Plant-Based & Alternative Proteins Evolution: Recent Breakthroughs Opening New Growth Avenues
The popularity of plant-based food trends and shifting demands for alternative proteins are primarily driven by customers’ preferences for novel alternatives, such as peas, canola, and faba beans. However, achieving the optimal taste, mouthfeel, and texture is one of the most pressing impediments for plant-based food industry players. Companies struggle with mass-level commercialization of plant proteins and turn customers into repeat buyers after an initial spike fueled by curiosity and ethical concerns.
According to a recent report, the plant-based food market is expected to reach $160 billion by 2030, indicating attractive growth avenues for business leaders. Ensuring nutritional similarity and sensory quality between plant proteins and traditional proteins is a challenging task for companies. Also, scaling such innovation is a capital-intensive activity for companies as it requires substantial investments in supply chain optimization, the integration of novel technologies, and the development of advanced ingredients.
Moreover, transitioning from niche novelty to making plant-based and alternative proteins a regular shelf product poses a significant obstacle to their mainstream adoption, thereby hindering new revenue streams.

How Plant-Based Food and Alternative Protein Trends are Driving Growth of the Global Food Market?
In 2025, the global plant-based protein market is valued at around USD 16 billion with a strong CAGR of around 7.2% through 2034. The growth of this segment is fuelled mainly by a combination of health, technological, and environmental factors, which are:
Expansion across Different Categories and the Flexitarian Trend
Plant-based seafood is preferred by around 60% of UK customers as a meat or fish alternative due to the adverse ecological implications of fishing. A flexitarian influence among customers is accelerating the growth of this segment. Plant-based meat alternatives are identified as among the most popular plant-based choices among customers, particularly those in the 25-39 age group.
Furthermore, a mixed trend is reported in the US population regarding protein consumption, shifting from traditional staples to innovative plant-based or alternative proteins. Around 90% of people consume animal-based proteins on a daily basis, while approximately 40% include plant-based proteins in their diet. This segmentation highlights opportunities for businesses to expand their market share in the future, driven by trends in animal-alternative proteins.
Functional and Localized Innovation
Localized innovation is a booming trend in the consumption of plant-based and alternative proteins, primarily driven by health awareness. For instance, in Brazil, more than 20% of customers are inclined towards milk substitutes designed explicitly for athletic recovery, indicating a health-focused innovation trend. Similarly, in China, 15% of people consume plant-based beverages almost daily, while in Thailand, 51% would adopt plant-based meat if it could have a similar texture, flavour, and feel to real meat.
Additionally, Chinese consumers are open to trying plant-based drinks with multiple plant protein sources, offering a broad scope for companies to innovate products with ingredients such as cashew and black bean. Therefore, it is crucial for companies to replicate the right mouthfeel to leverage this market trend accurately.
Diversification of Plant-Based Protein Sources
These new alternatives encompass precision-fermented and microbial proteins, denoting a swift switch from conventional proteins like wheat and soy. Additionally, rising allergies, sustainability concerns, and the ongoing pursuit of improved nutrition and taste are at the forefront of novel trends in the sector, driving technological innovation in protein extraction.
While soy and pea remain dominant, new protein sources such as fungi, algae, and seaweed are emerging as viable alternatives to traditional plant-based protein sources. Additionally, insect- and fermentation-based proteins are gaining interest due to their high efficiency and minimal environmental impact.
| Protein Type | Examples | Use or Application | Customer Appeal |
| Established Proteins | Soy, pea, wheat | Widely used in meat alternatives, dairy substitutes | Trusted, familiar, functional |
| Emerging Proteins | Almond, fava bean, lentil, chickpea, flaxseed | Used in plant-based beverages, snacks, dairy products | Nutritionally rich, novel textures and flavors |
| Novel Proteins | Mycoprotein, seaweed protein, insect protein | Exploratory use in next-gen alt-proteins | Sustainable, innovative, growing niche appeal |
| Nut & Seed-Based Dairy | Walnut, hazelnut, pecan, pistachio | Alt-dairy (milk, creamers, yogurts) | Clean-label, allergen-friendly options, rich flavors |
| Used in plant-based beverages, snacks, and dairy products | Soy/pea-based TVP, wheat gluten | Adds a meat-like texture to burgers, sausages, and more. | Enriches the eating experience and enhances the realism of meat alternatives. |
Rise of Cultivated and Hybrid Proteins
Lab-grown meat and hybrid proteins that combine plant-based ingredients with cultivated meat are gaining traction in current times. Alternative proteins blend taste, texture, and sustainability facets, which help companies address the challenges of off-taste in plant-based proteins or food products while managing environmental concerns.
