Certain foods and nutraceuticals are designed to release the active ingredients in a controlled manner or at a specific location for enhanced efficiency and proper absorption of the nutrients. Manufacturers and consumers alike have faced the problem of inefficient ingredient absorption due to the large molecular size and low solubility of active compounds. For ingredients to be absorbed effectively by the intestine, they have to survive the gastric juice, and their size needs to be smaller than 500nm. Efficient utilization of encapsulation technology and preparation of other controlled release systems will bring about a significant cost reduction, especially for those products that use premium materials. Further, effective controlled release delivery systems would reduce the dosage requirement and sensory and physicochemical challenges such as bitterness, unpleasant taste (of extracts such as turmeric), and texture-associated deformity.
Controlled Release Mechanism
A controlled-release preparation is released into the body in specified amounts over a specified period. It is designed to release the active ingredient gradually during any desired period. Controlled release delivery systems are involved with two main functions following forming a wall around the core material: (a) keeping and protecting the core material inside the shell during storage and (b) releasing the core material at the right time. The release of the interior contents of the capsules can happen under four different mechanisms: frustration, diffusion, dissolution or melting, and biodegradation.
Fracturation (Stimuli- Mechanical Pressure)
- External forces, such as pressure, shearing, heat, photo energy, or extra sonics, can fracture or break open the coating. Chewing is one of the most commonly used mechanical release methods.
Diffusion (Stimuli- pH, Water)
- Microcapsules are tiny capsules with a large surface area per unit of weight. Additionally, it may function as a semipermeable membrane, releasing the core material by a diffusion-controlled process. The slight heat application or increase of solvent (e.g., an increase of moisture content) heightens permeability by changing the crystalline state of the amorphous matrix into a more mobile rubbery form. Thus facilitating the flow of core material through the coating.
Solvent or Dissolution or Melting (Stimuli- pH, Water)
- The integrity of the coating can be destroyed by dissolution into an appropriate solvent or thermal means. Water-soluble coatings can be easily dissolved from around the core by increasing moisture in the systems. Thermal release is commonly used in fat capsules. In this case, the coating melts away from the core, thus releasing the core ingredients onto a desirable target.
Biodegradation – Chemical Reaction (Stimuli- Enzymes)
The degradation mechanism can accomplish release from microcapsules. The degradation process can be triggered by adding chemical/salt enzymes that weaken the wall material. Thus, the active compound is released at the targeted location. Under this mechanism, the wall material is generally engineered to be pH or enzyme-sensitive.
Technologies for Producing Controlled Release Delivery Systems
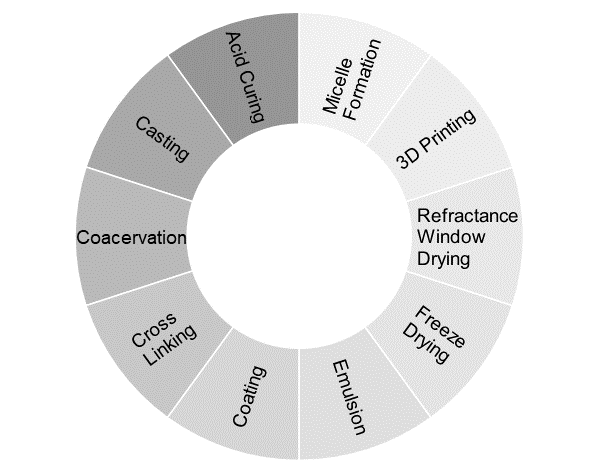
Suitable encapsulation technologies can be utilized to develop controlled release. The graph above depicts a few prominent controlled-release technologies. Generally, the technologies that work at low temperatures are preferred due to the thermal labile nature of most active constituents.
Ingredients for Producing a Controlled Release Delivery Systems
The effectiveness of a controlled release system depends on the encapsulation technology and carrier material. A carrier material with high-temperature stability and no characteristic organoleptic profile is usually preferred. However, the choice of material can also vary according to the encapsulation technology used.
Controlled Release Delivery Systems: Recent Innovations
The use of controlled-release systems in food products is increasing rapidly in response to dynamically changing consumer demand. Because many food extracts face challenges regarding stability and bioavailability, utilizing nascent controlled-release technologies and ingredients is the need of the hour.
