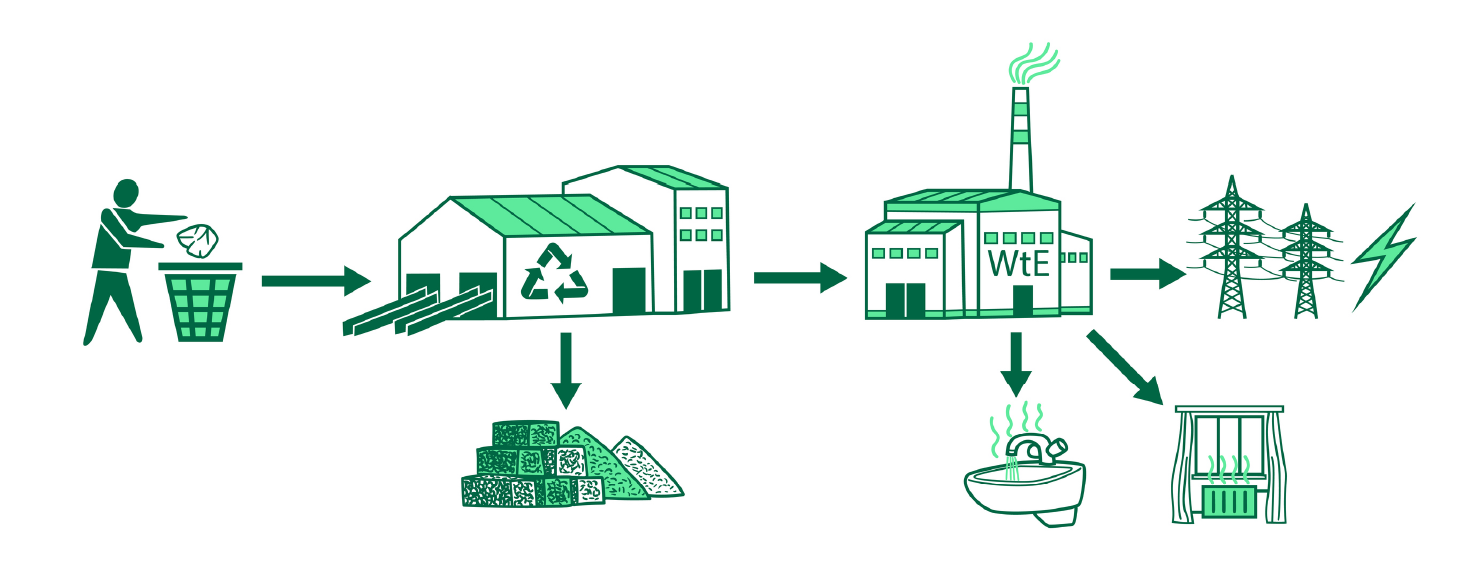
Waste Heat Recovery: Reutilizing the Excess Heat
Utilizing resources efficiently is crucial for the development of sustainable energy solutions. A large amount of global energy is consumed by the industrial sector, but a significant portion of it is wasted as heat. Waste heat recovery systems offer an effective solution to this issue, providing significant energy savings and reductions in emissions that contribute to both environmental and economic goals. Recent progress in thermal and physical waste management has led to increased adoption of waste heat technologies by many companies, enabling the recapture of lost energy for various applications.
Waste Heat Recovery Systems
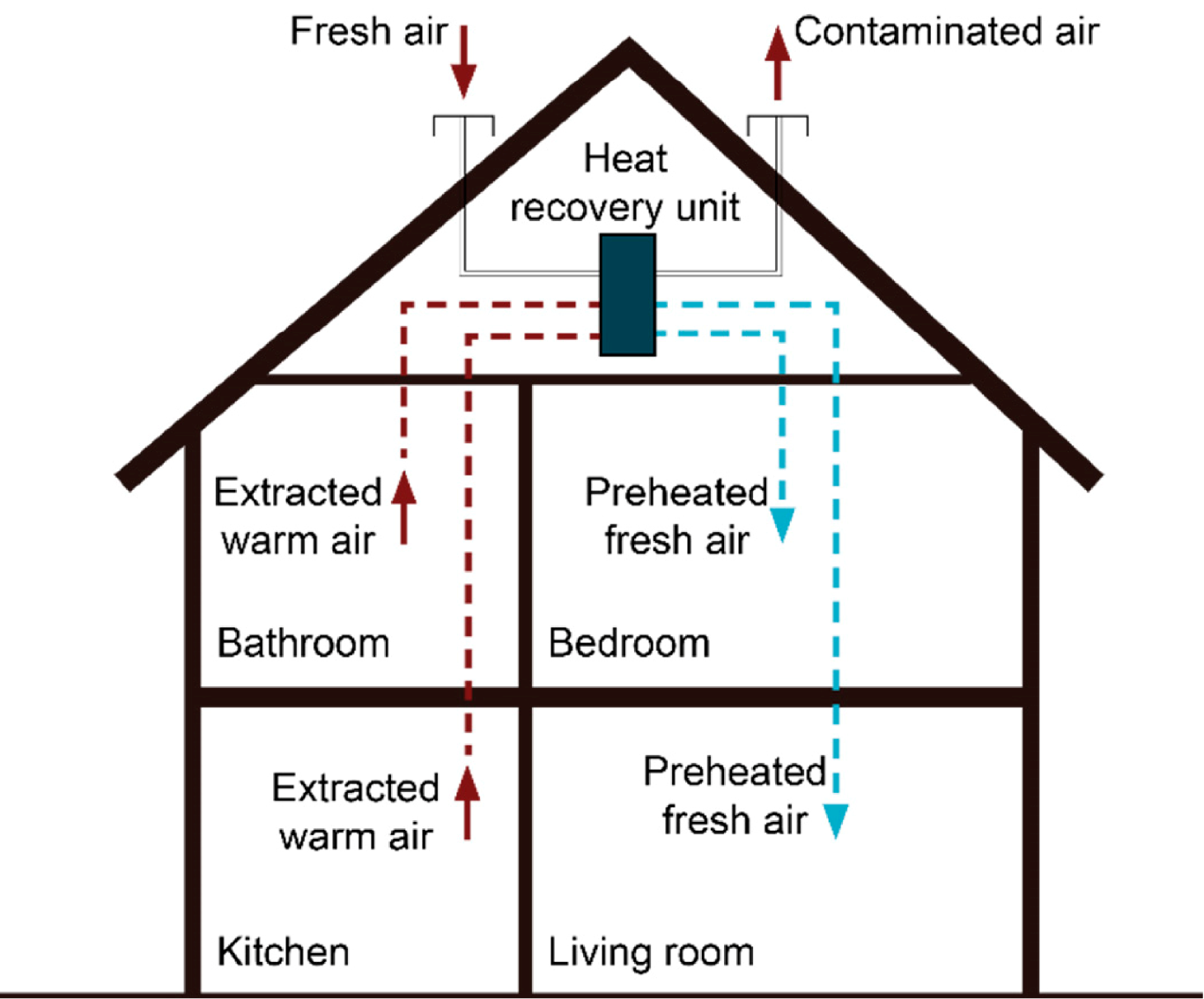
The transfer of energy from one air source to another with different temperatures is facilitated by a device placed in between, which is known as heat recovery. This process is crucial for capturing energy from unused heat, which is commonly generated in various industrial processes and energy production activities. Unused heat is generated when heat produced in a process is not utilized and is instead released into the environment through mechanisms such as radiation, cooling fluids, exhaust gases, or air. Despite being classified as waste, these heat streams often contain significant amounts of exergy, signifying unexploited potential for carrying out useful work using a variety of waste heat utilization technologies.
Technology Overview
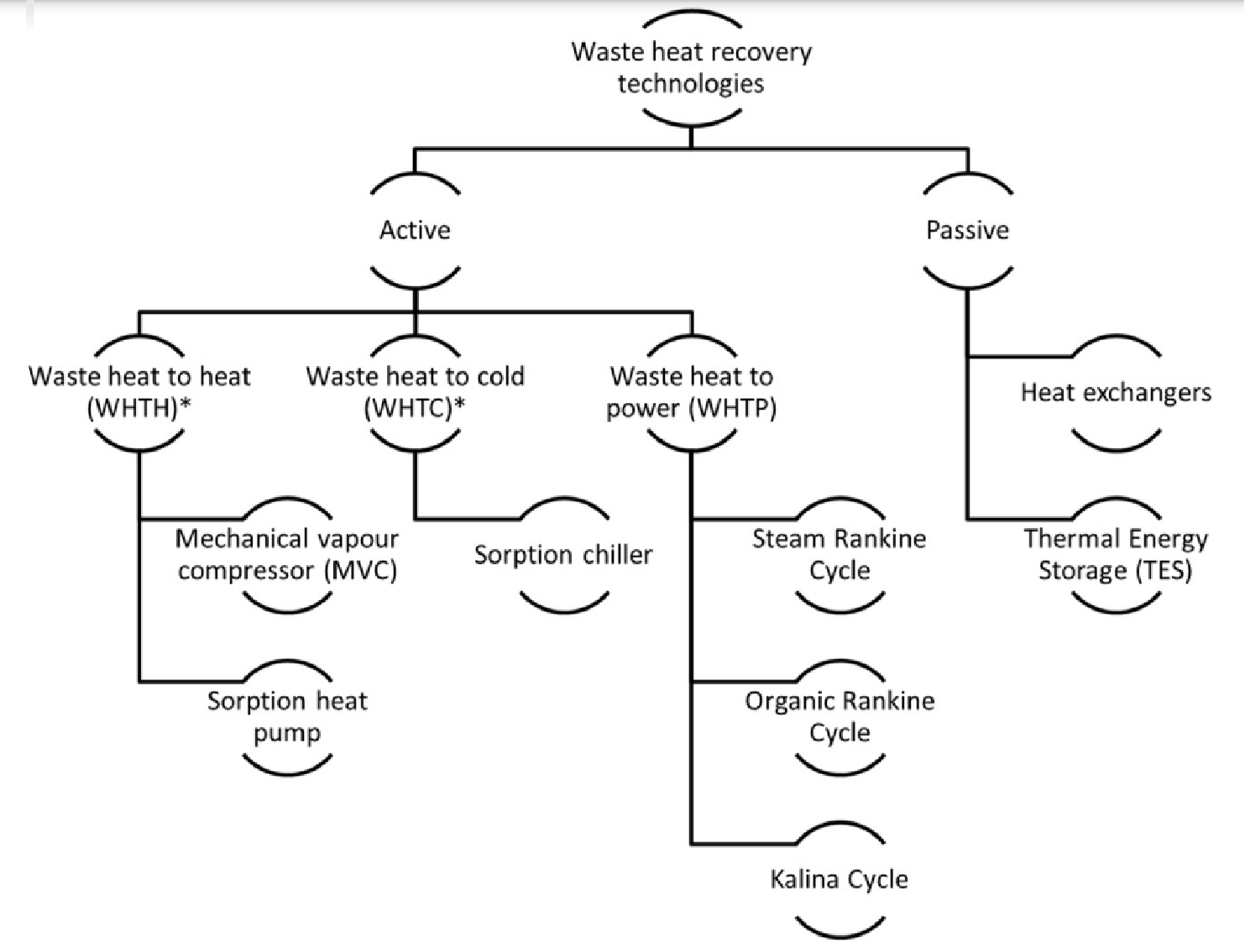