Innovations Addressing Growth Barriers and Reshaping the Plant-Based & Alternative Protein Market
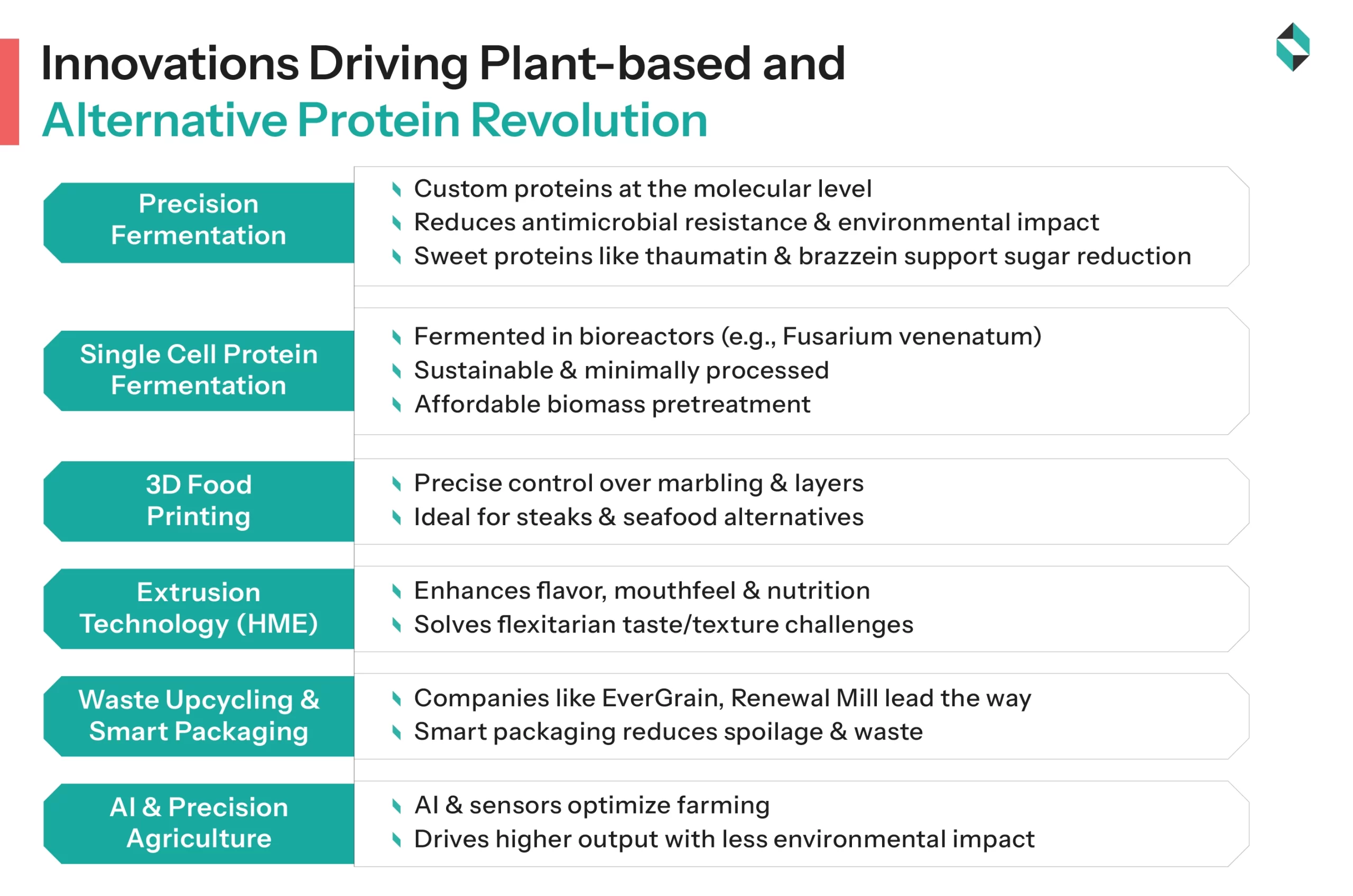
Precision Fermentation
Precision fermentation enables the production of animal-like proteins without the need for livestock. Companies utilizing PF can improve the nutritional profile and quality of alternative proteins while facilitating the production of custom proteins at the molecular level.
