Waste Management 4.0: AI at the Heart of Zero-Waste Future
As the world generates over 2 billion tons of waste each year, managing this waste with artificial intelligence (AI) has been transformative in the past few years. Also, as waste management is a key aspect of circularity, AI’s impact has been profound. It can handle everything, from automated waste sorting to predictive waste analysis. Each stakeholder in the waste management chain (brands, consumers, recyclers, and governments) is adopting AI for a data-driven and sustainable loop.
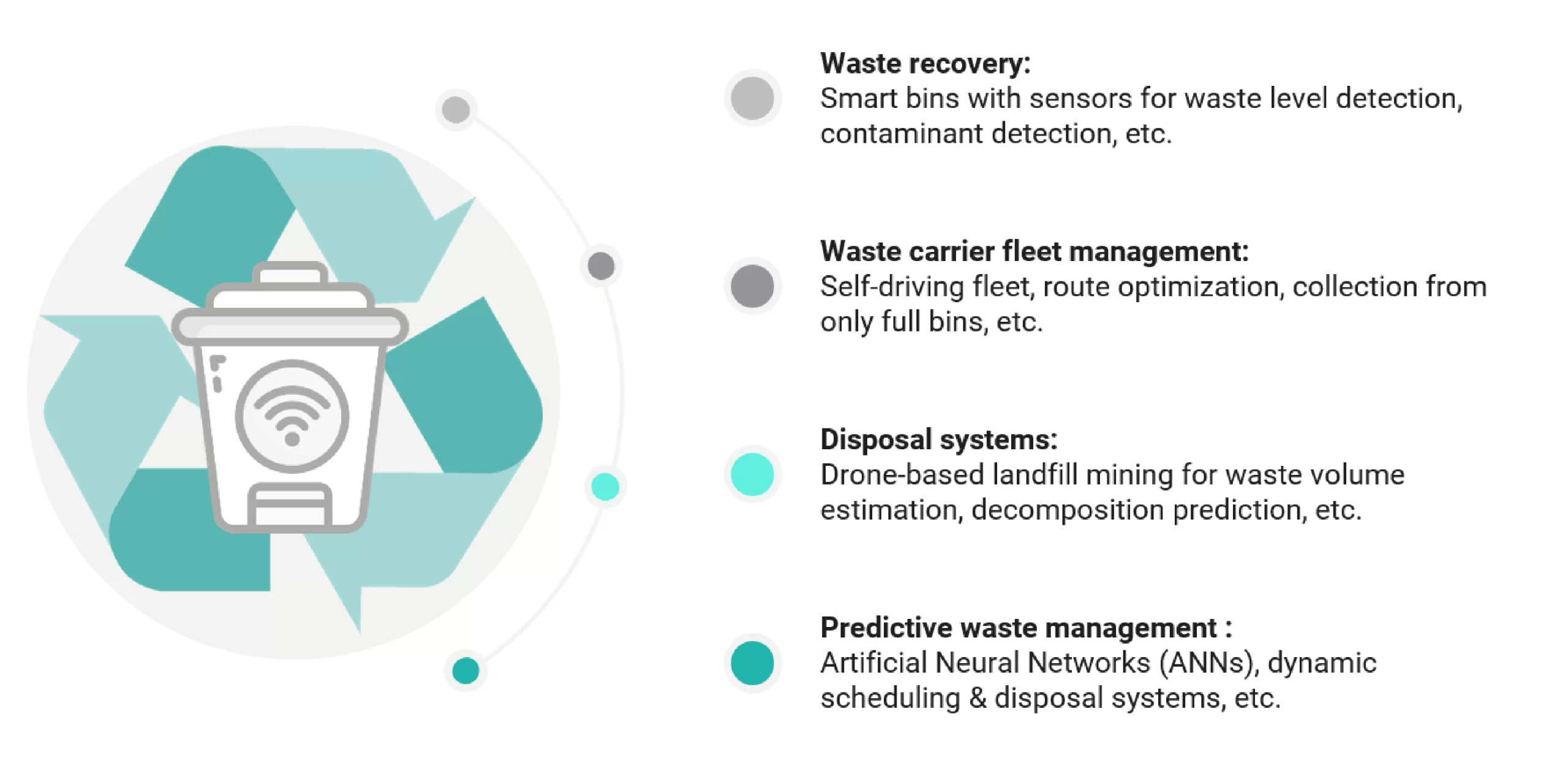
When it comes to waste recovery from businesses or consumers, smart bins are a leading solution. These bins are often equipped with sensors powered by AI to monitor and analyze waste levels, offering predictive insights about how full the bins are. They cut up to 80% of waste management costs through reduced labor, fuel, and transportation expenses.
