Smart Technologies in Wound Management
Wound healing has evolved much beyond the age of simple ointments and bandages. Imagine a world where your bandage not only covers a wound but also tracks the healing process. One of the most significant changes in this regard is the evolution of smart wound care devices. These technologies come equipped with sensors and other high-end technological features that are capable of monitoring wounds actively and providing important information to healthcare professionals. This development in the technology of wound care has revolutionized the process of treating wounds so that the process is now efficient, accurate, and friendly toward patients.
Importance of Advancements in Wound Management
Bridging smart equipment into any wound care practice has the revolutionary potential to transform the entire healthcare industry. The wound care processes would become increasingly streamlined and cheaper, as clinic visits would not be so frequent if so much of it could be monitored and done from remote ends. It would also allow patients to get care at home under supervision from healthcare professionals.
The analysis of data collected by these smart wound care devices would, in turn, help in determining various patterns and trends and laying better treatment protocols and personalized care programs. Such integration of technology into the treatment of wounds enables healthcare providers to base their decisions on evidence derived from objective data, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
The potential for innovation exists in creating affordable smart bandages and dressings with improved healing properties, including smart materials, temperature, moisture, and pH level sensors, as well as biodegradable materials that minimize the environmental footprint. The devices are instruments for improving the care rendered by healthcare workers, enabling enhanced patient-to-provider communication and coordination.
The following presented a comprehensive overview of urgently needed wound care from general towards smart wound management:
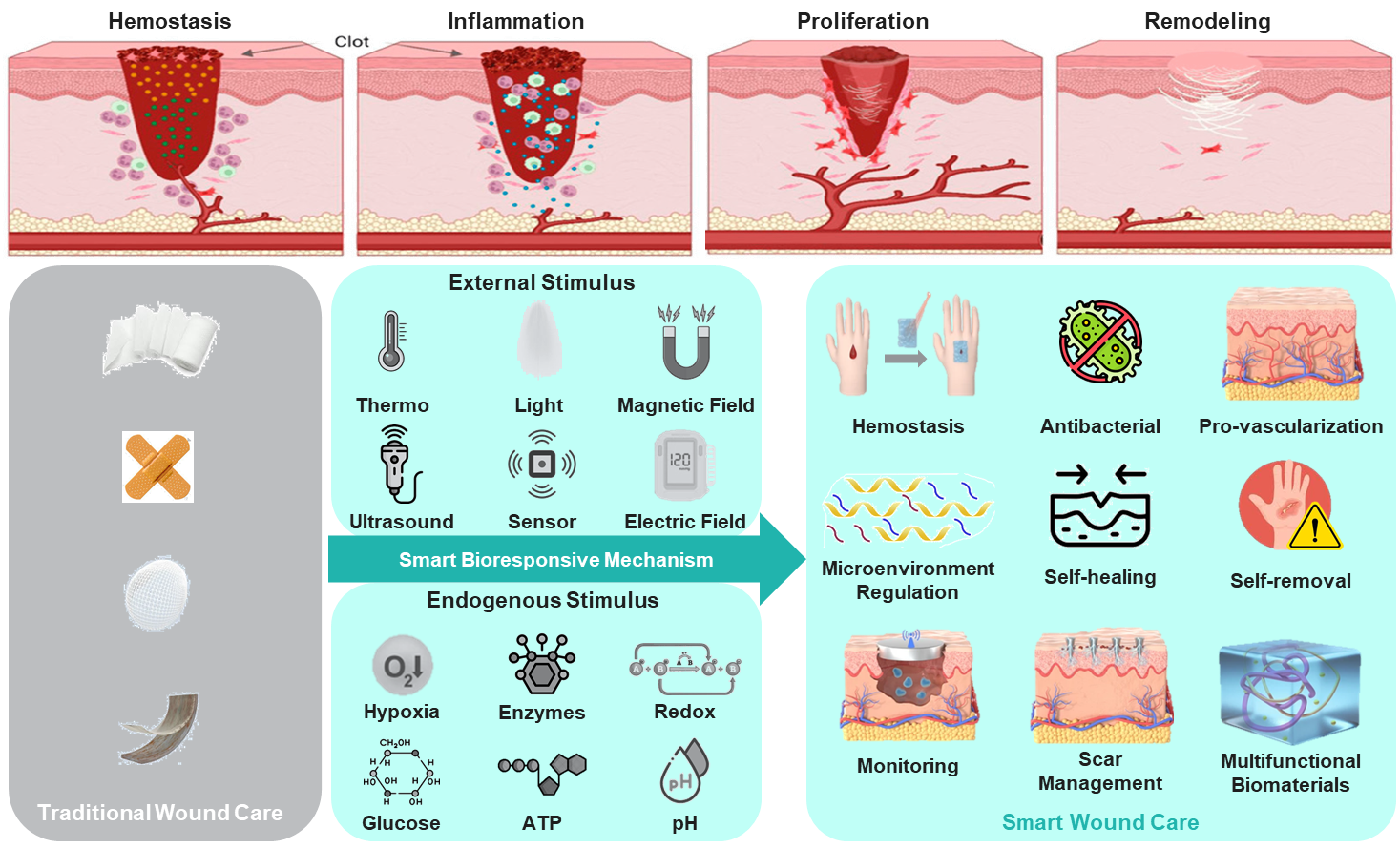
Figure 1: Overview of Transition from Traditional Wound Care to Smart Wound Care
Advanced Technology in Wound Management
Advanced technology has transformed how wounds are monitored and treated. Some of the most important wound care technologies include:
- Advanced Dressings: Smart dressings are manufactured to speed healing by creating an environment for moisture around the wound
- Negative Pressure Wound Therapy: This technology works by applying negative pressure to allow healing and minimize the danger of infection
- Biologics: Growth factors and stem cells are employed for enhancing tissue growth and wound healing
- 3D Bioprinting: Being able to print out living tissue is potentially transformative to wound healing
- Nanotechnology: Targeted treatments to a wound could be delivered via nanoparticles
- Artificial Intelligence: Machine learning algorithms will be able to predict outcomes from wound healing and recommend personalized therapy
Benefits of Smart Technologies in Wound Management
Intelligent technologies in wound care can assist clinicians in monitoring wounds, guiding treatment decisions, and enhancing healing outcomes.
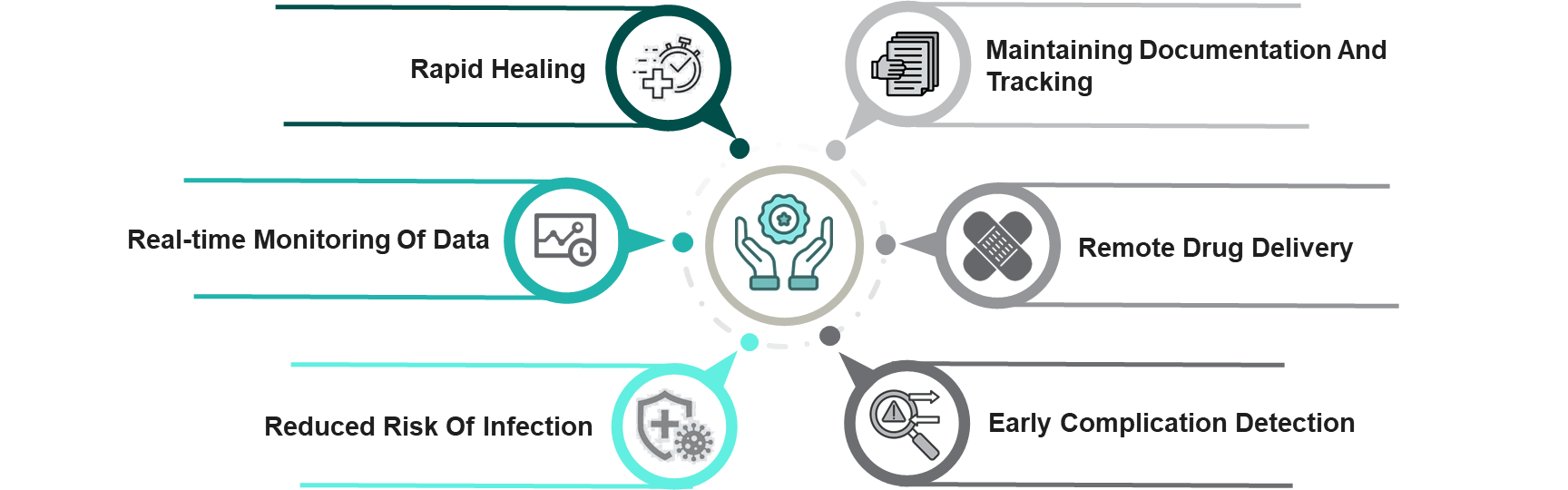
Figure 2: Benefits of Smart Technologies in Wound Management
