The Future of Chocolate: Exploring Cell-Cultivated Cocoa
Chocolate is one of the most beloved foods worldwide, but its primary ingredient—cocoa—faces significant challenges. Climate change, deforestation, labor exploitation, and fluctuating yields threaten the long-term sustainability of cocoa farming.
As global demand for chocolate continues to rise, researchers and companies are turning to cell-cultivated cocoa as a promising alternative to traditional cocoa farming. Cell-cultivated cocoa, produced through biotechnology and cellular agriculture, replicates natural cocoa’s flavor, texture, and composition without the environmental and ethical concerns of traditional farming.
This blog explores the market potential, recent trends, key players, benefits, challenges, technology, sustainability impact, and regulatory landscape of cell-cultivated cocoa.
Market Size & Growth Potential
The global chocolate industry is worth over $100 billion, with the cocoa market valued at approximately $16 billion. However, the industry is facing increasing pressure due to:
- Supply Chain Instability: Climate change and crop diseases are causing frequent disruptions in the cocoa supply.
- Environmental Concerns: Traditional cocoa farming is a leading cause of deforestation, particularly in West Africa, where 70% of the world’s cocoa is produced.
- Labor Issues: Cocoa farming has long been associated with child labor and unfair wages, raising ethical concerns.
- Rising Consumer Demand for Sustainability: Consumers increasingly seek eco-friendly, ethically sourced chocolate, driving interest in alternative production methods.
- Viral Disease of Cocoa Plant: It leads to declining harvests and increased costs to manage the disease. Additionally, it causes long-term damage to cocoa production by reducing productivity and eventually leading to tree death.
Market analysts predict that cell-cultivated cocoa could become a multi-billion-dollar industry in the next decade, as large-scale production becomes viable.
Recent Trends in Cell-Cultivated Cocoa
Investment & Corporate Interest
Several companies and investors are actively supporting cell-cultivated cocoa research and production:
- Celleste Bio, an Israeli startup, secured $4.5 million in funding to scale up cell-based cocoa production. Investors include Mondelez International’s SnackFutures Ventures, showing growing interest from major food corporations.
- Voyage Foods and Kokomodo are developing fermentation-based cocoa alternatives, reducing dependence on conventional farming.
- Sparkalis, the corporate arm of Puratos, invested in two major cell-cultivated cocoa startups
Consumer Preferences & Ethical Sourcing
- Fair Trade and Rainforest Alliance certifications have gained popularity, but cultivated cocoa offers a more radical solution by eliminating the need for traditional farming altogether.
- The rise of premium and functional chocolates, with added health benefits, is creating demand for customized cocoa formulations, which cultivated cocoa can provide.
Biotechnology & AI in Cocoa Production
- Companies are integrating precision fermentation and cellular agriculture to replicate cocoa’s chemical composition.
- AI is being used to optimize growth conditions in bioreactors, reducing costs and increasing efficiency.
- Companies like Celleste Bio are using AI-based computational models in combination with other technologies to optimize cell growth in controlled conditions.
Key Players in the Industry
Several start-ups and multinational corporations are shaping the future of cultivated cocoa:
- Celleste Bio (Israel): Focuses on cell-based cocoa production using biotech and AI-driven optimization.
- Voyage Foods (USA): Developing chocolate alternatives that mimic traditional cocoa flavors without using cocoa beans.
- Kokomodo (Israel): Specializes in plant cell technology to create climate-independent cocoa.
- Mondelez International: Through its SnackFutures Ventures, it is investing in sustainable cocoa alternatives.
Major chocolate manufacturers, including Nestlé and Mars, are also exploring alternative cocoa supply chains to reduce environmental impact.
Key Product Focus
Cocoa butter, cocoa powder, and cocoa liquor are important elements used immensely across industries, such as nutraceuticals, confectionery & snacks, and cosmetics. This is how different sectors use them:-
1. Confectionery
- Cocoa Powder: It is generally used in chocolate bars, truffles, and baked goods like cakes, cookies, and brownies. It provides the chocolate flavor without the fat content that cocoa butter provides.
- Cocoa Liquor: Cocoa liquor (or cocoa mass) is made by grinding cocoa nibs into a paste, and it contains both cocoa solids and cocoa butter. It is a core ingredient in chocolate production, contributing both flavor and texture to chocolates.
