly to fluctuating water levels, further enhancing their adaptability and effectiveness.
- Maintenance: Regular cleaning and inspection can help maintain the efficiency of the solar panels. Installers can also set up automated cleaning systems to reduce the need for manual cleaning.
- Cost: Floating solar farms can be more cost-effective using existing infrastructure, such as hydroelectric dam reservoirs, and combining offshore wind farms and floating solar farms to use the same transmission line.
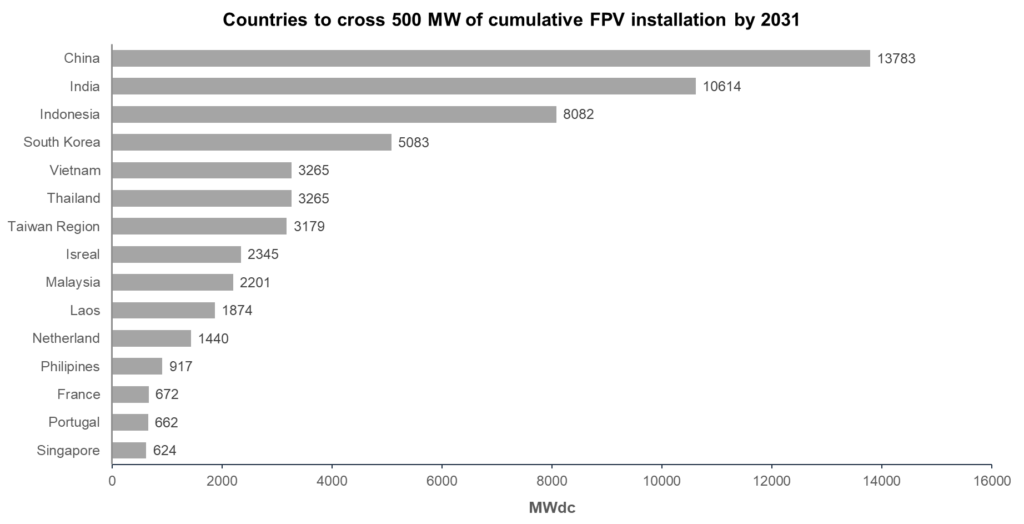
Figure 2: Nations to Cross 500 MW FPV Installations by 2031
Industrial Benefits Of Floating Solar Plants
- No land occupancy: Floating solar plants offer a distinct advantage as they require minimal land usage, with only limited areas needed for electric cabinets and grid connections. Their unique feature allows installation on various water bodies, including wastewater treatment ponds, hydroelectric dams, and drinking water reservoirs, without encroaching on valuable land space.
- Improved Efficiency: Floating solar panels can achieve higher efficiencies than PV panels on land because water cools the panels, leading to better performance.
- Environmental Advantages: Floating solar plants can help improve water quality by shading the water and reducing algae growth. They can also reduce evaporation by up to 70%, which can be beneficial in regions that experience periods of drought.
- Sun-tracking Capability: Large floating platforms can easily rotate horizontally and vertically to enable sun-tracking, maximizing solar energy capture.
- Energy Generation: One square acre of floating solar panels is capable of generating 500,000 kWh.
Floating Solar Projects In Germany, US
In the United States, the most substantial floating solar project in California is the Healdsburg Floating Solar Farm. As the power supplier Sonoma Clean Power reported, this impressive installation consists of 11,600 solar panels and can generate 4.8 megawatts of electricity. This output is sufficient to fulfill approximately 8 percent of Healdsburg’s electricity demands.
Across the Atlantic, Germany’s biggest floating solar plant is situated on an unused lake within a quarry in the town of Halternam Sea. Experts estimate that this remarkable endeavor will curtail CO2 emissions by up to 1,100 tons annually. Interestingly, in light of recent geopolitical events, such as Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, Germany and other European countries are intensifying their focus on renewable energy sources to decrease their dependence on Russian oil and gas.
The floating solar system incorporates a highly efficient PV concentrator known for its lightweight design. It allows it to float gracefully on various water bodies. Rafts securely anchor these systems, resting upon the surfaces of irrigation canals, water reservoirs, quarry lakes, and tailing ponds. Notably, such innovative systems are already operating in different parts of the world, including France, India, the UK, Korea, Japan, and the US.
India, Singapore Making Significant Strides In Solar Farming
In India, an ambitious 600-megawatt floating solar energy plant is being built at the Omkareshwar Dam, a renowned pilgrimage on the Narmada River in Madhya Pradesh. Moreover, plans are in place for an even more substantial 1 gigawatt floating solar power project at the Indira Sagar dam, also in Madhya Pradesh. The central Indian state is already generating 5,500 megawatts of energy from renewable sources. As reported by the Asian solar energy news site SolarQuarter, it aims to further augment this capacity to 20,000 megawatts by 2030.
Meanwhile, Singapore’s huge floating solar farm on a massive floating solar farm located on the Tengeh Reservoir. This impressive facility spans an area equivalent to 45 football fields and has a staggering 122,000 floating solar panels. Notably, it plays a crucial role in powering Singapore’s five water treatment plants and aligns with the country’s ambitious goal to quadruple solar energy production by 2025.
Future Scope Of Floating Power Plants
a) Growing innovations in floating technology
b) Increasing concerns about land-neutral energy generation and energy independence
c) Great potential and increasing awareness for floating PV.
d) Availability of water bodies and land issues are the leading accelerators for floating PV Solar Panels.
e) Increased efficiency of Floating PV over Land PV installed
f) Availability of trained manpower and Govt. Policies have boosted the confidence of investors.
g) Stable floating PV platforms result in minimum operation & maintenance costs.
h) The emergence of new markets and investments in India, China, Thailand, Malaysia, and other developing countries
Conclusion
Floating solar farms are a significant step in the global energy transition. With a market poised for healthy growth, this sector will soon move from a niche category to a rapidly maturing market. Strategic advancements in perovskite technology, AI-based operational efficiency, and strategic integration with hydroelectric and storage systems will pave the path for a better value proposition and credibility for this market. Though the market still faces challenges in the context of investments and environmental integration, innovation through international collaborations will pave the path for answers. The future of floating solar farms is efficient, scalable, and sustainable with an intelligent bottom line.
Let's Take the Conversation Forward
Reach out to Stellarix experts for tailored solutions to streamline your operations and achieve
measurable business excellence.