- Rapid Healing: Intelligent technologies can aid in accelerating the process of healing, thereby resulting in faster recovery periods for patients
- Real-time Monitoring of Data: Monitor a wound at all times without requiring invasive dressing adjustments, which reduces the frequent visits to the clinic, facilitating convenience, cost reduction, and managing their own care from home
- Reduced Risk of Infection: Healing of the wound is enhanced with minimum manipulation of the tissue, reducing the risk of infection
- Early Complication Detection: Notifies healthcare providers if there is any change in the wound, such as increased redness or swelling, that could signal an infection or other complications
- Remote Drug Delivery: The remote-controlled and timely sample withdrawal into the wound for promotion of healing and minimizing the demand for frequent visits
- Maintaining Documentation and Tracking: Allows the storage of detailed information of the wound size, depth, and other features for better assessment of healing progress by healthcare professionals
Market Dynamics
The market dynamics of smart technologies in wound management include the following drivers, opportunities, and challenges:
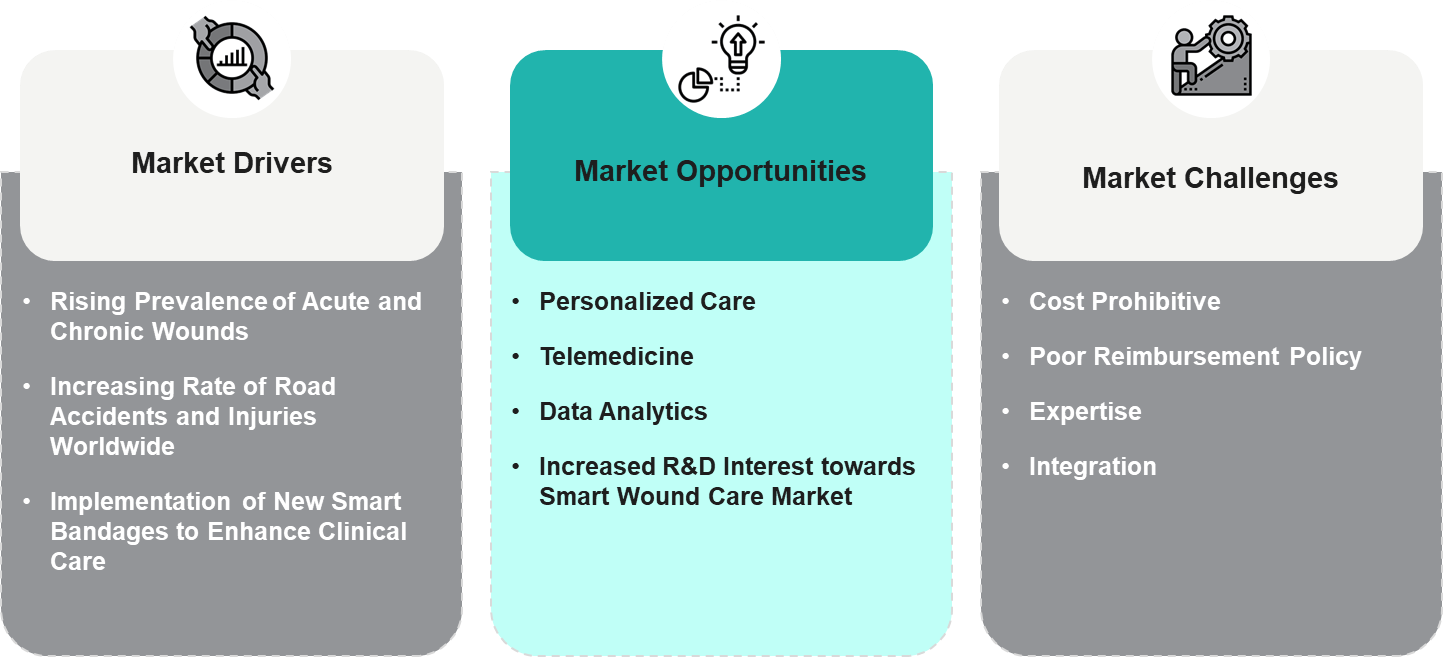
Figure 3: Market Dynamics of Smart Technologies in Wound Management
Market Drivers
- Rising Prevalence of Acute and Chronic Wounds: Owing to population aging and an upsurge in diabetes as well as other conditions, there is a need for improved solutions for wound care
- Increasing Rate of Road Accidents and Injuries Worldwide: This causes trauma, such as severe burns, fractures, and lacerations. The healthcare system is confronting a heightened need for sophisticated techniques to treat these injuries quickly and effectively.