As the world shifts towards clean and more energy-efficient practices, fleet management is benefiting from AI. This technology streamlines route sequencing and minimizes missed pickups, leading to substantial fuel cost savings. Advanced features like digital connectivity allow fleet drivers to communicate directly with residents.
For instance, in highly regulated cities like California, waste haulers often use time-consuming manual processes for data collection, which can lead to errors. Integrating in-cab tablets with vehicle systems can allow real-time data access, improving accuracy, compliance, and decision-making. Drones are becoming the prime aerial tool in waste management to survey large areas, such as landfill waste collection and dumping grounds. Often equipped with remote sensors such as Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR), gas sensors, thermal cameras, and imaging technologies, they create detailed 3D maps of the area. It offers insights into the structural layout, optimum dumping volume, decomposition limits, and optimum landfill space utilization. Recently, the USEPA approved the “SnifferDRONE,” which detects methane leaks with over 90% accuracy within 35’ of the reported GPS coordinates.
Additionally, artificial neural networks (ANNs) can be trained with historical data and images to create a predictive model for waste volume estimation; they can also be trained to identify types of waste for easy sorting and recycling systems.
Market Momentum: Growth and Trends in AI Waste Management
Western countries (Canada, USA, UK, Austria, Germany, and Switzerland) embrace the power of AI with hefty investments, R&D hubs, and active government support. For instance, the USA has raised nearly half a trillion dollars in AI investment over the last decade. The government also backs R&D with initiatives like the National Artificial Intelligence Research and Development Strategic Plan, designed to enhance AI capabilities across sectors while ensuring adherence to ethical and legal standards. The UK, Germany, and Canada foster research activities with prominent universities like Oxford, Cambridge, the University of Toronto, Fraunhofer, etc., and are the homes for the AI sector’s influential figures.
In contrast, only a handful of nations in the Global South (China, India, Japan, Singapore, New Zealand, and South Korea) are forging ahead to achieve circularity through AI. However, these regions often face the “AI divide” concerning inadequate infrastructure advancements, data literacy, and weak government policies. These countries are creating grounds for AI-powered waste management by fostering collaborations and leveraging advanced algorithms and machine learning.
China has emerged as one of the leading investors within the AI ecosystem, with over $120 billion in the last few years, followed by India (>$11 B), South Korea (>$9 B), and Singapore (>$7 B). The numbers clearly illustrate the AI surge: The prediction is that AI in waste management is set to achieve a market of over $18 billion in the coming decade.
Meet the Game-Changers: Key Entities in AI Waste Tech
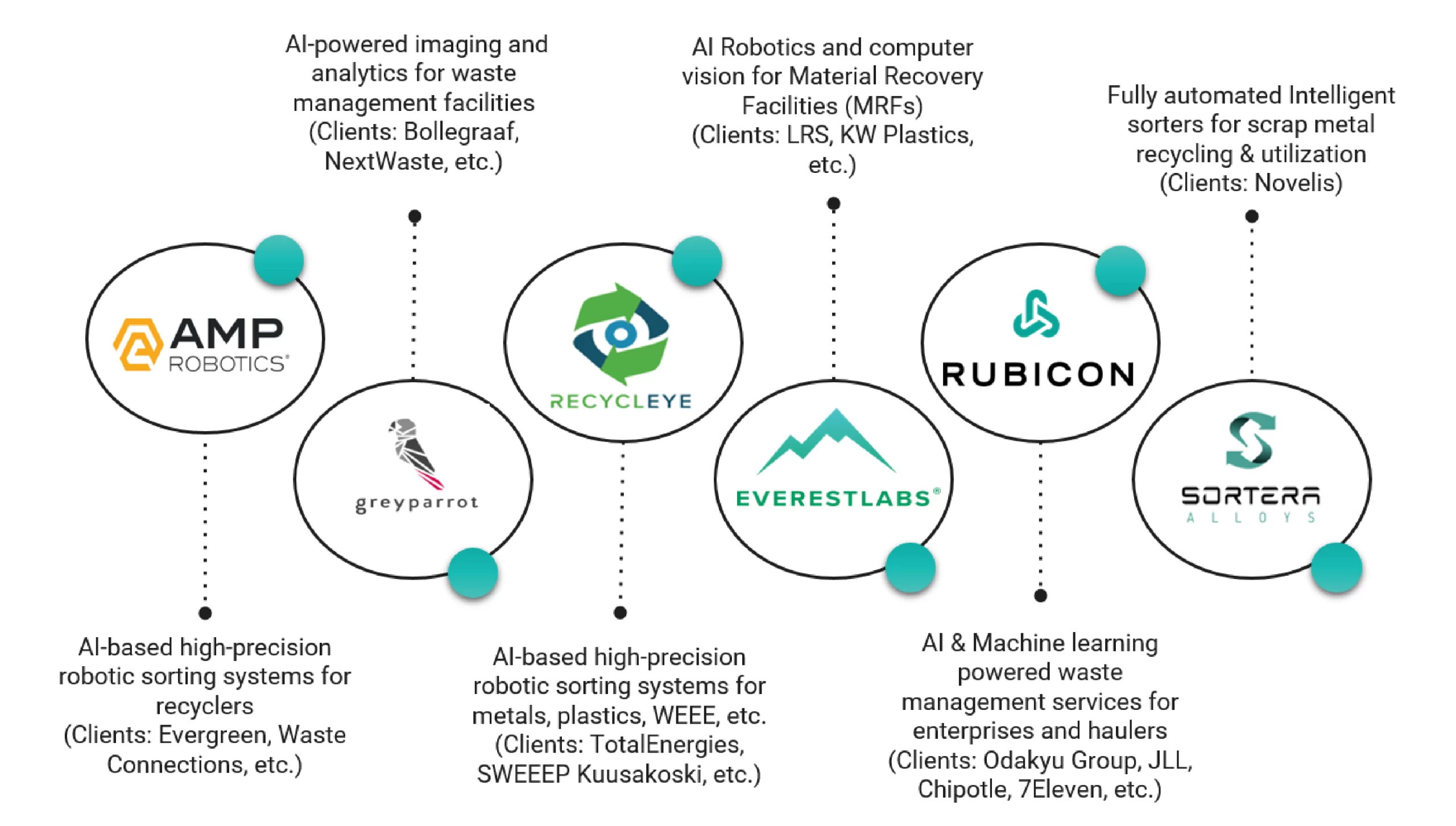
