The ready-to-drink (RTD) market underwent a 360-degree change in the last two decades as consumer demand shifted to functional, natural, and healthier beverages with essentially low levels of calories, sugar, and alcohol content. It is a booming market that stood at USD 89 billion in 2021 and is expected to touch USD 142 billion by the end of this decade. While the manufacturers strive to comply with these new norms, they are also trying to address the complexities of manufacturing, supply chain, and improving the end-user experience.
The most significant share of impediments lies at the manufacturing end, where beverage makers need to keep drinks healthy and organic with distinct USPs and extended shelf life. These obstacles have opened doors to a lieu of innovations that integrate various concepts like blockchain, digital twins, AI, robots, etc., in the manufacturing process. In this blog, however, the focus remains solely on the breakthroughs that will help companies uphold the evolving standards of quality, processing, tracing, monitoring, and sustainability.
RTD Beverages: Quality
Quality is one of the most prominent differentiating attributes of canned products like RTD beverages. The biggest challenge is to retain the nutritional value of fruit-based or protein-based beverages without compromising their physiochemical properties. Health drinks, especially fruit-based drinks, have high concentrations of bioactive compounds (BCs) that favor the user’s well-being and health. However, several BCs are thermolabile and lost as the drinks pass through high-temperature preservation treatments. Also, some of the commonly used sterilization and pasteurization techniques cause physiochemical changes in the products, neutralizing the very intent of their production. Apart from that, there is the issue of microbial, enzymatic, and spore activity that needs to be controlled to keep the drink fresh till its final consumption. All these complexities demand advanced solutions that are both technologically sound and sustainable. Here are a few innovations that offer competent answers to these questions:
Innovations
- Blue Light Technology: It emits light through Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) at a preset wavelength to inactivate microbes and mitigate environmental contamination. A team of UGA researchers claims that Blue Light will be highly effective in combating microbes like Salmonella and Listeria monocytogenes and prevent the formation of biofilms on food and beverages. It may become a critical tool in controlling foodborne illnesses in the coming years.
- Hydrodynamic Cavitation: It is a non-thermal process that inactivates microbes and enzymes at low temperatures and preserves natural BCs present in food and drinks to retain their organoleptic characteristics, keeping their freshness and taste intact for a considerable period.
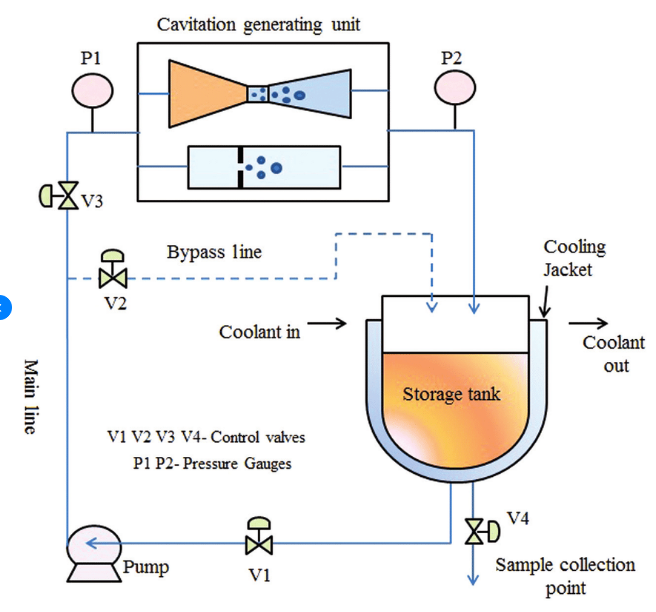
Figure 1: Schematic Diagram of Hydrodynamic Cavitation Reactor (PC: Researchgate)
- Raslysation: It is an Ultra Violet (UV) technology introduced by a Danish firm, Lyras. Currently, it is employed by Novozymes, a biotech group, to inactivate microorganisms in liquid foods. It filters out spores and bacteria and is considered a potent alternative to pasteurization in the near future.