- Implementation of New Smart Bandages to Enhance Clinical Care: With advancing technology, new and innovative solutions for wound care are being created all the time to enhance patient outcomes. Thus, smart technologies become an appealing choice.
Market Opportunities
- Personalized Care: Technology advancements are paving the way toward personalized treatment plans for each patient based on individual needs
- Telemedicine: Technical Integration with Temperature & PH Sensors, Smart Telephones, and Smart Glances now bring remote monitoring and telehealth services that help widen access to advanced wound care
- Data Analytics: Through the use of data analytics, healthcare professionals can make better wound care management decisions
- Increased R&D Interest in Smart Wound Care Market: More investment in developing more efficient, AI-based wound monitoring devices, smart dressings, and remote therapy can enhance overall wound management effectiveness
Market Challenges
- Cost Prohibitive: Some smart technologies cannot be afforded as the implementation costs may seem high to smaller healthcare facilities
- Poor Reimbursement Policy: Failure of reimbursement for advanced technologies may act as an inhibitor for the general adoption, causing restrictions upon patients’ access to innovative treatment approaches, notwithstanding their possible perks
- Expertise: Smart technologies for wound care may need some training on the part of the healthcare workers for effective application of smart technologies for wound care.
- Integration: For a full realization of its benefits, smart technologies would have to be integrated with the existing framework
Latest Advancement in Smart Wound Management
Smart wound management progress has resulted in the creation of new products with the aim of promoting healing and tracking wound status efficiently. The following are some prime examples:
- Cyber Skin (California Institute of Technology): This is a next-generation smart bandage that will assist in providing better treatment of chronic wounds. The high-tech bandages can monitor and adjust automatically to the changes within the wounds so that the wound can get even better treatment than it would be able to using normal bandages.
- Water-Powered Electrotherapy Bandage (North Carolina State University): Uses water to power a battery and electrodes, producing an electric field that speeds up the healing of wounds. It is inexpensive, around $1 per dressing, and does not use electronics.
- Electrospun Nanodiamond-Silk Fibroin Membranes (Shandong First Medical University & Shandong Academy of Medical Sciences): Functional membranes include both biosensors and wound healing platforms. They have nanodiamonds with nitrogen vacancy centers that allow for temperature sensing to monitor infection or inflammation. The silk fibroin matrix facilitates cell growth and accelerates healing.
- Electrical Stimulation Suture (Donghua University): A completely biodegradable and self-electrifying material used in sutures, which will aid in the healing of wounds even without employing any additional approaches like using external electric devices.
- Deep Learning (University of Macau): It is a future prediction for the process of healing of wounds based on the features of the collagen fibers as seen in the histological images of wound tissues. This method employs the exceptional learning capacities of such models to capture different feature variations based on the categories of histological images and classify them into several stages of the wound healing process.
- Collagen-related Theranostic Wound Dressing (University of Leeds): Integrating a collagen-based wound dressing with a halochromic dye (BTB) that changes color under alterations of pH, which are associated with infections, produces an advanced dressing for both the healing of wounds and the real-time monitoring of infection. The drop-cast samples retain the dye for several years and have been ascertained to show high biocompatibility.
Key Players in Smart Wound Management
Key players working in smart technologies in wound management include medical device companies, technology innovators, and leading vendors:

Figure 4: Notable Players in Smart Wound Care
Conclusion
These technologies are changing healthcare in the direction of wound management; patients will have faster healing, better outcomes, and innovative solutions. The future of smart wound care is happening with innovations and new products coming from advanced technologies. The life of smart wound care in healthcare, however, will depend on the efforts to embrace these technologies and the overcoming of challenges.