- Cocoa Butter: Cocoa butter is used as the primary fat in chocolate. It gives chocolate its smooth, creamy texture and helps it melt at body temperature, enhancing the sensory experience.
2. Snacks
- Cocoa Powder: It is used in snacks like chocolate-flavored granola bars, snack cakes, and energy bars. Cocoa powder adds flavor and color to the products.
- Cocoa Liquor: In snack formulations, cocoa liquor can be used to provide a rich, deep chocolate flavor in combination with cocoa powder.
- Cocoa Butter: Cocoa butter can be incorporated into snacks like chocolate-coated nuts, fruits, or crisps, as well as in energy bars for its smooth texture and high-quality fat profile.
3. Nutraceuticals
- Cocoa Powder: Cocoa is rich in flavonoids, particularly epicatechins and catechins, which have antioxidant properties. It is often added to health supplements, functional foods, and beverages for its potential cardiovascular and cognitive health benefits.
- Cocoa Liquor: Similar to cocoa powder, cocoa liquor can be used in nutraceuticals for its antioxidant properties. Some high-cocoa-content products are marketed for their potential to improve heart health and lower cholesterol levels.
- Cocoa Butter: Cocoa butter has moisturizing properties, and its high content of healthy fats makes it suitable for inclusion in nutraceutical products, especially those targeting skin health and anti-aging.
4. Cosmetic Products
- Cocoa Butter: It is commonly utilised in skincare products like body butters, lotions, anti-stretch mark creams, and lip balms, following its better moisturizing properties, providing skin elasticity and hydration.
- Cocoa Liquor: The antioxidant-rich cocoa liquor is utilized in certain skincare products, such as facial creams and lotions, due to its potential anti-aging properties and its ability to boost circulation.
- Cocoa Powder: This powder is used in formulations for soaps, face masks, and body scrubs due to its antioxidant properties. The ingredient is also used for its natural color in makeup products, including eyeshadows and bronzers.
Benefits of Cell-Cultivated Cocoa
Environmental Sustainability
- Prevents deforestation by eliminating the need for large-scale cocoa plantations.
- Reduces carbon footprint by avoiding the emissions associated with land clearing, transportation, and processing.
- Uses significantly less water and land compared to traditional cocoa farming.
Ethical & Social Benefits
- Eliminates the use of child labor and unfair working conditions in cocoa farming.
- Provides a stable and climate-independent supply chain, reducing reliance on seasonal farming.
Quality & Health Advantages
- Can be customized for specific health benefits, such as higher antioxidant content or lower fat levels.
- Avoids contamination with pesticides and heavy metals, common issues in conventional cocoa farming.
Challenges & Roadblocks
High Production Costs
- The cost of bioreactor technology and cell growth media is still high, making cultivated cocoa more expensive than traditionally farmed cocoa.
- As the industry scales, economies of scale and technological advancements are expected to bring costs down.
Consumer Perception & Acceptance
- Many consumers remain skeptical of lab-grown food, associating it with artificial or unnatural products.
- Effective marketing and consumer education will be crucial for widespread acceptance.
- Economic feasibility of cell-cultivated cocoa
Regulatory Uncertainty
- Unlike traditional cocoa, cultivated cocoa does not yet have clear regulatory guidelines in many markets.
- Companies must work closely with food safety authorities like the FDA and EFSA to obtain necessary approvals.
Role of Technology in Scaling Production
Bioreactor Optimization
- Advanced bioreactors allow for the large-scale production of cocoa cells in controlled environments, ensuring efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
AI & Machine Learning
- AI is used to monitor and optimize growth conditions, leading to higher yields and lower operational costs.
Biotechnology & Cell Line Development
- Establishing stable and efficient cell lines plays a major role in producing consistent and reproducible high-quality products that meet industry standards and consumer preferences.
Fermentation & Flavor Engineering
- Fermentation techniques help develop the natural flavor profile of cocoa, ensuring cultivated cocoa tastes identical to farmed cocoa.