The utilization of waste heat from industry can be classified into passive or active technologies. The outcome varies based on whether the heat is utilized at the same temperature level, at a lower temperature, or if it is converted into a different form of energy or a higher temperature. The two most common passive technologies are thermal energy storage devices and heat exchangers. These methods can be applied in an industry to recycle or reuse waste heat for preheating or heating other operations. Waste heat can be used for three different kinds of active applications: heating (WHTH), cooling (WHTC), or power generation (WHTP). Prominent technologies for waste heat recovery are listed below:
| Technologies | Temperature Range | Benefits |
| Heat Recovery Steam Generator | High | Recover waste heat from the exhaust of industry and produce steam that can be used for process heating or power generation, thereby improving overall efficiency. |
| Waste Heat Boilers | Medium –High | Extract heat from medium – high-temperature exhaust gases and produce steam as an output. |
| Regenerative Burners | High | It reduces fuel consumption by preheating the combustion air & improves combustion efficiency. |
| Recuperators | Low – High | It lowers the energy consumption by preheating the system’s intake air and applies to low- to high-temperature applications. |
| Regenerators | Medium – High | It recovers waste heat from high-temperature applications such as furnaces and coke ovens. |
| Thermoelectric Generation | Medium – High | The system generates electricity directly from waste heat. |