Controlled Release Delivery Systems: Extended Release Supplement
An energy supplement beverage from Nano Pharmaceutical Laboratories, ZümXR Extended Release Energy Supplement, relies on liquid-suspended nano-spheres that distribute and dissolve throughout the body over time. Moreover, the extended-release “spheres” provide long-lasting energy benefits (US20110195157A1). However, while the product’s liquid part includes functional ingredients that provide immediate health impact, this two-phase delivery system and nanotechnology create a new model for high-performance energy.
Controlled Release Delivery Systems of Flavor
Keva Flavor’s specialized encapsulated flavor powders (Enkap) protect flavoring compounds’ volatile and sensitive molecules. Encapsulated flavor powder ensures excellent flavor stability and controlled release, reducing flavor decomposition during processing, storage, and distribution. Spray-drying technology is used for encapsulation, and the resultant powder has a wide application area, including powder soft drinks, health drinks, dry premixes, chewable tablets, effervescent tablets, etc.
Flavor Stability- Processing Conditions
Wixon (WO2003013273A1) has developed a stable flavor encapsulated in carbohydrate-based material through its proprietary encapsulation technology-FlavorFresh SR. Also, it is water-soluble, free-flowing, and easy to use. It maintains up to 10 times more stabilized flavor components than its conventional counterparts. Currently, it is available in vanilla and maple flavors.
Sustained Release of Caffeine
OmniActive Health Technologies (India) has developed a sustained caffeine-release supplement- Xtenergy (WO2020194282A1). Sustained-release formulations (based on shellac, acrylate, alginate, and HPMC) have been developed to maintain prolonged energy levels throughout the day with a steady release of caffeine over a more extended period, thus eliminating the need for repeat consumption of caffeine and possibly reducing some of the adverse effects of caffeine associated with a caffeine crash.
Significant Players in the Controlled Release Delivery Systems Domain
AnaBio Technologies
AnaBio Technologies is a specialist micro encapsulation company based in Cork, Ireland. It focuses on improving the functional properties of ingredients, such as probiotics, vitamins, caffeine, creatine, leucine, vegetable proteins, oils, and antioxidants for food, beverages, sports nutrition, medical, and animal feeds. Its patented microencapsulation technology (US20190289896A1) involves coating sensitive bioactive ingredients. It comes with a microscopic layer to mask the unpleasant flavor, which improves the solubility in liquids and protects against harsh environmental settings, heat, moisture, and oxygen.
TasteTech
TasteTech has been a manufacturer of controlled-release flavorings and ingredients since 1992. They are pioneers in creative microencapsulation technology and cater to leading food manufacturers. Their range of products can increase shelf life, improve taste and texture, protect key ingredients from moisture and contamination, mask bitter notes, and reduce cost. Their key encapsulation technologies include matrix encapsulation, core-shell encapsulation, and spray drying. Application areas include bakery, confectionery, chewing gums, sports nutrition, etc.
Firmenich
Firmenich is one of the most prominent perfume and tastant companies. They create world-class products through their technological advancement and shape the future of taste and nutrition. They have designed four major encapsulation technologies based on the functional properties required- Durarome® (Long lasting freshness by protecting flavors from oxidation and interaction), Flexarome® (Processing-resistant, multi-sensory Flavors), Thermarome® (Superior taste and extreme manufacturing process-resistant properties), and Captarome® (Superior taste with high-performing economic Flavors).
Nulixir Inc.
Nulixir is a nano-biotechnology company that develops and manufactures smart nano-carriers. It is called nano-vesicles, which enhance the performance of functional ingredients in food & beverage products. These specialized food-grade nano-vesicles are designed to mask functional ingredient flavors and tune their regulation in the body. This specialized food grade enhances functional ingredients’ performance in food & beverage products. Their products are available in solid powder and liquid concentrate formats, which can be incorporated into various food & beverage products (US11123291B2).
Conclusion
Controlled release systems are currently used in various food and beverage products to provide functional benefits. It also helps control the delivery of flavor, bioactive constituents, nootropics, and probiotics at a targeted location in the body. With changing consumer behavior and rising health concerns, consumers seek healthier food products with improved health impact. Controlled release possesses the potential to meet the consumer’s demand through requisite product modification and even through new product development. Using suitable encapsulation technology and carrier material, controlled delivery of active constituents, including drugs, cannabinoids, and fragrances, can also be achieved in the near future to promote the use of this active ingredient in a broad range of food products.