Additionally, it helps in mitigating issues of antimicrobial resistance, animal welfare, and environmental concerns, as PF-derived ingredients provide organoleptically and functionally favorable options at competitive prices. Thaumatin, mycodulcein, brazzein, and monellin are other PF-derived ingredients that are sweeter than sugar, enabling sugar reduction in F&B while meeting evolving customer preferences for ecosustainable, flavourful, and tasty foods.
Single Cell Protein(SCP) Fermentation: Mycoprotein and Mycelium
Single Cell Protein addresses cost and scalability issues, as well as pervasive concerns related to climate change and food security. This innovation utilizes ionic liquids for affordable biomass pretreatment, incorporating immobilized cellulases for stability, and designing improved reactors, such as gas-lift and membrane bioreactors, to mitigate mass transfer inefficiencies during fermentation.
Here, mycoprotein is extracted from the fermentation of fungi in bioreactors, and then excess RNA is removed through heat treatment to form a meat-like product. Mycoprotein offers a whole food, minimally processed, and sustainable protein alternative. Quorn Foods pioneered the use of fermentation technology for mycoprotein, establishing both the process and market demand. While air-lift fermentation of Fusarium venenatum remains the only profitable large-scale method, growing global interest has led to the establishment of several startups and pilot plants.
3D Food Printing
3D printing technology facilitates precise control over the structure and texture of plant-based protein, allowing for the accurate replication of complex marbling patterns found in animal meats. For instance, companies like Redefine Meat and Novameat utilize this innovative technology to produce plant-based steaks and seafood alternatives.
Extrusion Technology
High-moisture extrusion (HME) technology improves the texture and taste or flavour of plant-based products by aligning protein structures to mimic muscle fibres. Better texture and consistency are crucial challenges for businesses as they struggle to increase consumer acceptance of plant-based food products, particularly among flexitarians. Here, HME helps closely mimic the sensory experience of meat while maintaining the nutritional density of alternative proteins.
Companies like Heura and Beyond Meat are utilizing this method to meet customer demands for alternative proteins with plant-based ingredients in products such as burgers and chicken alternatives.
Waste Upcycling and Smart Packaging
EverGrain and Renewal Mill are transforming food by-products into high-protein ingredients, fostering sustainability in the sector through innovative technologies. Apart from this, smart packaging solutions, such as Mimica’s freshness indicators, decrease food wastage while improving shelf life, which ultimately enhances customer confidence.
AI and Precision Agriculture
AI-driven agriculture is optimizing the cultivation of protein-rich crops, such as soy and peas. Precision agriculture utilizes sensors, AI, drones, and automated systems to augment crop production and assure resource efficiency. From autonomous tractors to AI soil health monitoring platforms like CropX, these technologies are enhancing revenues while decreasing environmental impact.
Business Implications and Growth Avenues
Business avenues for the plant-based food market are both promising and challenging; the most notable ones include:
- Product Flavour or Taste: Taste and texture remain primary consumer concerns for customer dissatisfaction, hindering the widespread consumption of plant-based food products and alternative proteins. Investments in precision fermentation and AI-powered ingredient optimization will be key to meeting the demands surrounding the flavour or taste of plant-based proteins. Apart from this, the use of alternative protein sources like the Andean lupin and the mung bean is recommended for texture as well as taste improvement in plant-based foods.
- Diversification: To stand out, F&B companies must explore untapped ingredients like microalgae, black beans, pistachios, and cashews, catering to diverse regional preferences and dietary needs.
- Investment and Collaboration: The pace of innovation will require ongoing capital investment and collaboration across industries from biotech and agriculture to retail and logistics for players in the F&B sector, particularly in nutrition, dairy, meat, and alternatives sub-sectors.
Bottomline
Plant-based and alternative proteins are experiencing a sharp growth trajectory, with innovative technologies such as precision fermentation, SCP fermentation, and AI-driven agriculture opening new avenues for industry players. However, extensive opportunities to lead this domain in next-generation formulations can only be effectively leveraged by alleviating the dominant challenge of off-taste in plant-based protein products. The integration of emerging innovative solutions, such as advanced extrusion, smart binders, and clean-label coloring agents, is future-proofing the growth path for market players.
The F&B consulting team at Stellarix helps companies navigate the pressures of increasing sustainability requirements, clean label innovation demands, and the ongoing need to align product portfolios with evolving customer preferences. Our R&D services support companies in exploring and seizing profitable innovation opportunities through data-driven insights and deep industry expertise, covering market testing, product launches, reformulation, and cross-functional collaboration.
Let's Take the Conversation Forward
Reach out to Stellarix experts for tailored solutions to streamline your operations and achieve
measurable business excellence.