| Thermionic Generator | High | It produces an electric current through temperature difference between two media without the use of any moving objects. |
| Thermo Photo Voltaic Generator | Low – High | The system is used to directly convert radiant energy into electricity and offers better efficiency. |
| Direct Contact Condensation Recovery | Medium – High | The system is used to transfer heat from immiscible liquid-liquid and solid-liquid or solid-gas. It uses a direct mixture heat exchanger without a separating wall. |
| Organic Rankine Cycle | Low-Medium | The system utilizes organic materials with high vapor pressures and low boiling temperatures as the working fluid to generate electricity. As a result, it improves efficiency. |
| Kalina Cycle | Medium-High | It uses a mixture of water and ammonia as the working fluid in a closed cycle to generate electricity. It offers a better result when the recovered heat is off medium-high grade nature. |
| Thermal Energy Storage | High | It is utilized in thermal power plants & waste heat recovery systems, to enhance performance and reduce the impact of fluctuations. |
Out of the above-listed technologies ORC, Kalina cycle, thermal energy storage, and thermoelectric generation are discussed below:
- Organic Rankine Cycle: Waste heat recovery using ORC can help reduce CO2 emissions from industries. In order to produce electricity from waste heat at lower temperatures, ORC systems use organic fluids—such as those found in geothermal sources and industrial processes—that have lower boiling points than water.