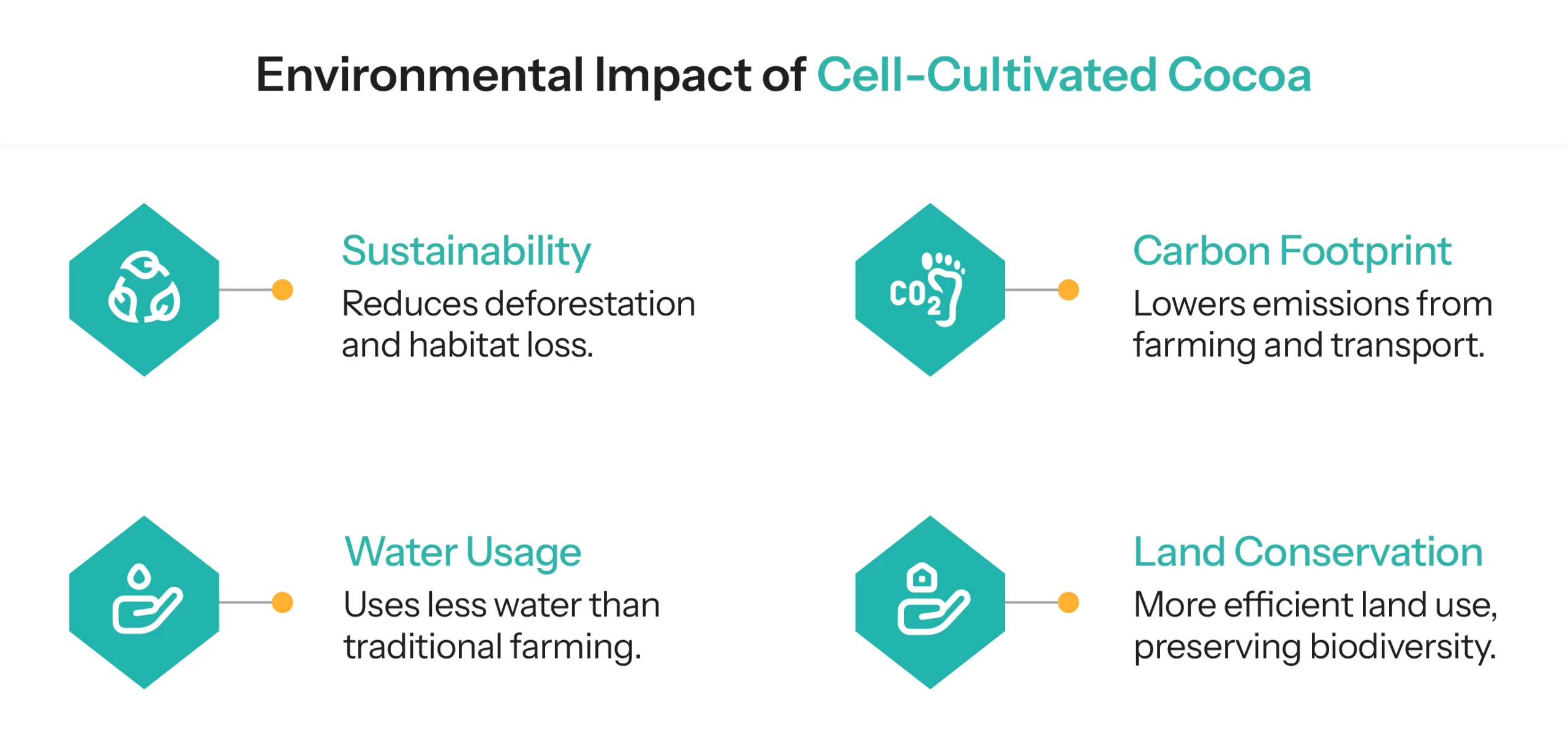
Sustainability & Environmental Impact
- A comparison of traditional cocoa farming and cultivated cocoa highlights the sustainability benefits:
Traditional Cocoa Farming
- Causes significant deforestation, particularly in the Amazon and West Africa.
- Requires large amounts of water and land, contributing to biodiversity loss.
- Heavily reliant on pesticides and chemical fertilizers.
Cell-Cultivated Cocoa
- Requires minimal land and water.
- Eliminates the need for deforestation and protects biodiversity.
- Reduces carbon emissions by cutting out long-distance transportation and deforestation-related CO2 release.
Companies adopting cultivated cocoa may also qualify for carbon credits and sustainability certifications, making it an attractive investment.
Regulatory Landscape & Future Outlook
Current Regulatory Status
- Cultivated meat and dairy products have gained regulatory approval in some countries, such as Singapore and the United States.