- Laser Absorption Spectroscopy: Concerning beverages, this technology is used to scale the quantity of gas present in the headspace of bottles. Its application in the assembly line helps to remove defective bottles. Apart from that, it also measures nitrogen dosing the bottles.
- Supercritical Pasteurization: The process involves the usage of supercritical carbon dioxide for pasteurization, and just like raslysation, it is deemed a potent alternative to the conventional pasteurization technology that often destroys natural BCs in beverages.
Processing
The rise in demand for clean-labeled, minimally processed beverages mandates deploying new processes that can maintain sensory and nutritional quality. Most of such techniques are still in the R&D phase, but a few are being deemed potent for commercial applications:
- Ceramic Membrane Technology: It addresses beverages’ turbidity and bacterial count. Successful implementation of this technology will prevent corrosion and temperature resistance in drinks while preserving their aromatic attributes.
- Electrospun Nanofibrous Films: The membrane generated by Electrospun Nanofibers exceeds the flow capacity of regular membranes by approximately twenty times. They offer a fantastic alternative for removing suspensions and other harmful beverage components through filtration. The electrospinning process creates nanofibrous films of pores with tiny diameters and high porosity. It may play a vital role in the processing of beers and fruit juices in the near future.
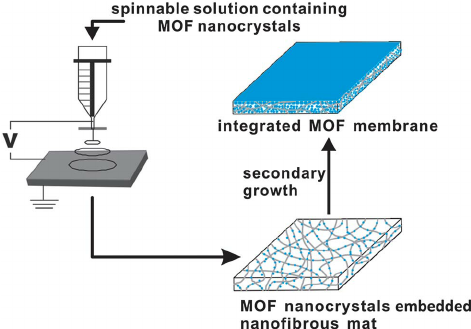
Figure 2: Schematic Illustration of Electrospun Nanofibrous Film
- Filler Efficiency: It reduces the wastage of carbon dioxide and increases the consumption of beverages during processing. If used properly, this technique will allow 70-80% filling of CO2 in the beverage and reduce its wastage by fifty percent.
- Oxygen Inhibition Technology: The oxygen inhibition technique prevents oxygen from entering the liquid during the blending phase and thus brings down the level of dissolved oxygen in the final product. It is critical in avoiding foaming and enhances a beverage’s stability at higher temperatures.
- De-Alcoholization: As the name implies, it removes alcohol from beverages. Under this umbrella term, the beverage industry actively prefers and incorporates methods such as reverse osmosis and vacuum stripping into the production line through simple assembly.
RTD Beverages: Traceability, Monitoring, And Control
Traceability, control, and monitoring are crucial in beverage processing. Even the smallest mistakes can result in significant errors. There are a few advancements in this aspect that may play a key role in the near future:
- IIoT: It offers multi-purpose, low-cost devices that check various added attributes of beverages like fluid properties, flow rate, gas percentage, turbidity, and so on. It updates the results in real-time and alerts if any beverage property changes.
- Blockchain: It will benefit backward and forward traceability of the complete production process. It will give the manufacturer full control of factory floors, supply chain, and final transactions with quick identification of errors.
- Digital Twin: These virtual replicas of the complete manufacturing framework allow operators to remotely test, control, and operate all activities. It also plays a crucial role in visualization, preliminary tests, and rectifications virtually before the real trial runs.
- IoT And AI-based Fermentation Tank: By leveraging AI and IoT, it is possible to place a sensor on each barrel to analyze all activities simultaneously and report errors or changes before the entire batch spoils. In the coming years, it may eliminate the requirement for manual sampling.
RTD Beverage: Advanced Technologies
Several advanced tech developments will assist the beverage industry in adapting to changing market dynamics. These developments will lead to significant cost savings and improve process flow. The most recommended ones include:
- Forward Osmosis: A beneficial technology for high-quality fruit-based beverages. It helps extract the best from products, whether raw materials or active ingredients. It creates an osmotic difference between the feed and draws solutions, allowing smoother water movement through the membrane.