- Kalina Cycle: The process of the Kalina Cycle entails the utilization of a blend of ammonia and water as the working medium. The use of waste heat is made more efficient and allows for boiling at lower temperatures. It is possible to adjust the composition of the working fluid through distillation, leading to enhanced efficiency.
- Thermal Energy Storage: TES is widely used in industrial waste heat recovery systems. Its utilization in thermal power plants and waste heat recovery systems can enhance performance and reduce the impact of fluctuations.
- Thermoelectric Generation: Thermoelectric devices are made out of semiconductor materials and it is used for high-temperature waste heat recovery that generates electrical current when they face a temperature differential between two surfaces without the use of any moving objects.
Benefits of Waste Heat Recovery System
- Reduction in Pollution: When toxic combustible wastes are burnt in incinerators, it serves two purposes- recovering heat and reducing environmental pollution levels.
- Reduction in Energy Costs: Recovered waste heat can directly replace purchased energy, reducing energy costs.
- Reduction in Equipment Sizes: Waste heat recovery reduces fuel consumption which reduces the produced flue gases. This results in a decrease in the sizes of all flue gas handling equipment such as fans, stacks, ducts, and burners.
- Reduction in Auxiliary Energy Consumption: Reduction in equipment sizes also brings additional benefits in the form of reduced auxiliary energy consumption, such as electricity for fans and pumps.
Applications of Waste Heat Recovery System
- Space Heating: Space heating represents one of the most immediate applications for recovered heat, especially in regions with cold climates where heating requirements are substantial.
- Automotive Industry: Waste heat recovery systems in vehicles can enhance fuel efficiency by utilizing exhaust heat to power auxiliary systems. This also includes using hot water or steam generated from compressors to support various production processes where heat is required.
- Hot Water Supply: Recovered heat is highly efficient for heating water, utilized in laundry services as well as in facilities & sanitary applications.
- Electronics Sector: Sterilization within clean rooms relies heavily on hot water or steam and is essential for maintaining the controlled environmental conditions required for electronics manufacturing.
- Metal and Plastic: Processes like injection molding and metal fabrication rely on heat to improve the properties of materials in the metal and plastics industries.
Key Players

ABB’s Waste Heat Recovery System (WHRS) is meant to capture a specific amount of the heat and friction energy that is typically lost. By doing so, it improves fuel efficiency, reduces the need for auxiliary engines, and lowers emissions.
Thermal Energy International’s heat lost through the boiler’s flue gas exhaust is recycled by the FLU-ACE® heat recovery system, a direct contact condensing heat recovery system. It reduces energy consumption as well as reduce greenhouse gases and other emissions.
BOGE DUOTHERM heat recovery system can save money by recovering up to approximately 72% of the energy input used in compression in the form of heat. This recovered heat can be used to supplement heating or for pre-heating water for industrial processes.
Towards Sustainability
Several companies are integrating heat recovery systems, thereby contributing to a more sustainable future:
- Nestle is utilizing GEA’s heat recovery system, which harnesses exhaust gases from the spray drying equipment to produce 80°C hot water for its operation. This initiative supports Nestle’s sustainability agenda by reducing carbon emissions, dust emissions, and water demand, thus supporting their climate strategy, focusing on renewable heat energy.
- ROWI, has enhanced energy savings and operational reliability, with the installation of three new ELGi air compressors equipped with ELGi Heat Recovery System (HRS). This installation allows ROWI to efficiently reduce energy consumption, and reuse waste heat from the compressors to heat their production spaces.
Future Prospects and Innovations
The ongoing research and development efforts are focusing on overcoming barriers to waste heat recovery and advancing state-of-the-art technologies, despite the challenges. Novel materials with enhanced thermal conductivity and stability can improve the efficiency and durability of waste heat recovery systems. Heat recovery equipment available today can be constructed from specialized materials capable of withstanding elevated temperatures, chemicals, and corrosion.
Additionally, economizers in condensing boilers, manufactured from materials resistant to corrosion, can capture both sensible and latent energy from exhaust gases. Advancements in system integration and control technologies have the potential to simplify the incorporation of waste heat recovery in various applications and industries.
Conclusion
Waste heat recovery offers a significant opportunity to improve energy efficiency, reduce emissions, and promote sustainability. Implementing waste heat recovery technologies can help companies and organizations run more efficiently while stopping global warming. The industrial sector plays an important role in global energy consumption, but a substantial amount of energy is wasted as heat. Waste heat recovery systems provide a compelling solution, offering significant energy savings and emissions reductions. Many businesses are using waste heat solutions more frequently due to recent improvements, which enable them to recover lost energy for various uses.