e-Powertrain: Driving Tomorrow’s Mobility
From internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles to the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs), the primary component in this transformation is the e-powertrain. An e-powertrain typically refers to the various components responsible for converting electrical energy stored in batteries into mechanical energy, thereby propelling the vehicle’s mobility. Normally, it is the “heart” owing to the number of components tied together to perform flawlessly for the effective functioning of an EV. Unlike gasoline-powered vehicles, electric vehicles use electric motors that function with electricity stored in batteries to turn the wheels. The design and efficiency of the e-powertrain play a crucial role in determining the performance, range, and efficiency of an EV.
Key Components of an e-Powertrain
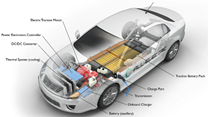
The vehicle’s operation relies on several essential components that comprise the e-Powertrain. Together, these components ensure effective energy conversion, seamless power delivery, and optimal overall vehicle performance.
Electric Motor
The e-Powertrain’s key component is the electric motor. To move the car ahead, it transforms electrical energy from the battery into mechanical energy. Induction motors and permanent magnet synchronous motors (PMSM) are the two main kinds of electric motors found in EVs. The vehicle’s total performance is directly impacted by the motor’s efficiency and power density, which refers to the amount of power it can generate for its size.
Power Electronics
Power electronics control the transfer of electrical energy between the battery and the electric motor. These components comprise the onboard charger, DC-DC converter, and inverter.
- Inverter: This gadget converts the direct current (DC) electricity stored in the battery into alternating current (AC) to power the AC motor.
- DC-DC Converter: It steps down the high voltage from the main battery to lower voltages needed for auxiliary systems, such as lights, infotainment, and climate control.
- Onboard Charger: This system allows the vehicle to charge from external power sources (such as wall outlets or fast chargers) by converting AC electricity from the grid into DC electricity suitable for the battery.
These electronics also regulate the power delivery to ensure smooth acceleration, braking, and energy regeneration.
Battery Pack
The battery pack stores electrical energy for the motor. Commonly used battery chemistries include lithium-ion and solid-state batteries. The battery pack is typically located in the vehicle’s floor or undercarriage, allowing for better weight distribution and increased cabin space. The battery’s capacity determines the vehicle’s range, with larger battery packs providing longer driving distances.
Transmission/Reduction Gear
Traditional vehicles often rely on complicated multi-speed transmissions, where gears shift to adjust the power from the engine to the wheels. Electric vehicles (EVs), on the other hand, use a single-speed reduction gear, which simplifies the process. Without requiring gear changes, this gear transforms the electric motor’s high rotating speed into the appropriate speed for the wheels.
Electric motors smoothly distribute power across a wide range of speeds without the need for manual gear shifting. The motor’s output is always in line with the vehicle’s speed thanks to the reduction gear’s usually constant ratio. This simplification in the drivetrain helps improve overall efficiency, reduces maintenance costs, and enhances the driving experience.
Thermal Management System
Electric motors, inverters, and batteries generate heat during operation. Efficient thermal management is crucial for maintaining the optimal performance and longevity of the e-Powertrain components. Cooling systems, typically involving liquid cooling, circulate coolant through the motor, inverter, and battery pack to prevent overheating. An effective thermal management system helps maintain the vehicle’s efficiency and prevents damage to sensitive components.
Recent Developments in e-Powertrain
Electric vehicles (EVs) benefit from new e-Powertrain technology, which enhances their efficiency and power while reducing cost. Key innovations include:
DriveONE ePowertrain: The DriveONE ePowertrain from Huawei utilizes AI Flash Charging high-voltage technology to address key issues in EV four-wheel drive systems, featuring a 220 kW asynchronous front drive and a 270 kW synchronous rear drive, as announced at Auto Shanghai 2021. This 800 V high-voltage architecture enables ultra-high horsepower, flash charging (30% to 80% SOC in 15 minutes), and impressive acceleration, with the ARCFOX αS HI reaching 0-100 km/h in 3.5 seconds. Compared to traditional systems, Huawei’s solution boosts cruising range by 5%. Huawei DriveONE ePowertrain utilizes patented “Franklin” deflection technology, combined with conductive grease, to protect motor bearings against electrical corrosion. The patented anti-condensation connector from Huawei prevents moisture accumulation through rigorous testing, ensuring safety and reliability.
E-axle: BOSCH has developed the eAxle system, a compact and cost-effective electric drive solution for battery-electric and hybrid vehicles. By integrating the electric motor, power electronics, and transmission into a single unit, it directly powers the vehicle’s axle, enhancing efficiency and reducing complexity. With up to 96% efficiency and silicon carbide technology, the eAxle improves driving range and reduces battery size. The system offers scalable power from 50 to 300 kW, providing flexible performance with adjustable torque (1,000 to 5,500 Nm) and motor speeds up to 18,500 rpm. Its modular design simplifies installation, lowers component costs, and eliminates the need for separate components and cables. At just 85 kg for a 150 kW unit, the eAxle is a lightweight, high-performance solution suitable for a wide range of vehicle types.
OCTOPUS Project: The OCTOPUS project is Bentley Motor’s three-year research initiative to create a rare-earth magnetic-free electric vehicle axle as part of its plan to launch a fully electric car by 2026. The OCTOPUS project aims to develop a top-tier e-axle powertrain by 2026, utilizing advanced materials and processes.