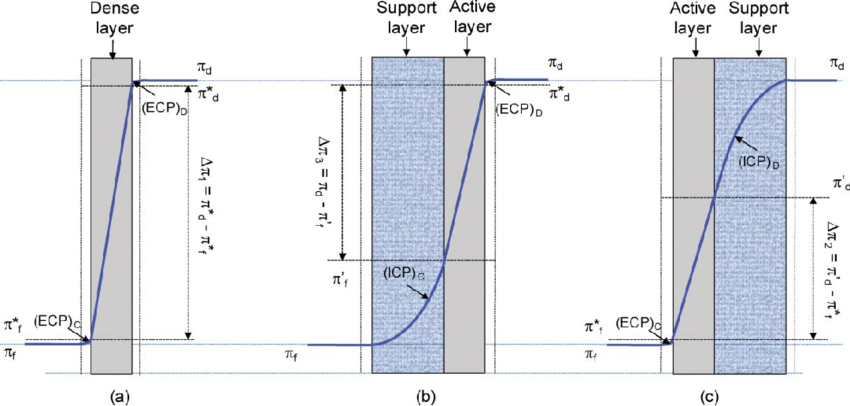
Figure 3: Schematic Presentation of Forward Osmosis Mechanism
- Automated Cap Chute Changeover: It eliminated the need for manually changing bottle caps, saving time and labor. The system consists of pneumatic cylinders that contract, extend, and push over plates to ease access to the bottle cap.
Ultra Clean Leakage Valve: The system helps maintain the hygiene and nutritional value of the beverage by blocking the entry of microbes into the product’s chamber. It also extends the overall shelf life of the product.
Sustainability
The food and beverage industry is working hard to align its modus operandi with the evolving sustainability standards. Along with all other changes, this is a key focus area for the industry. Here are a few noteworthy developments:
- Hydraulic Valve: Conventional valves are several steps behind as they reduce energy consumption and flawless precision by 90%. It also prevents the unrequired mixing of liquids as the eliminated water is in an incompressible form.
- Sustainable Homogenizer: It recaptures the freshwater in cooling transmission oil and lubricating plungers. The recaptured water is then sanitized, cooled down, and reverted to the homogenizer. The technology helps reduce freshwater consumption by 97%.
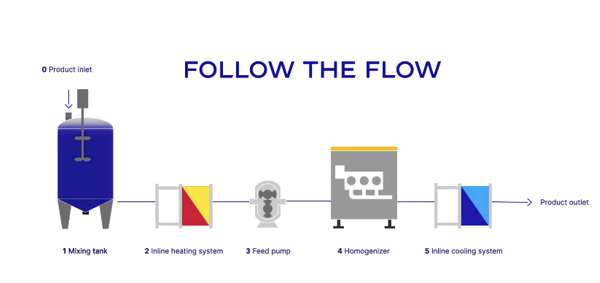
Figure 4: Schematic Diagram Of Sustainable Homogenizer
- Impeller Blade Design: Blade designs have a crucial role in the efficiency of the process. Hence, hydrodynamic blades narrow the mixing time, enhance mixing efficiency, and reduce power consumption during the mixing phase.
- Carbon Capture: Boiler-generated steam sterilizes beverages and leads to the generation of large quantities of carbon. Companies and organizations are now implementing various carbon capture technologies, such as carbon capturing. The beverage processing unit uses the captured carbon for carbonating drinks, optimizing carbon utilization and reducing the carbon footprint of beverage manufacturing units.
Final Word
All the innovations mentioned above regarding RTD beverages are incredible and will push beverage processing to new heights. However, they are accompanied by high costs, which may slow down new entrepreneurs. Besides that, ingredient quality and consistency will still be critical. Therefore, the manufacturers must strengthen the supply chain and focus on suppliers’ contribution. There is also an imminent need to consider material attributes as they deeply impact the functionality and efficiency of the production line. Lastly, the industry must carefully tackle the manual versus automation debate and ensure a smooth transition at each level.