The prominent players in the AI-led waste management domain offer a broad spectrum of offerings, ranging from sorting technologies to re-utilization methods. They cover everything with real-time monitoring, retrofittable AI sorting robots, and data analytics for material recovery. Innovators like Altaroad, SmarterX, Safi, ZenRobotics, and CleanRobotics are advancing the industry with AI-driven platforms for decision support, quality control, robotic sorting, and smart bin solutions.
For instance, Suez uses Qualiwaste Tri (in collaboration with Altaroad) for waste sorting, which has led to a 20% increase in sorting performance at their business waste center in Cheviré. Veolia has developed an in-house AI platform and deployed it across its global sites, enabling real-time water, energy, and waste monitoring. With this platform, they have reached a 90% waste characterization accuracy in their largest waste-to-energy plants in France.
Similarly, Zen Robotics collaborated with Remeo and STADLER in a recycling facility in Finland. Valuable and pure materials from waste streams in construction, demolition, and other sectors are being captured with AI-powered robots that can pick up objects weighing up to 30 Kg.
Decoding Regulations
The utilization of AI in waste management is on the brink of a significant transformation. As we enter the next decade, innovative platforms and models are expected to be widely implemented. The drive for circularity, backed by stringent recycling mandates under the Packaging and Packaging Waste Regulation (PPWR) and reinforced through Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) systems, is accelerating AI adoption, particularly in North America and Europe, which dominate over 60% of the market share of waste management.
Countries like the USA, Canada, China, Finland, Singapore, etc., are in charge of creating smart cities that prioritize waste management alongside sustainability initiatives. Countries like India, Thailand, Kenya, Saudi Arabia, etc., are expected to attract hefty smart city investments by 2025.
Still, obstacles remain, including digital literacy gaps and data privacy compliance issues, underscoring the need for continued collaboration among technology developers, waste management entities, and regulatory bodies.
The Future of AI in Waste Management
As AI advances its integration in waste management, there is potential for smarter sorting, predictive analytics, and optimized resource recovery. However, challenges such as high CAPEX, data security, and workforce reskilling or upgrading are significant barriers, particularly in developing countries. AI is expected to cut landfill waste by millions of tons in the coming decades and improve recycling rates through innovations like smart, self-sorting bins and waste-to-energy systems. As costs decrease, the synergy of AI with IoT and robotics will enhance efficiency and sustainability. Nevertheless, success hinges on collaboration among governments, tech providers, and operators to create 360-degree secure solutions to transform waste into resources.
Let's Take the Conversation Forward
Reach out to Stellarix experts for tailored solutions to streamline your operations and achieve
measurable business excellence.