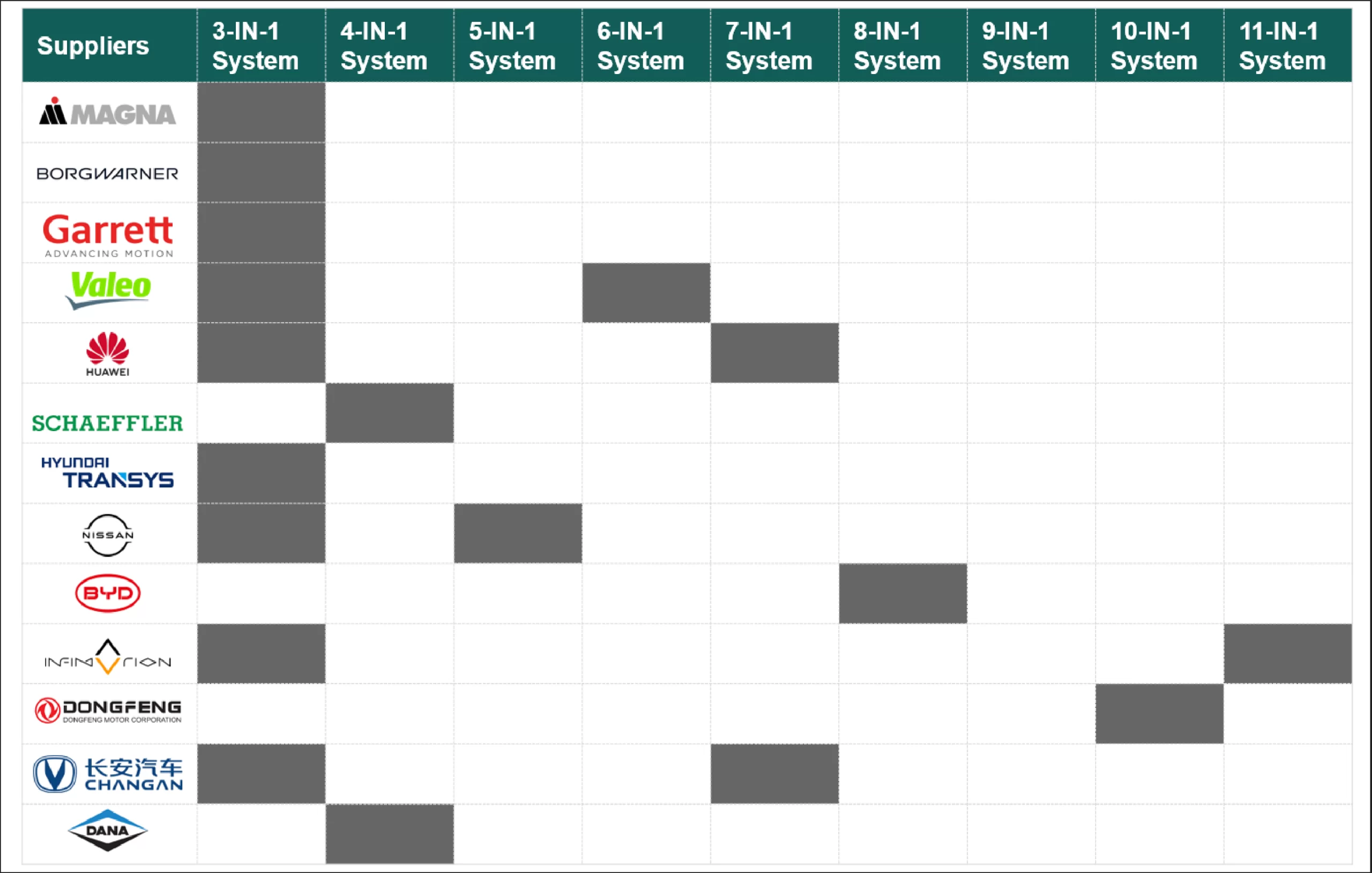
Key Manufacturers and Their Integrated e-Powertrain Systems
In the electric vehicle (EV) industry, several automakers and suppliers have developed integrated e-Powertrain solutions that combine key components, such as electric motors, inverters, transmissions, and power electronics, into a single, cohesive system. Below are key manufacturers with their e-Powertrain systems:
Ecosystem of e-Powertrain
The ecosystem analysis of the electric powertrain market reveals a diverse range of stakeholders, including raw material suppliers, component manufacturers, electric vehicle (EV) manufacturers, and end-users. Electric powertrains are built around three core components: the electric motor, power electronics, and the battery. The ecosystem is shown below:

Conclusion
The development of integrated e-powertrain systems plays a crucial role in driving the transition to electric mobility. Manufacturers now prioritize performance improvements and cost-effectiveness because electric motors and other essential components, such as power electronics and batteries, have become increasingly complex.
The expansion of the e-Powertrain ecosystem will continue to meet the increasing demand for electric vehicles as manufacturers advance through new technologies and adapt to consumer needs and regulatory requirements. Electric vehicle adoption is expected to accelerate worldwide, reshaping the automotive sector through the introduction of greener transportation solutions. The successful development of electric powertrains and the full realization of the electric vehicle market depend on coordinated efforts among component suppliers, vehicle manufacturers, and policymakers.
Let's Take the Conversation Forward
Reach out to Stellarix experts for tailored solutions to streamline your operations and achieve
measurable business excellence.