- Cell-cultivated cocoa is still awaiting approvals, with companies engaging in discussions with regulatory bodies.
Projected Timeline
- 2025-2027: More companies enter the cultivated cocoa market, with pilot products launching in limited markets.
- 2028-2032: Scaling efforts reduce costs, and regulatory approvals expand globally.
- 2035 and Beyond: Cultivated cocoa achieves cost parity with traditional cocoa, becoming widely available.
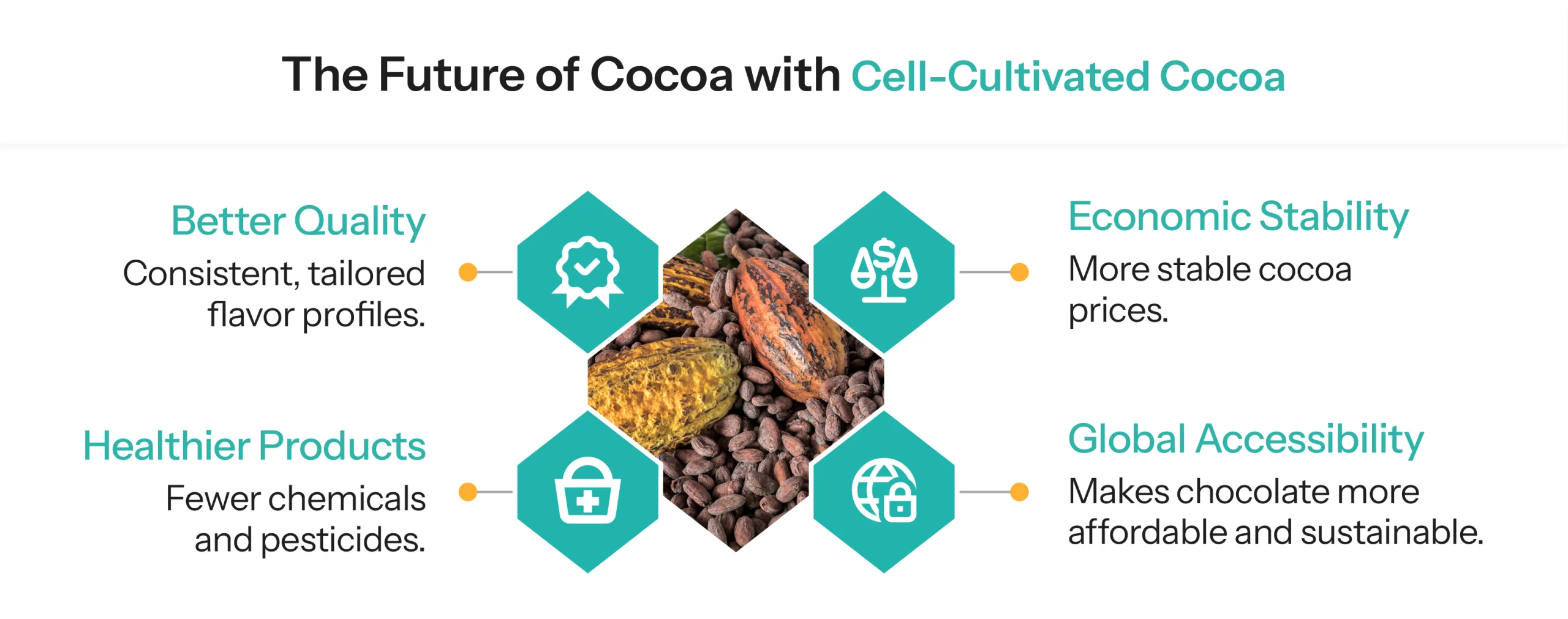
As food technology advances, cultivated cocoa could redefine the chocolate industry, making it more sustainable, ethical, and resilient.
Conclusion
Cell-cultivated cocoa presents a groundbreaking solution to the challenges faced by traditional cocoa farming. With corporate investment, AI-driven optimization, and regulatory progress, cultivated cocoa is poised to play a major role in the future of chocolate production.
As global demand for chocolate grows, the industry must choose between continuing unsustainable farming practices and embracing technological innovation for a better future.
Let's Take the Conversation Forward
Reach out to Stellarix experts for tailored solutions to streamline your operations and achieve
measurable business excellence.



